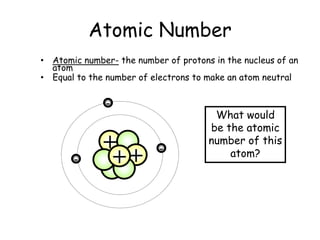
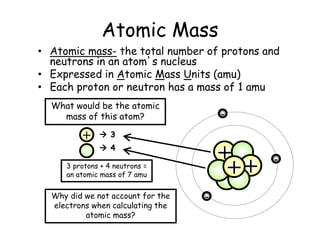
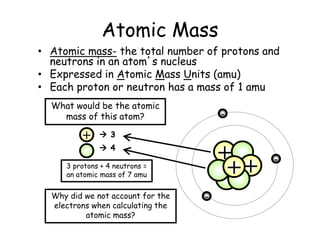
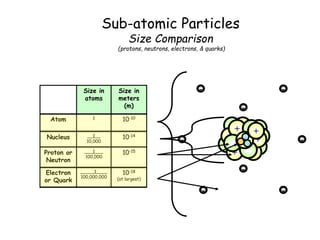
- Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the three main subatomic particles that make up atoms. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge.
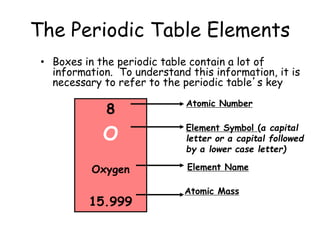
- The periodic table contains information about each element, including the element symbol, name, atomic number, and atomic mass. The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, while the atomic mass takes into account the total number of protons and neutrons.
- Electrons are not counted in the atomic mass because they are much smaller than protons and neutrons, and have a negligible contribution to the overall mass of the atom.