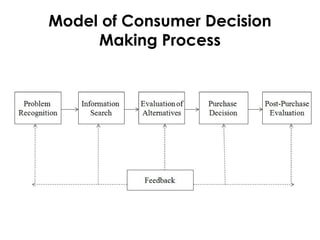
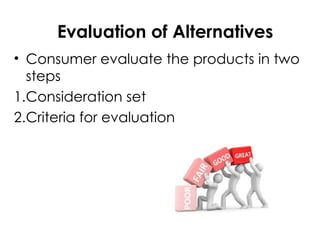
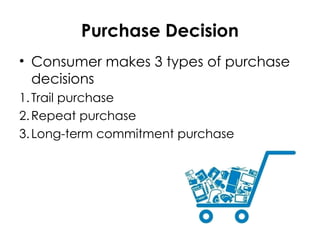
The document outlines the consumer decision-making process, covering stages such as problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decisions, post-purchase evaluation, and customer satisfaction. It emphasizes how consumers identify needs, seek information, and make purchase choices based on evaluations of product attributes, brand loyalty, and satisfaction with outcomes. Additionally, it highlights the importance of marketing strategies that address consumer problems and the role of customer service in ensuring satisfaction and retention.