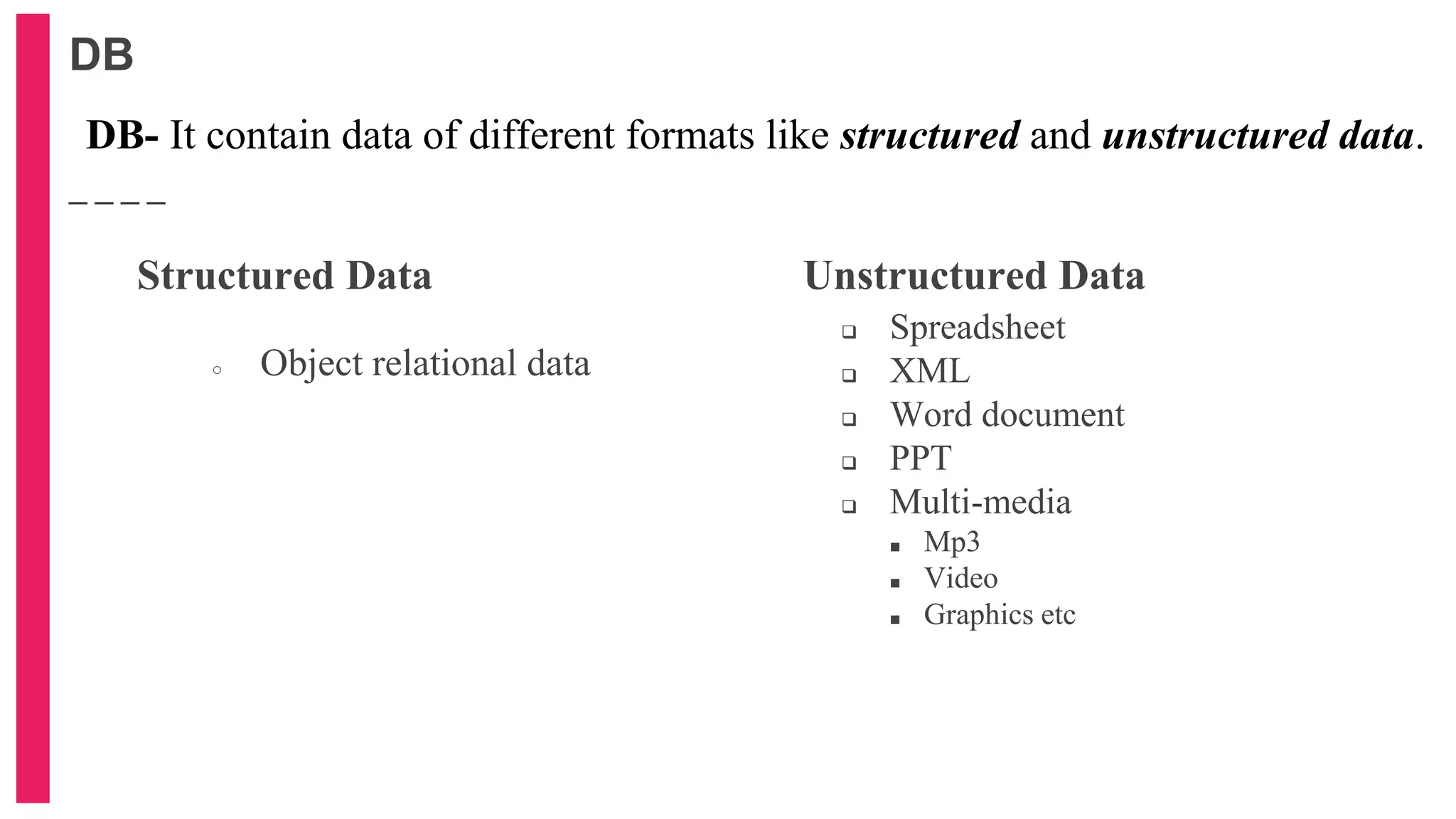
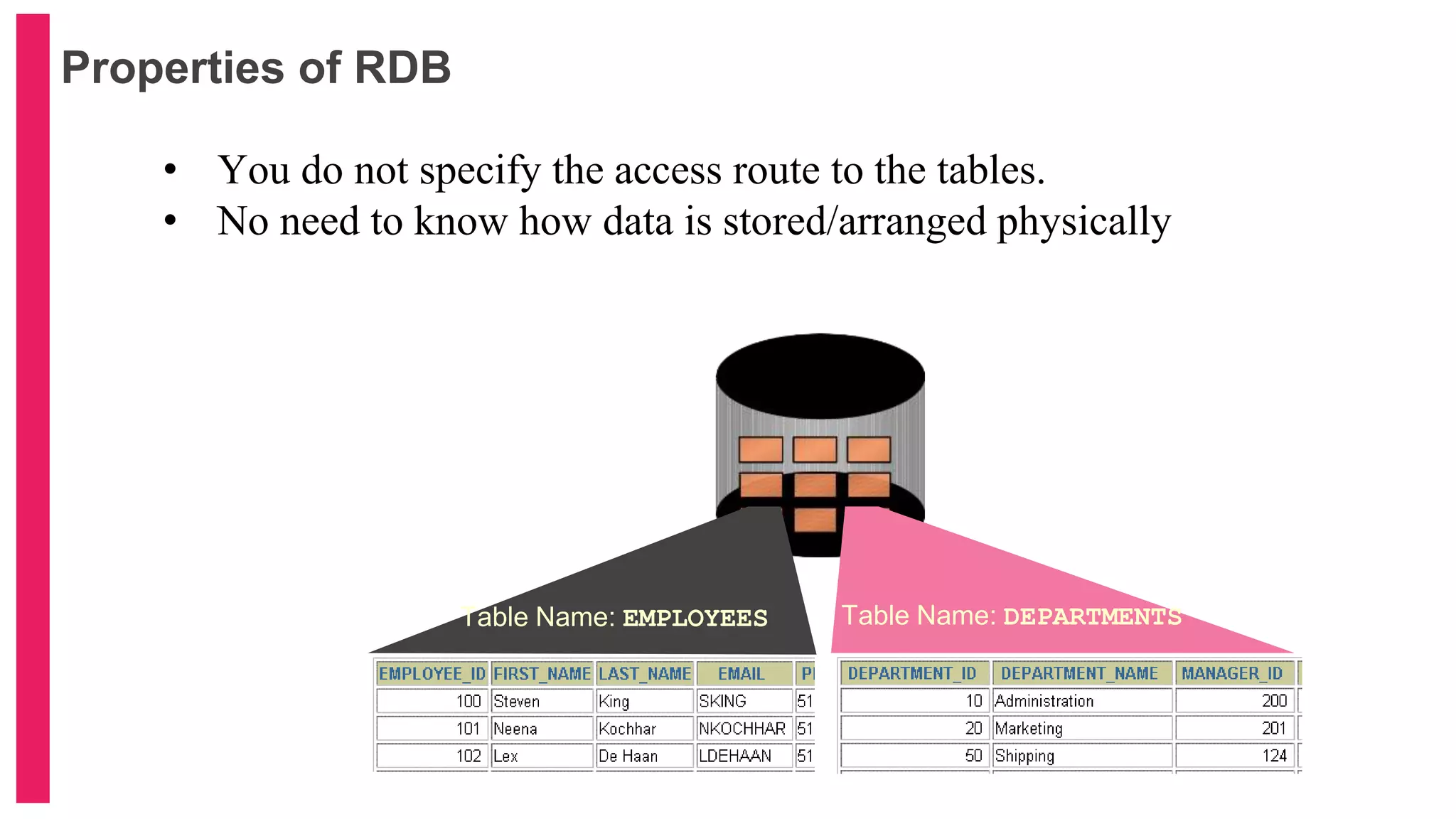
