SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is a powerful and widely used image format that offers superior scalability, flexibility, and quality. Unlike raster formats such as PNG and JPEG, SVG is based on XML, making it easily editable and perfect for web applications, UI elements, and vector-based illustrations.
This PowerPoint presentation provides an in-depth look at SVG, covering:
Introduction to SVG – Learn what SVG is and how it differs from other image formats.
Benefits of SVG – Discover why SVG is preferred for logos, icons, and responsive design.
Basic SVG Syntax – Explore the XML-based structure of SVG and its key elements like <circle>, <rect>, and <path>.
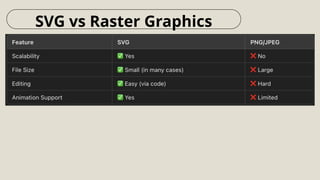
SVG vs. Raster Graphics – Understand the differences between vector and raster formats, including file size, scalability, and performance.
SVG Styling & Animation – Learn how to style SVG using CSS and animate it with JavaScript or the <animate> element.
Using SVG in Web Development – Find out how to embed SVG in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Best Tools for SVG Creation & Optimization – Get insights into top tools like Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape, and online converters.
Working with SVG
While SVG is great for scalable and responsive graphics, sometimes you may need to convert it to a PNG for compatibility with certain applications or platforms. If you ever find yourself needing a quick conversion, you can use this online tool very easily. fileverter.com/converter/image/svg-to-png to easily turn SVG files into PNG format without losing quality. It’s a simple way to get the best of both worlds—scalability when you need it and traditional image formats when required.