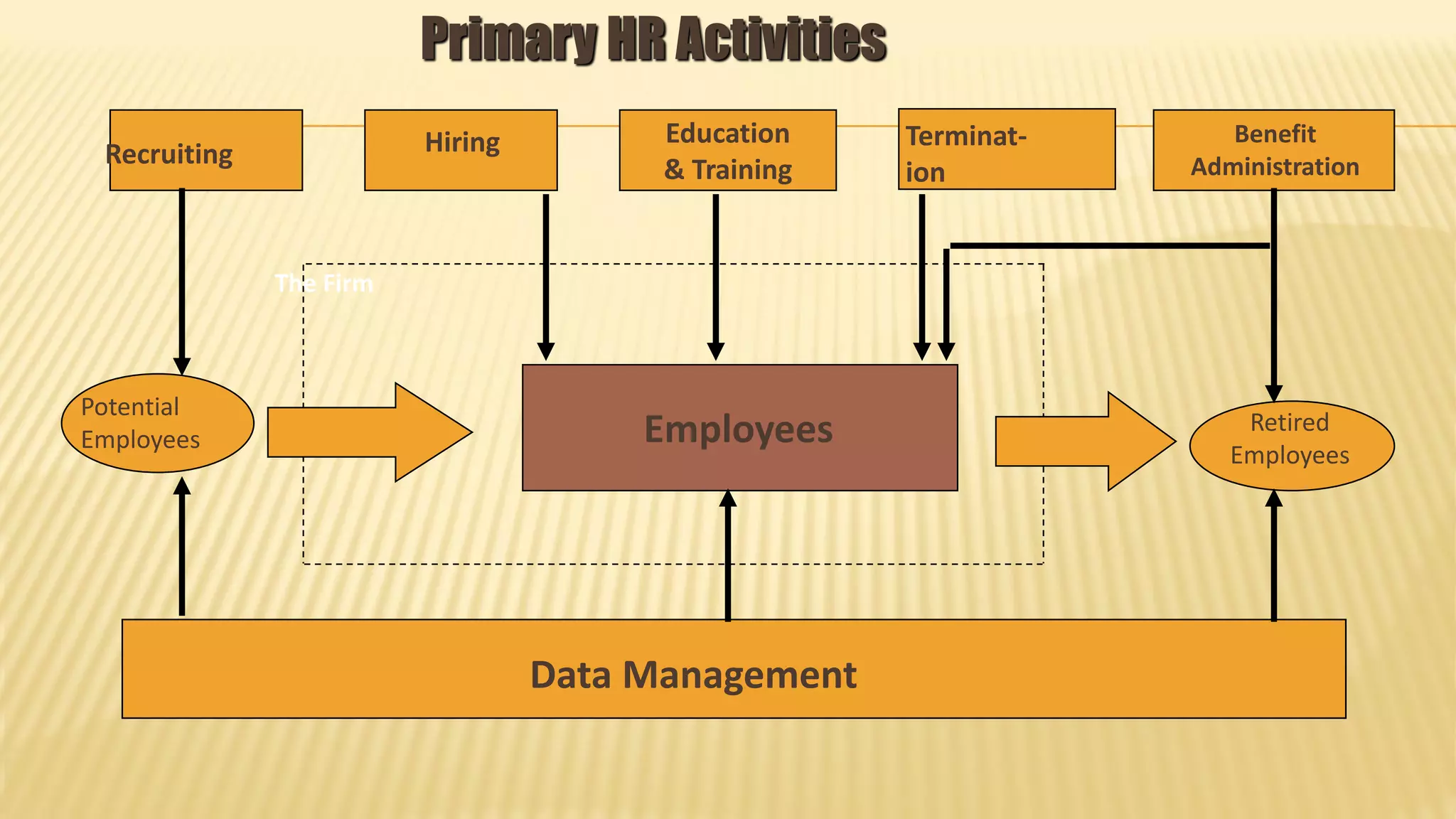
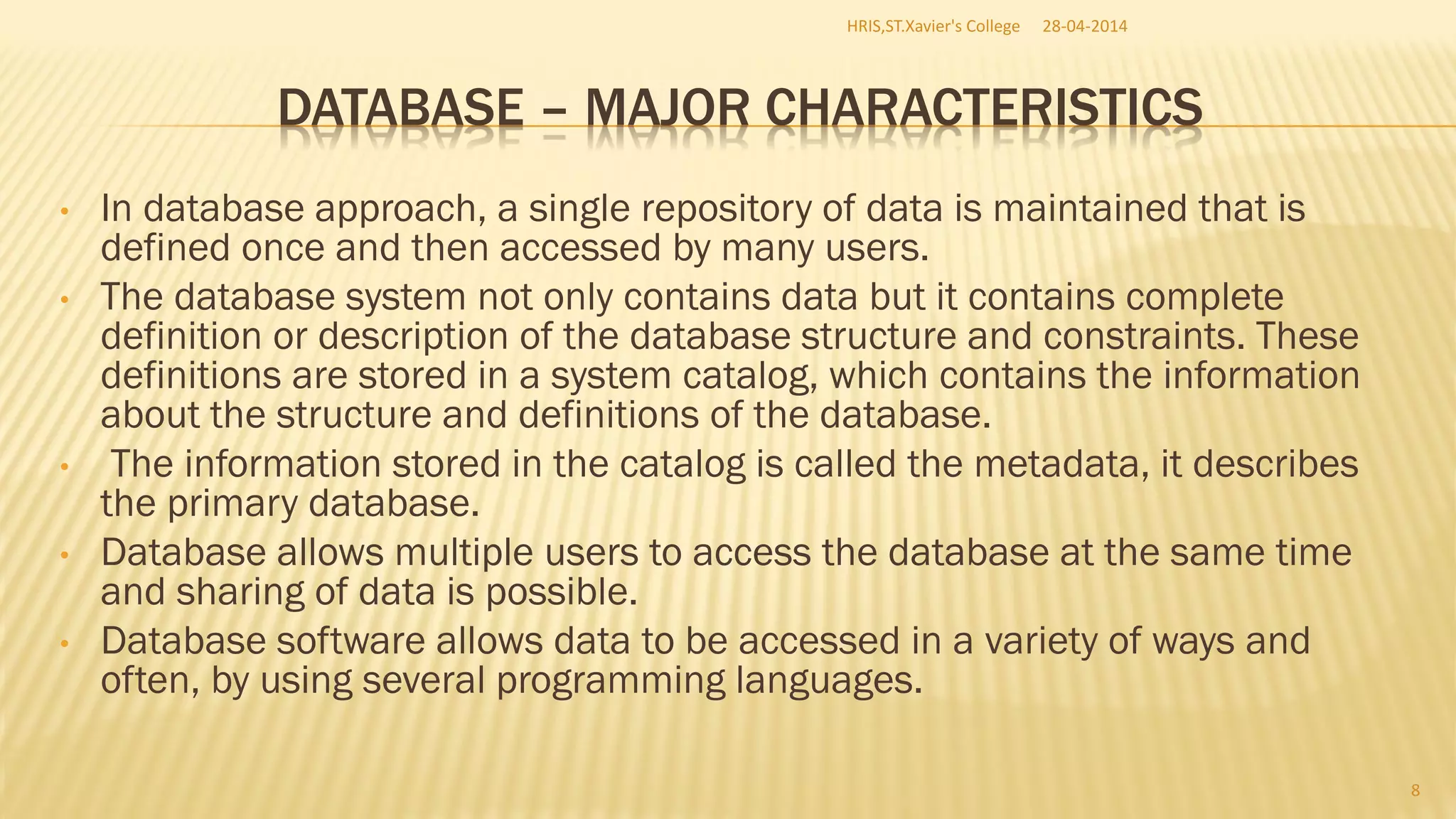