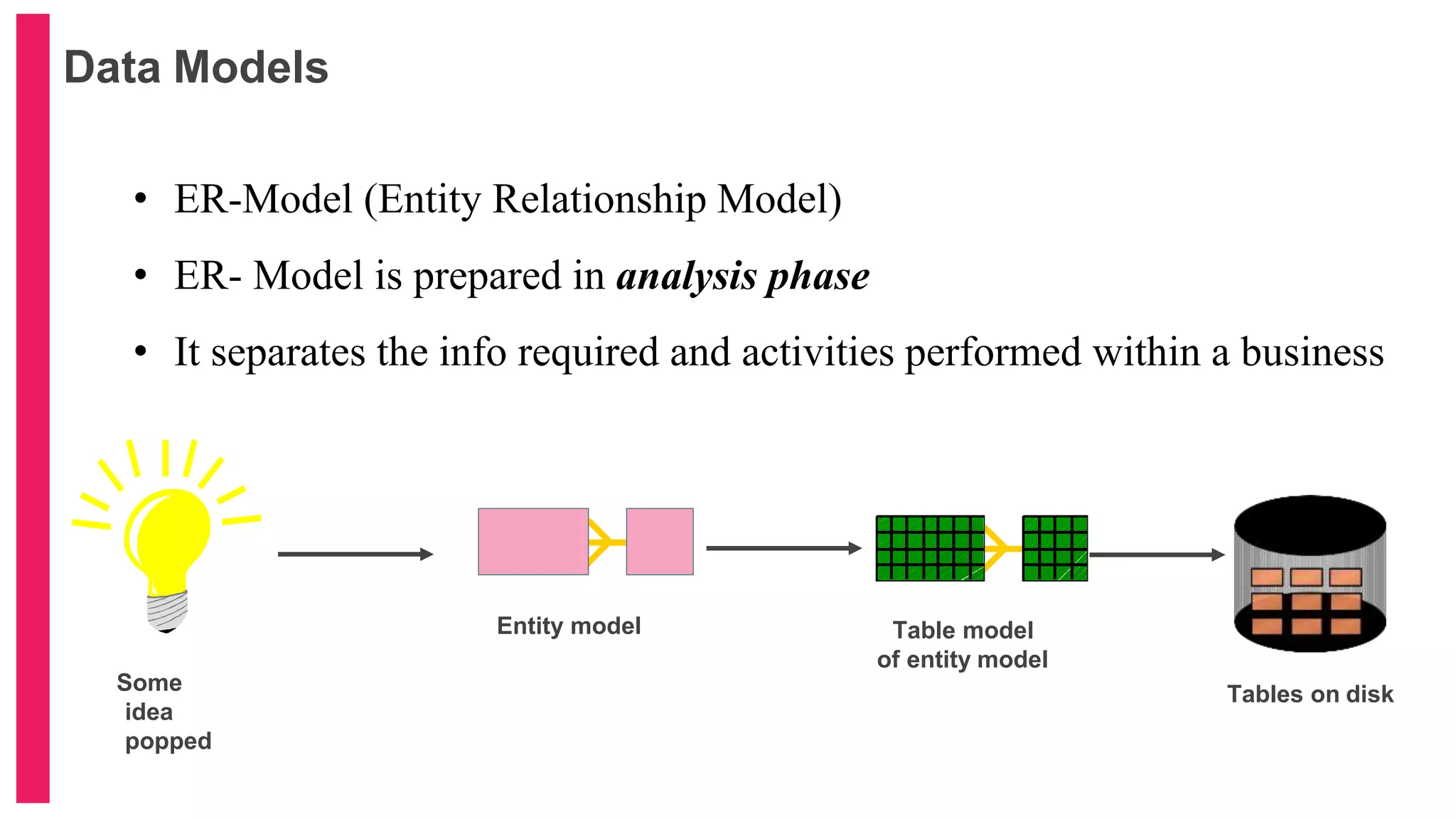
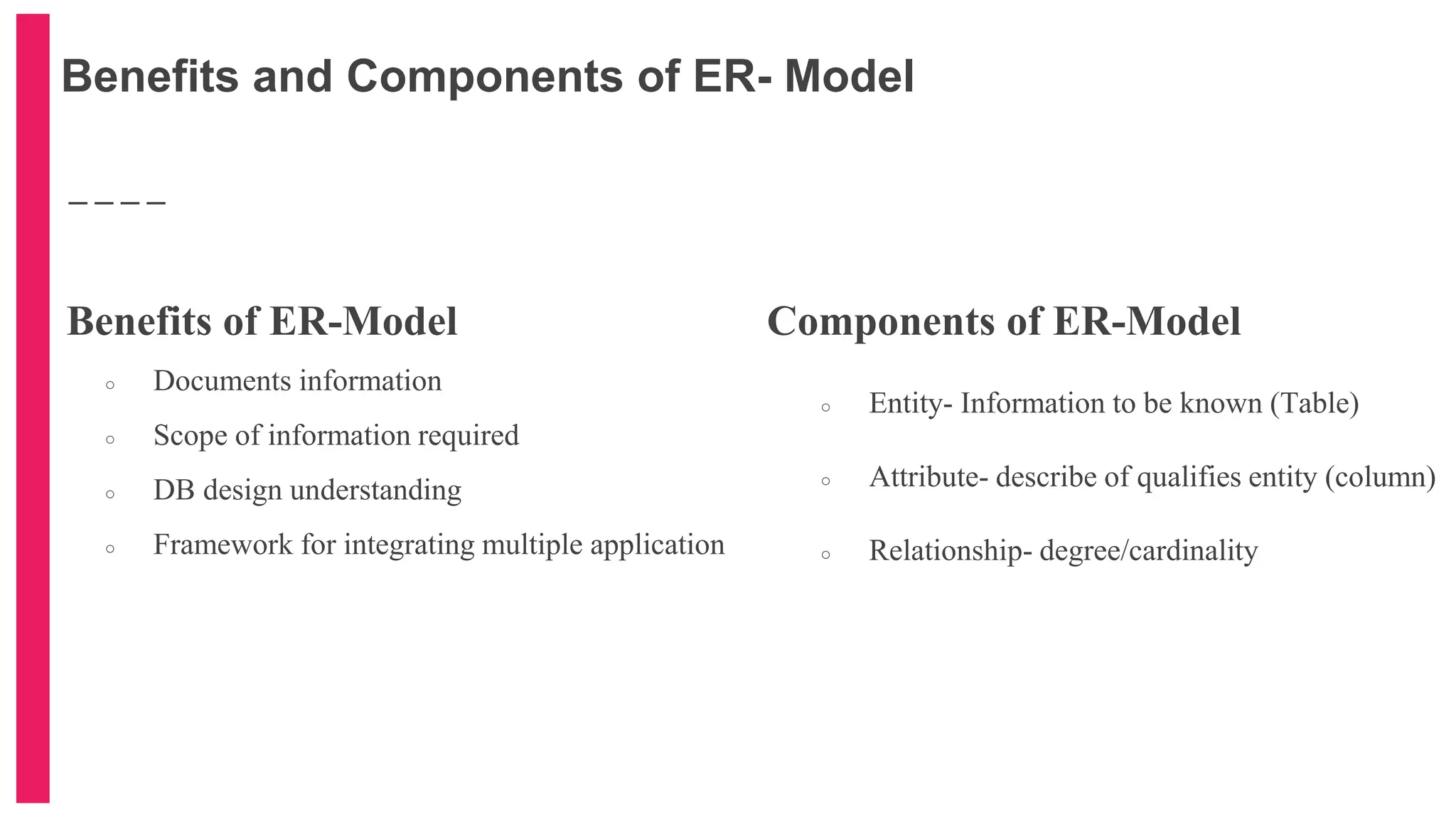
