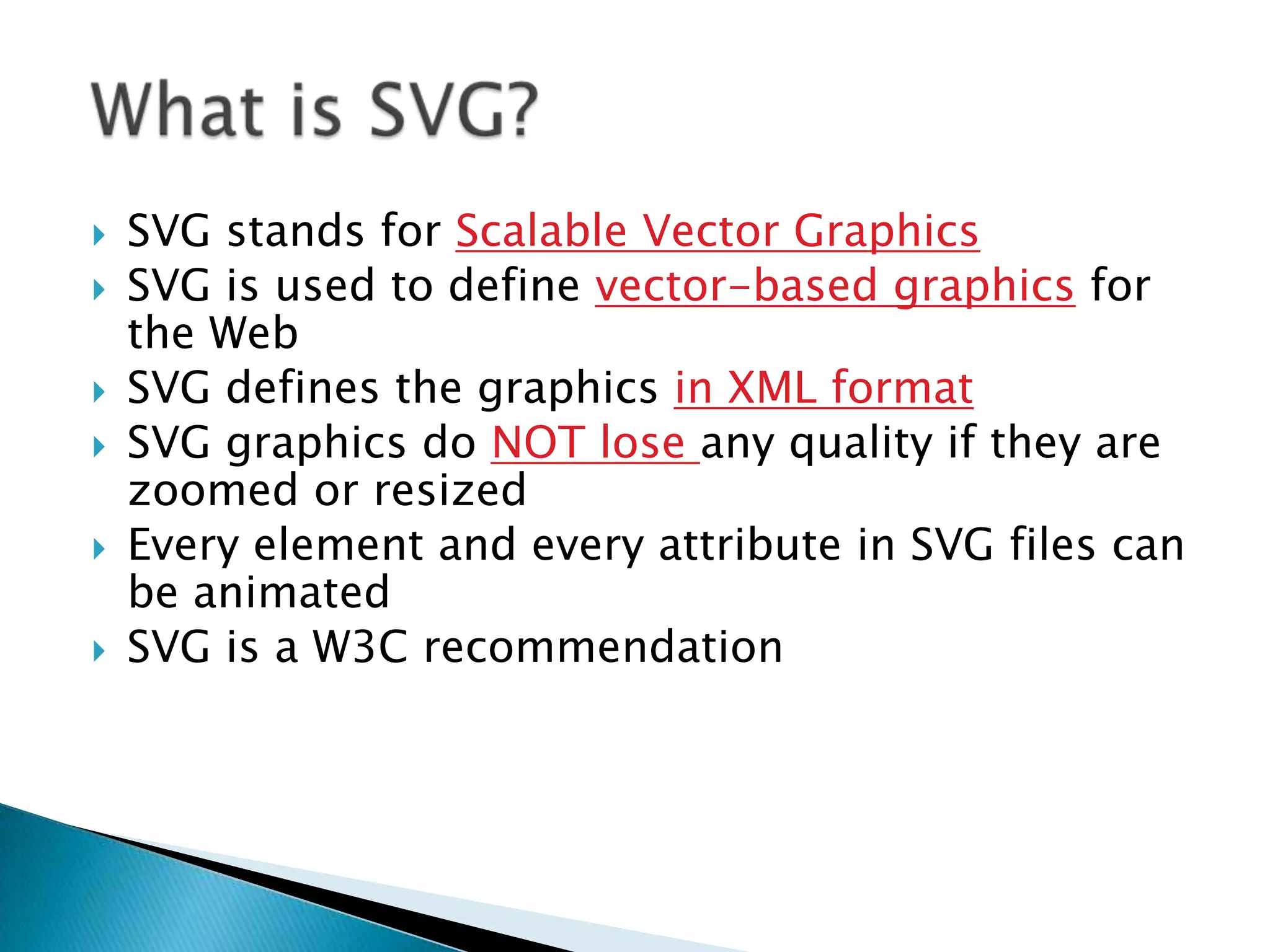
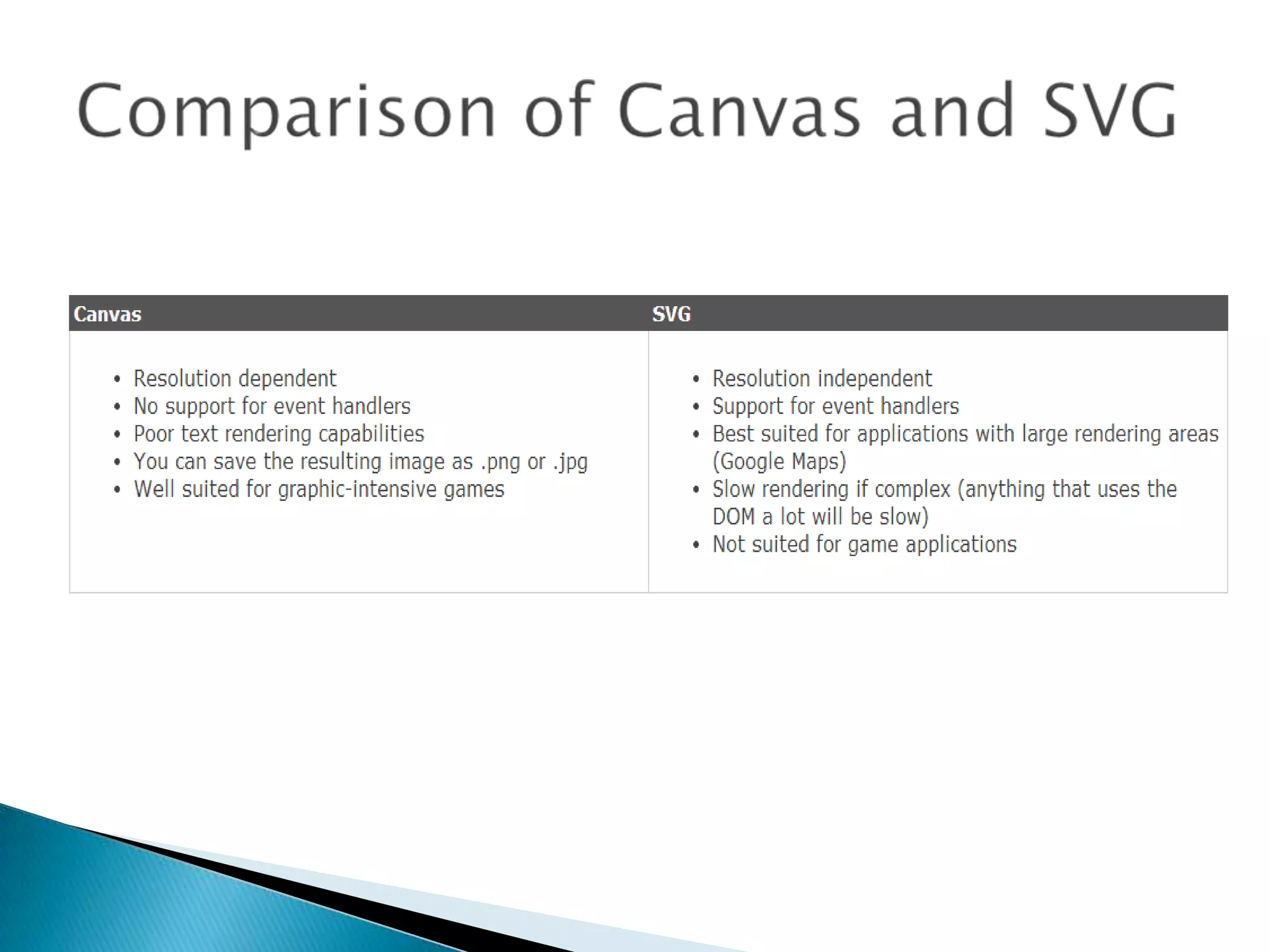
SVG allows for scalable vector graphics on the web. It uses XML to define vector shapes and graphics that can be scaled or resized without loss of quality. SVG graphics can be created and edited with any text editor, searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed. They are also scalable, zoomable, and can be printed at high resolution. In HTML5, SVG elements can be directly embedded into web pages using SVG tags. SVG is XML-based so each element is available in the SVG DOM and can have JavaScript event handlers attached.