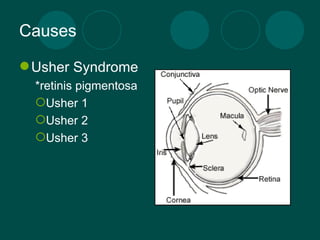
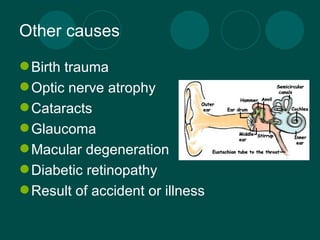
Deaf-blindness is a complex disability caused by a combination of hearing and vision loss. There are several potential causes including genetic conditions like Usher Syndrome. The impact on individuals varies depending on factors like the age of onset and severity of sensory losses. Assistive technologies and interventions like sign language, Braille, and mobility aids can help deaf-blind people communicate and navigate the world. Organizations provide support through services, education, and advocacy to improve quality of life for those with deaf-blindness.