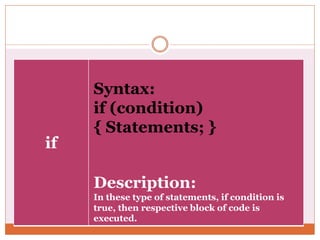
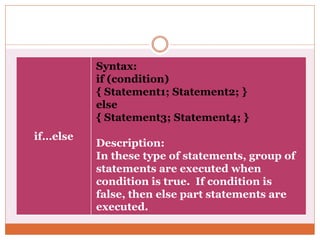
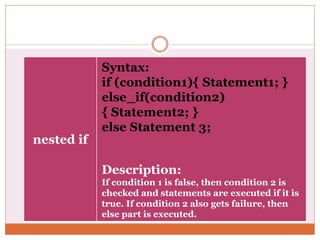
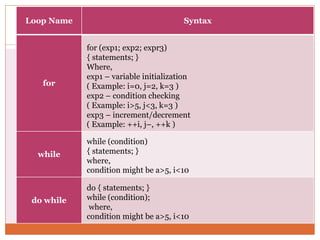
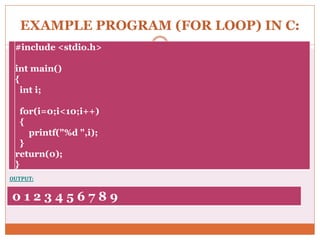
The document discusses decision control statements (if, if-else, nested if) and iterative loop control statements (for, while, do-while) in C programming. It provides the syntax and description of each statement type, examples of each in C code, and describes how each statement is used to control program flow based on conditions being true or false.