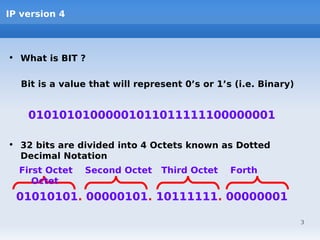
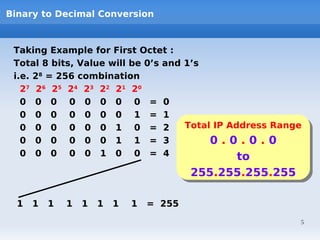
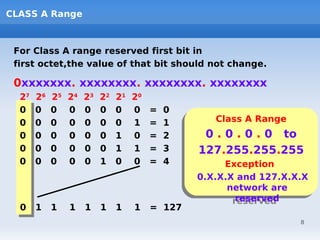
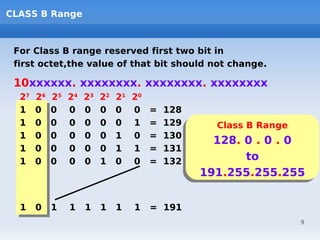
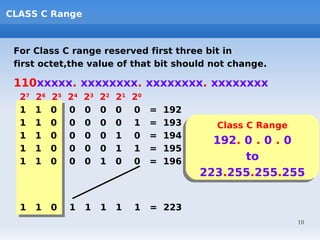
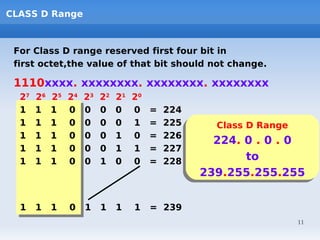
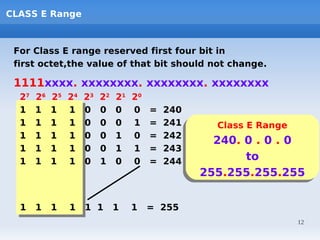
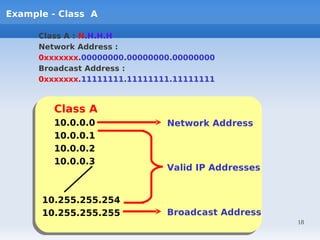
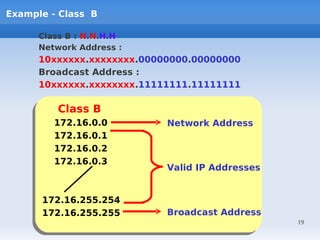
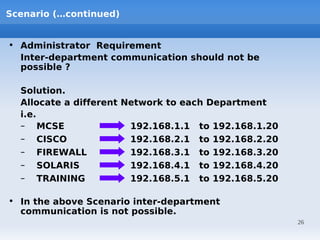
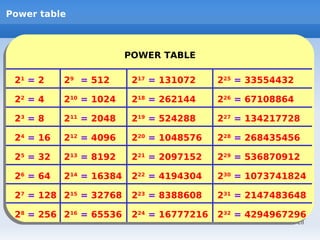
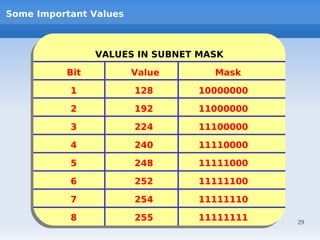
IP addressing uses logical addressing at the network layer. There are two main versions - IP version 4 uses 32-bit addressing, while IP version 6 uses 128-bit addressing. IP addresses are divided into classes based on the number of network and host bits. Each class supports a different number of networks and hosts per network. Private IP addresses are set aside for internal networks not connected to the public internet. Subnet masks are used to distinguish the network and host portions of an IP address.