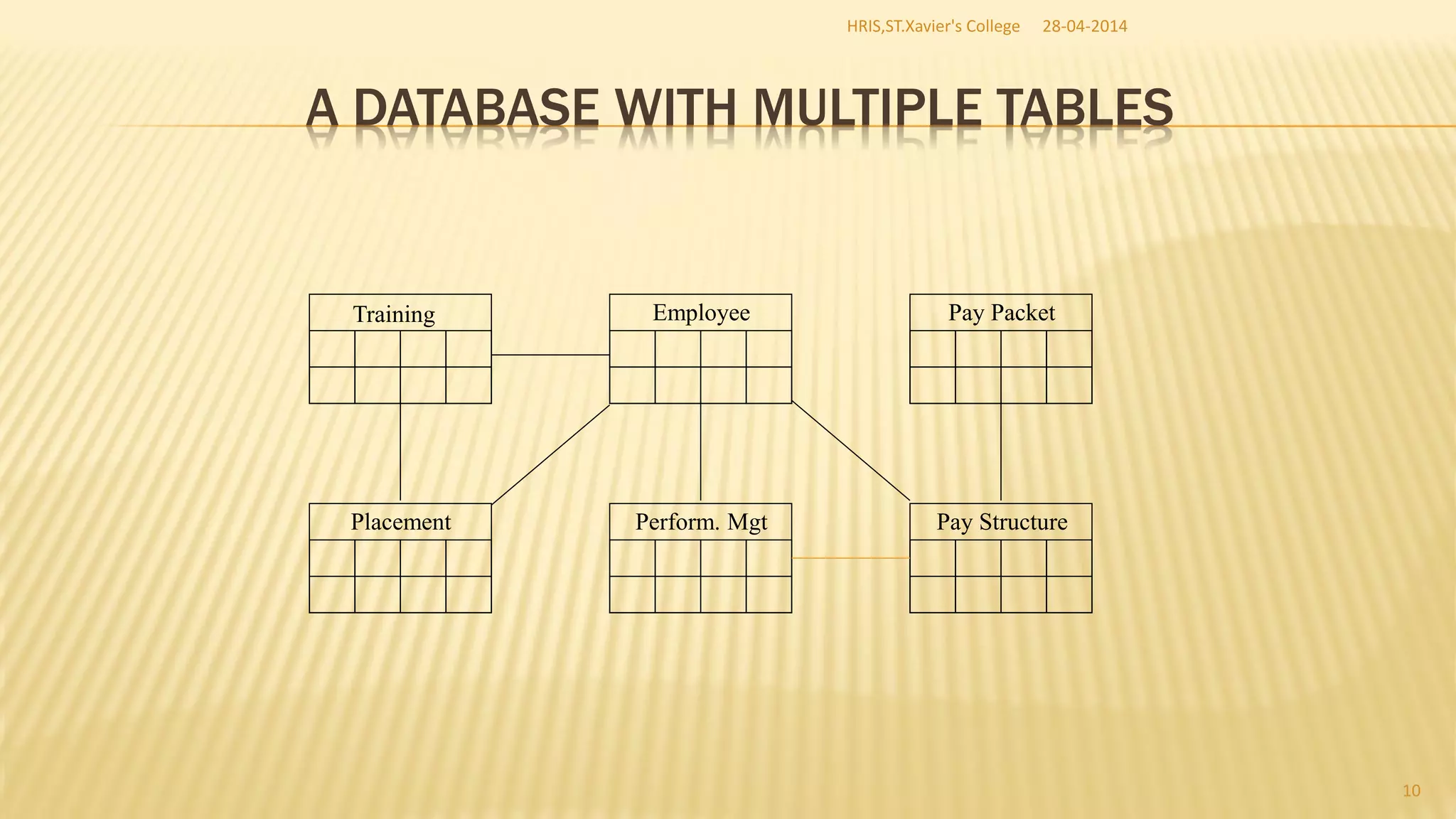
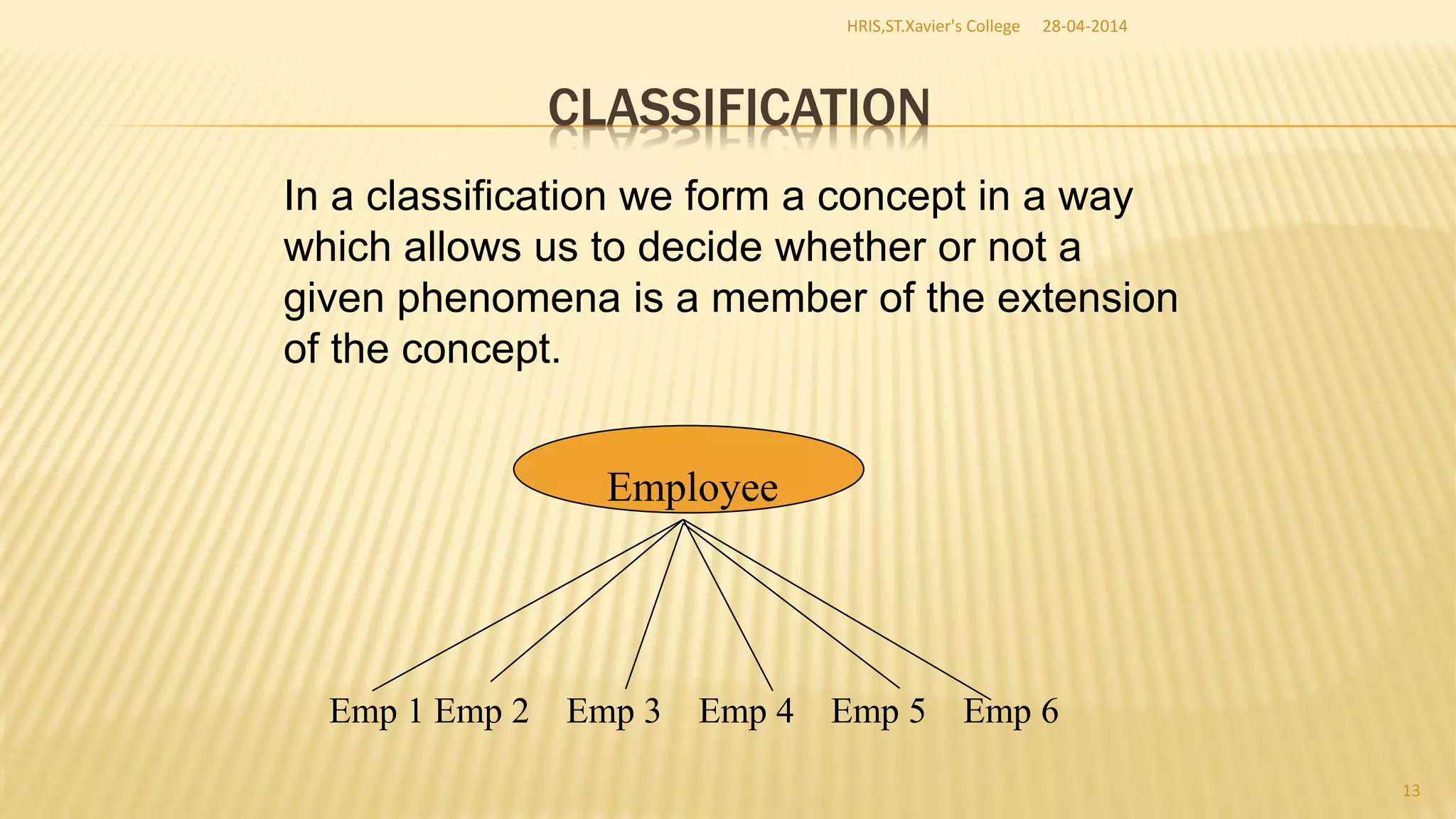
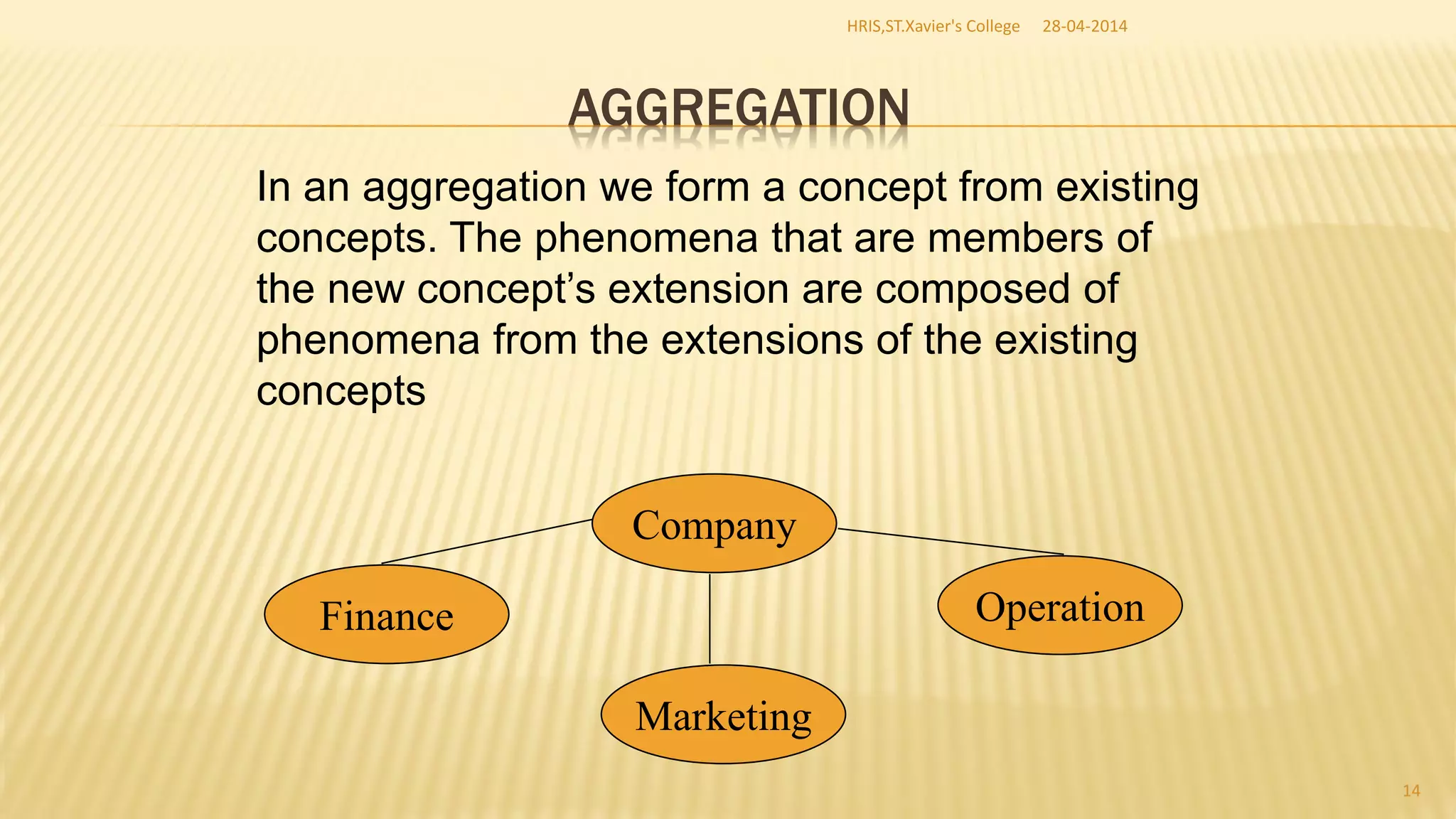
