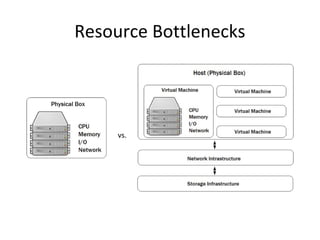
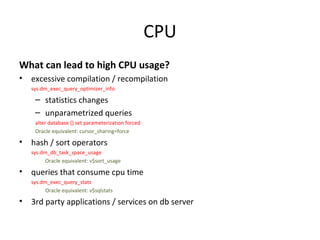
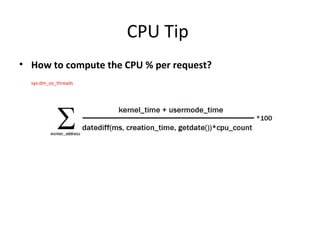
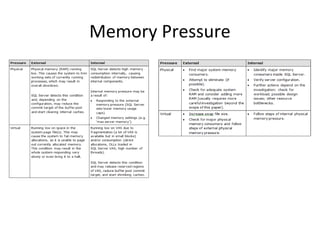
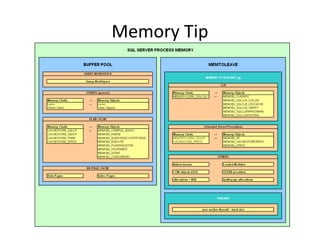
This document discusses various resource bottlenecks that can occur in SQL Server including CPU, memory, I/O, network, and tempdb bottlenecks. It provides system views and metrics to identify the cause of bottlenecks and monitor resources. Specific issues covered include excessive compilation, hash/sort operations, large scans/sorts, memory leaks, storage performance, parallelism levels, and missing indexes that can lead to slow queries. The document demonstrates using SQL Profiler to troubleshoot performance issues.