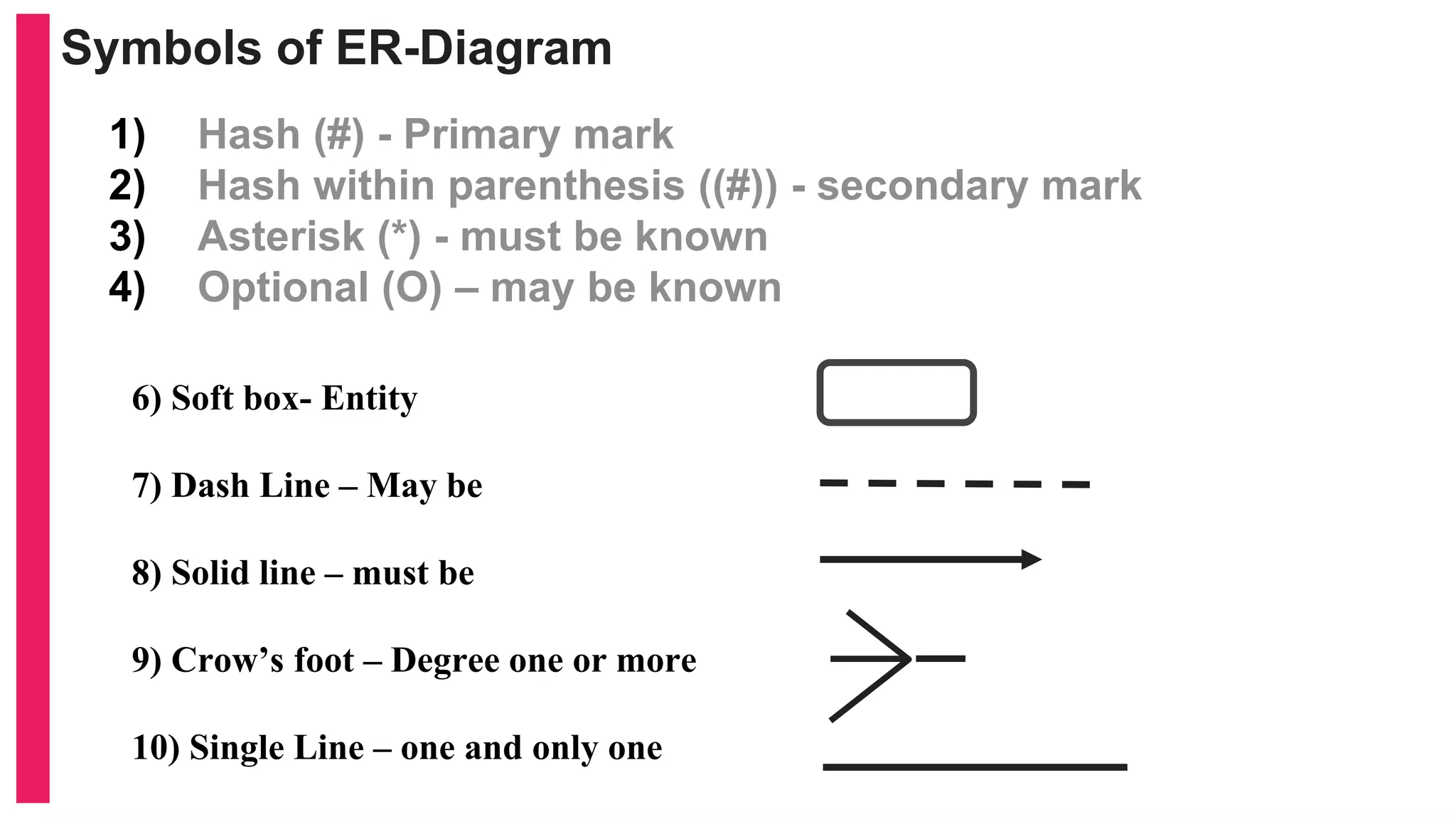
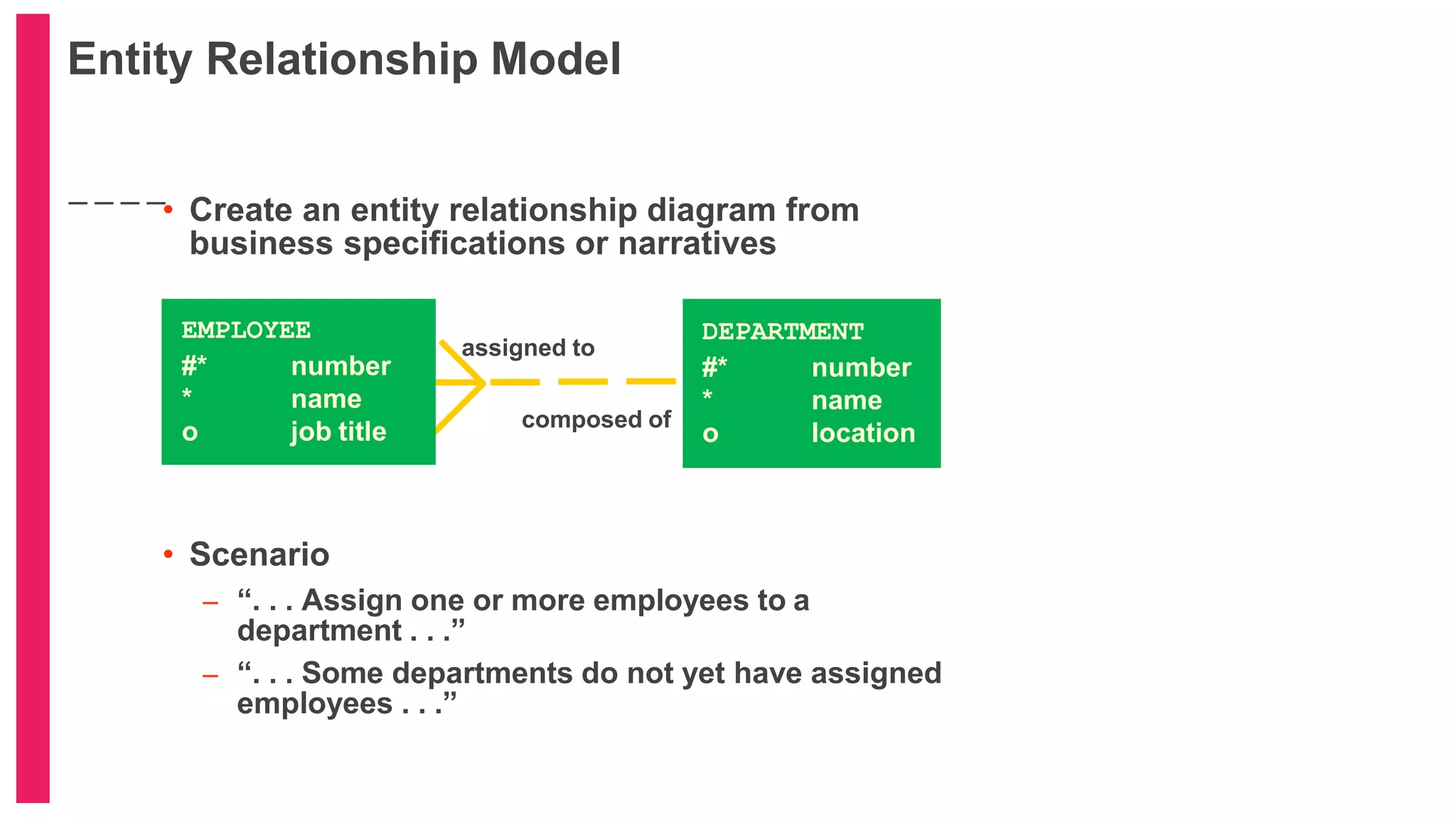
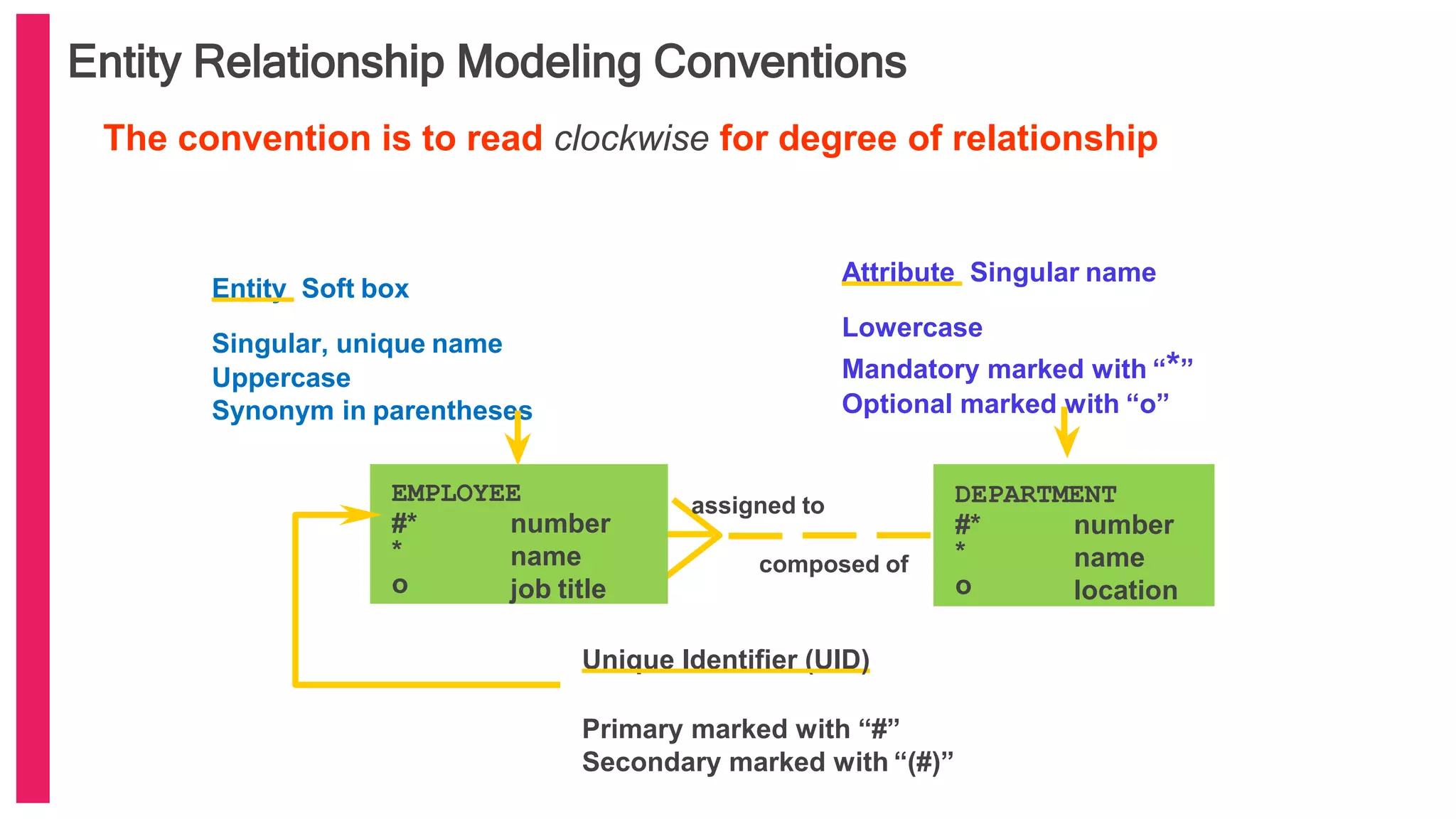