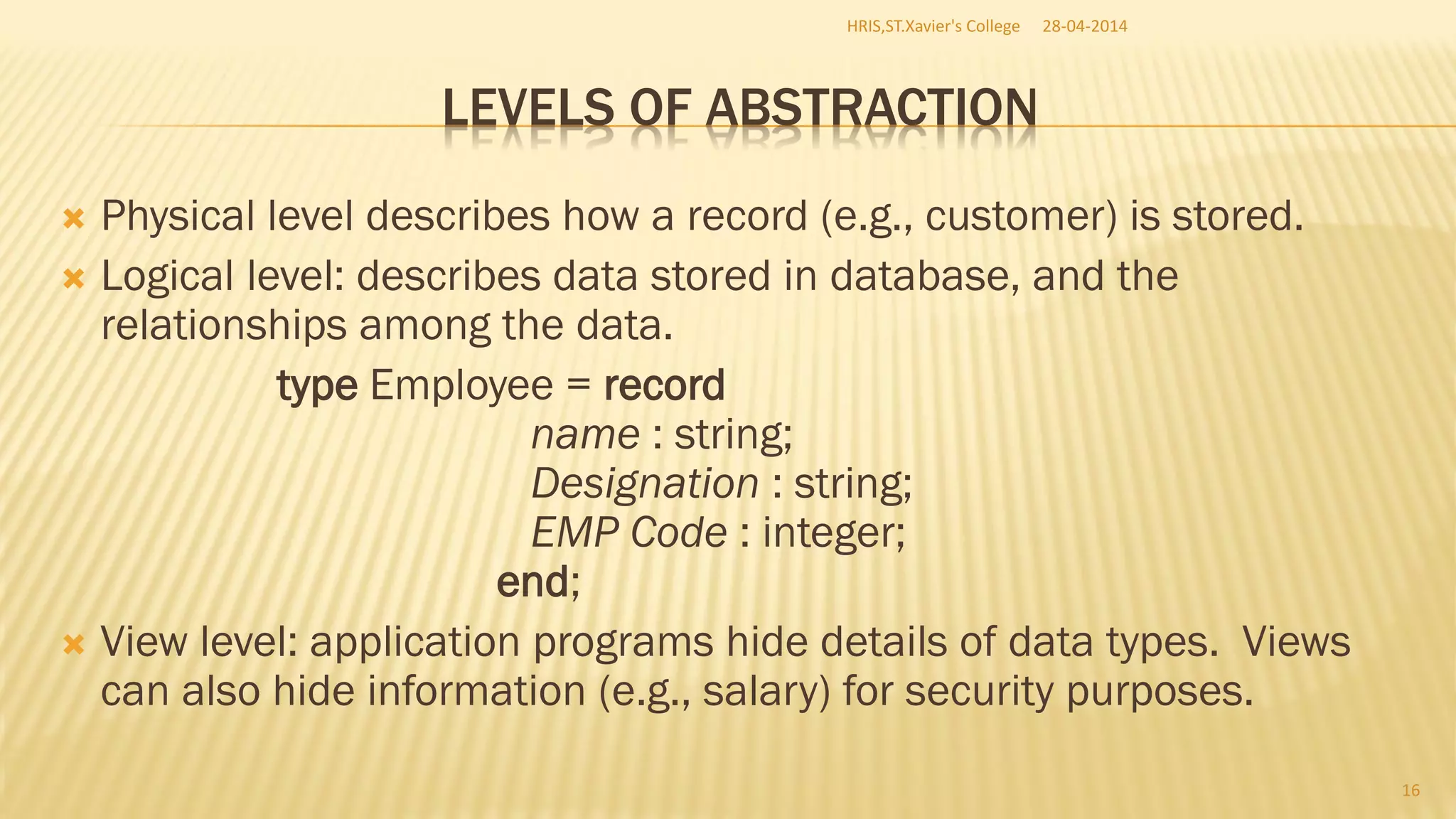
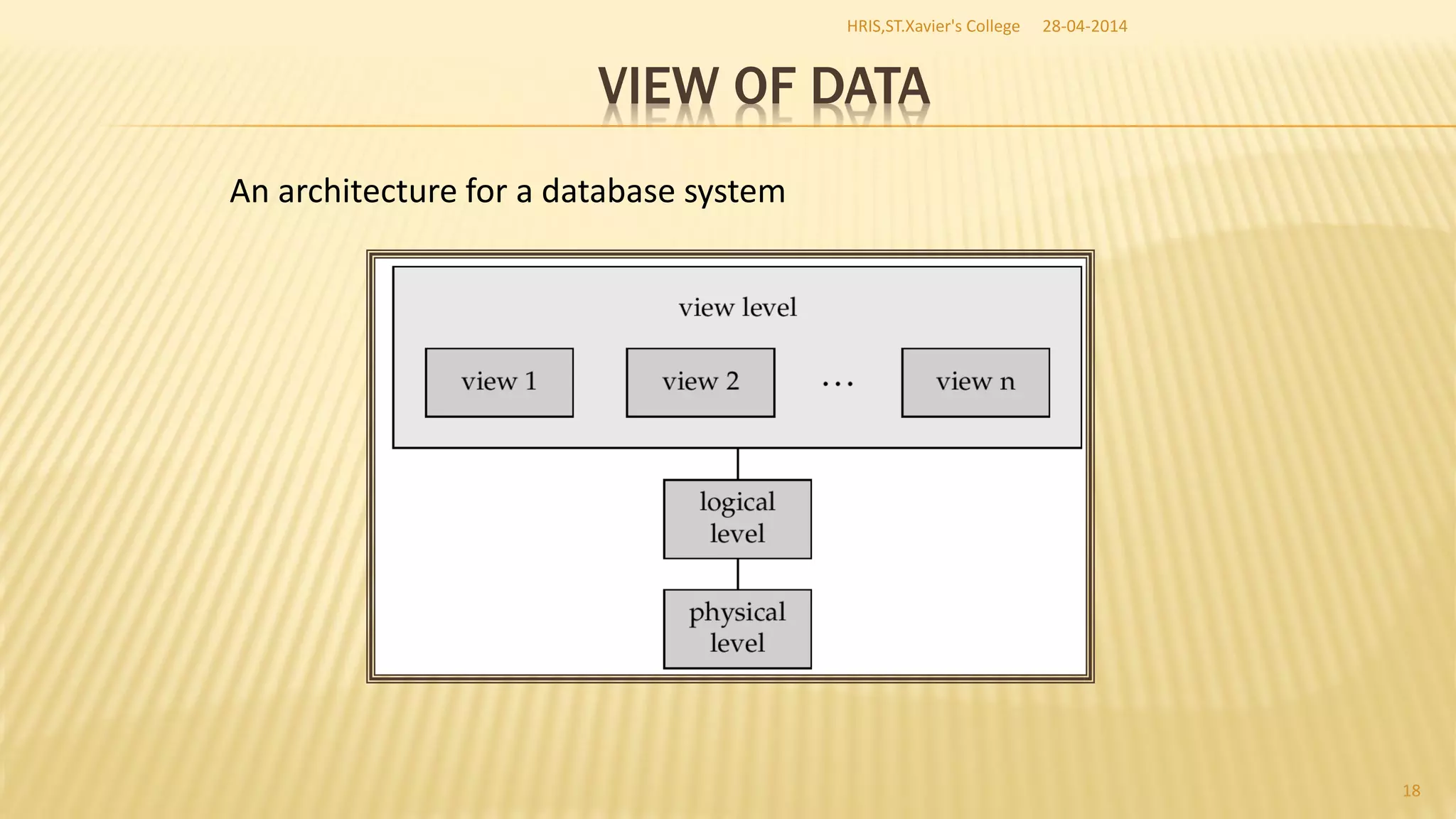
