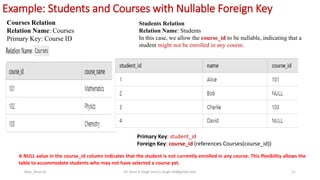
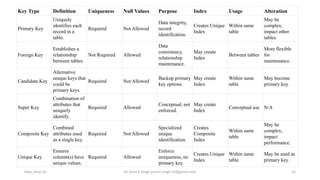
The document provides an overview of keys in database relations, explaining their definitions and types including primary, candidate, alternate, super, composite, foreign, and unique keys. It illustrates how primary and foreign keys function within student and course relation examples, highlighting the flexibility in allowing nullable foreign keys. The document also outlines the purpose, uniqueness, null value handling, and index usage associated with each key type.