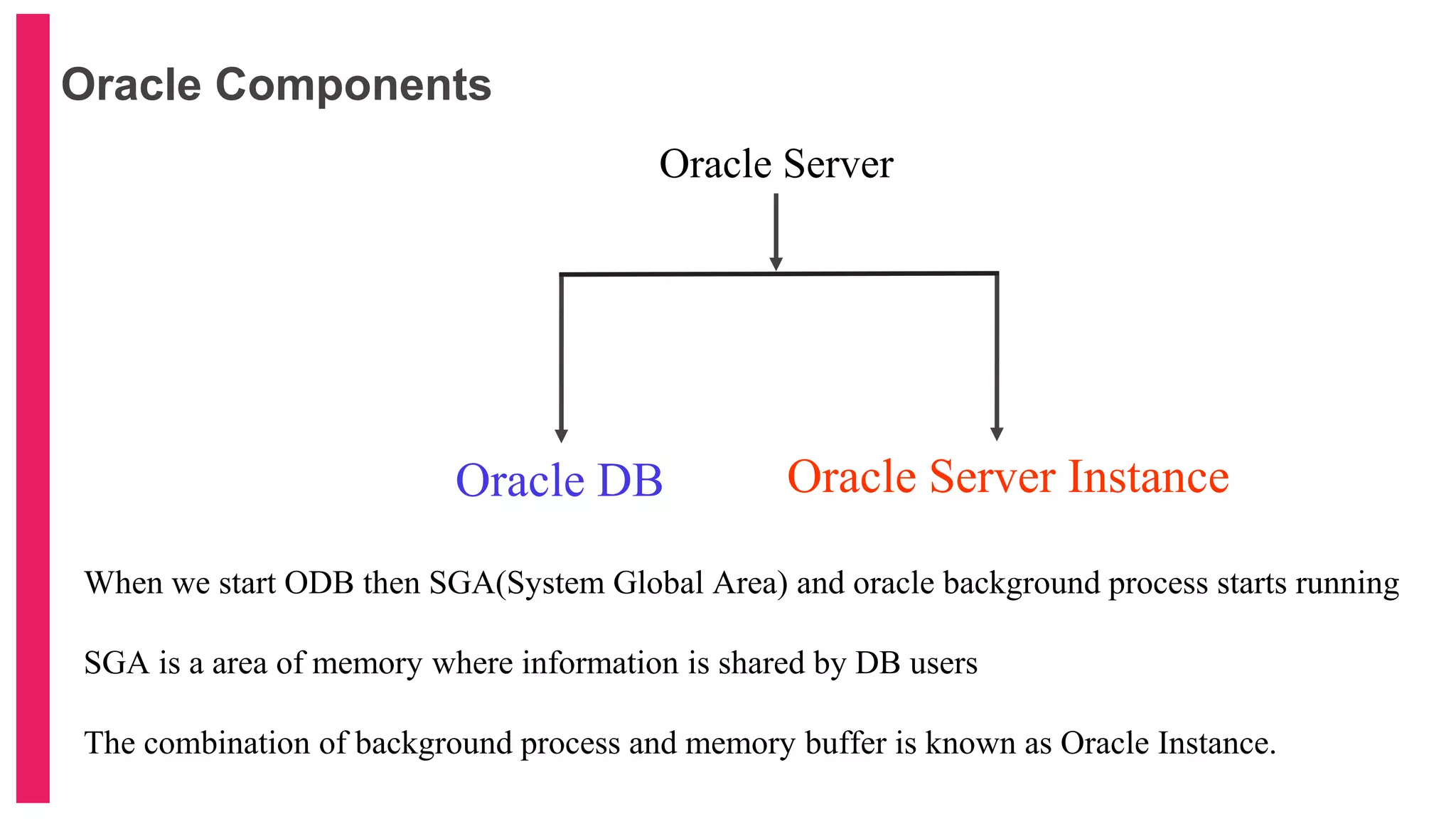
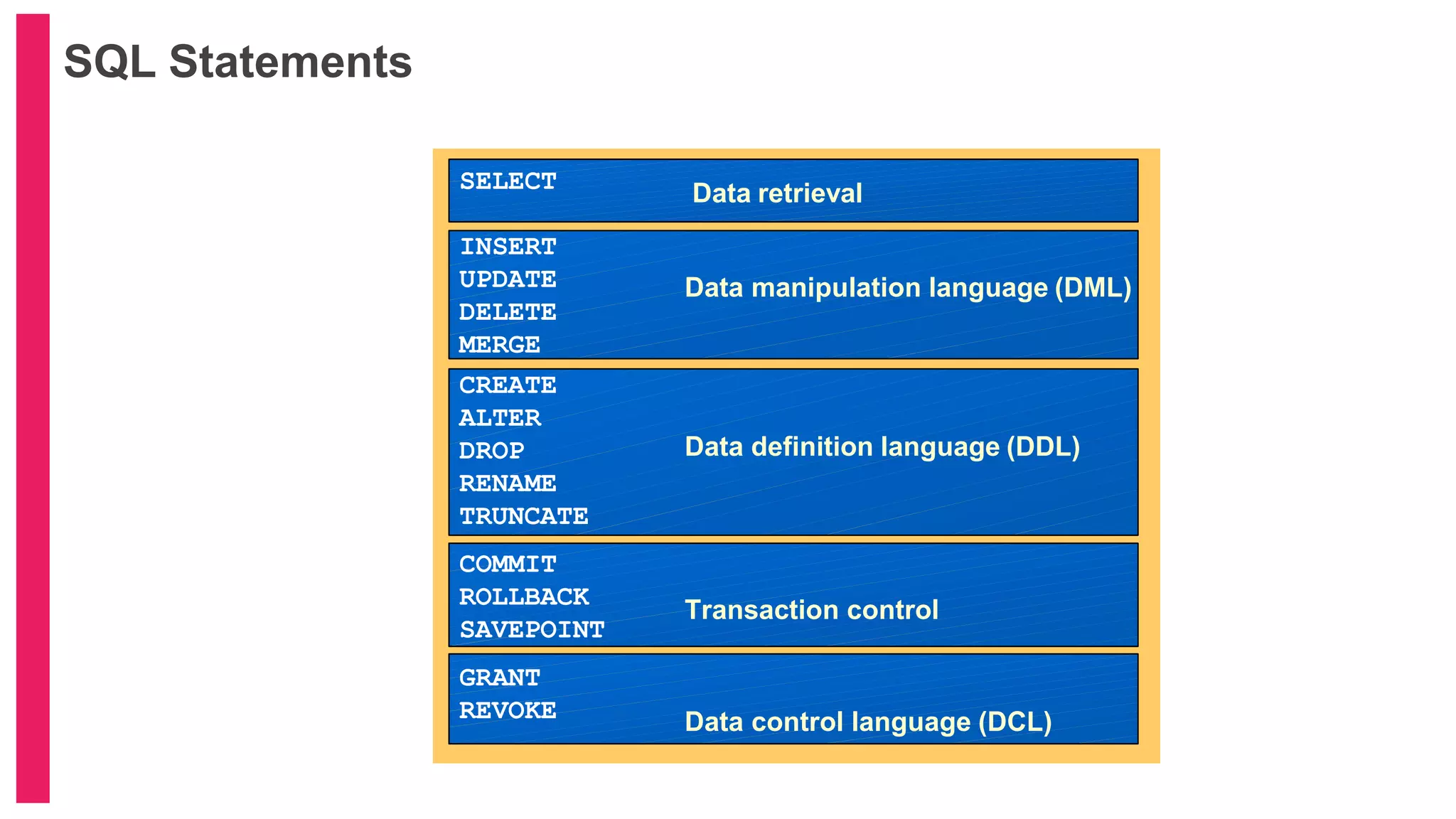
The document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS) with a focus on relational databases (RDB) and the ER model. It covers key concepts, properties of RDB, and components of the entity relationship model, including symbols used in ER diagrams. Additionally, it discusses the features of Oracle 9i and provides resources for further learning.