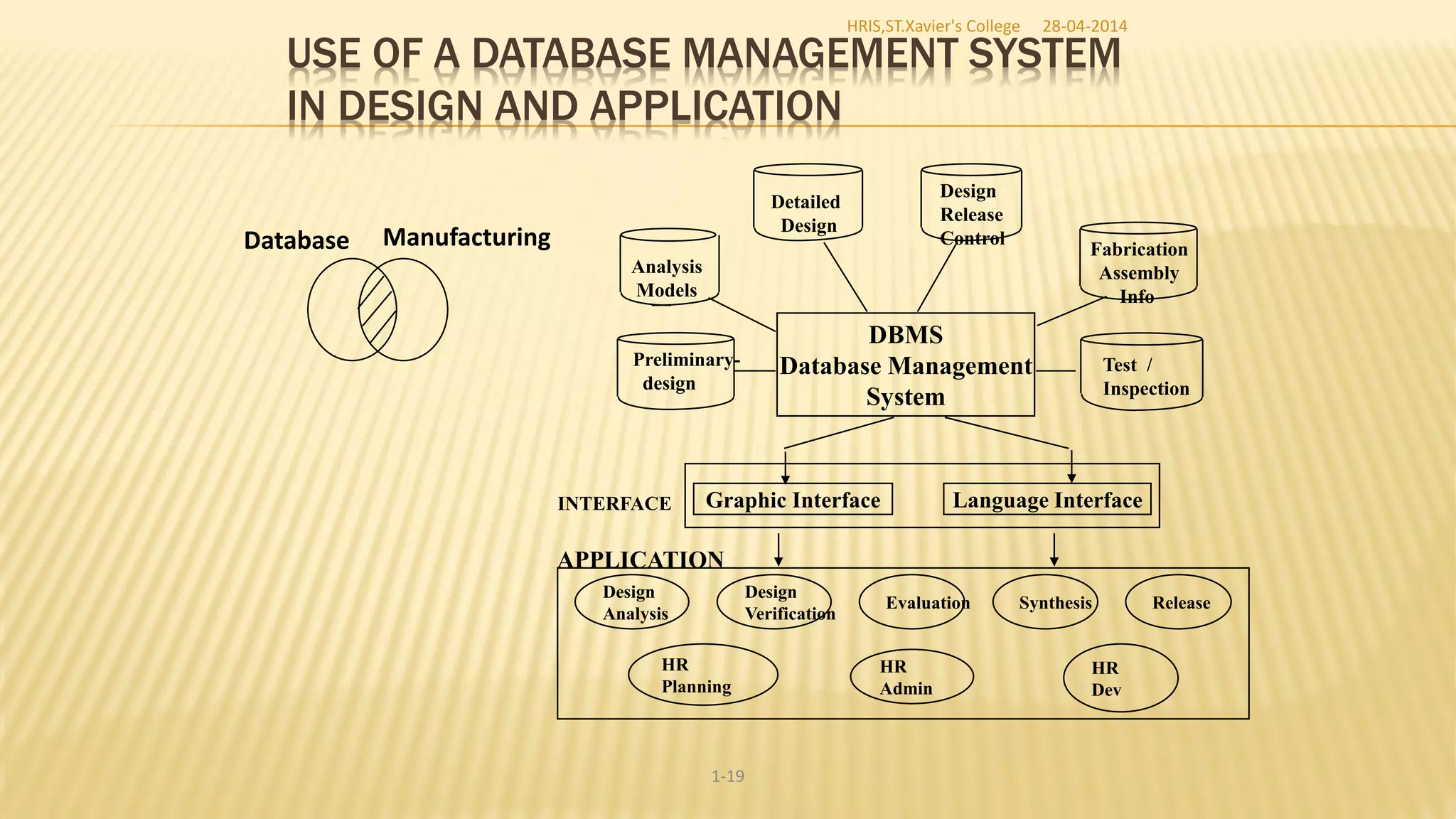
This document discusses database management systems and concepts. It defines a database as a collection of interrelated data stored and managed using database management software to allow for data storage, retrieval, and updates. It describes key database concepts like normalization, distributed processing, database administration, and the roles of various users who work with databases like analysts, designers, administrators, and end users.