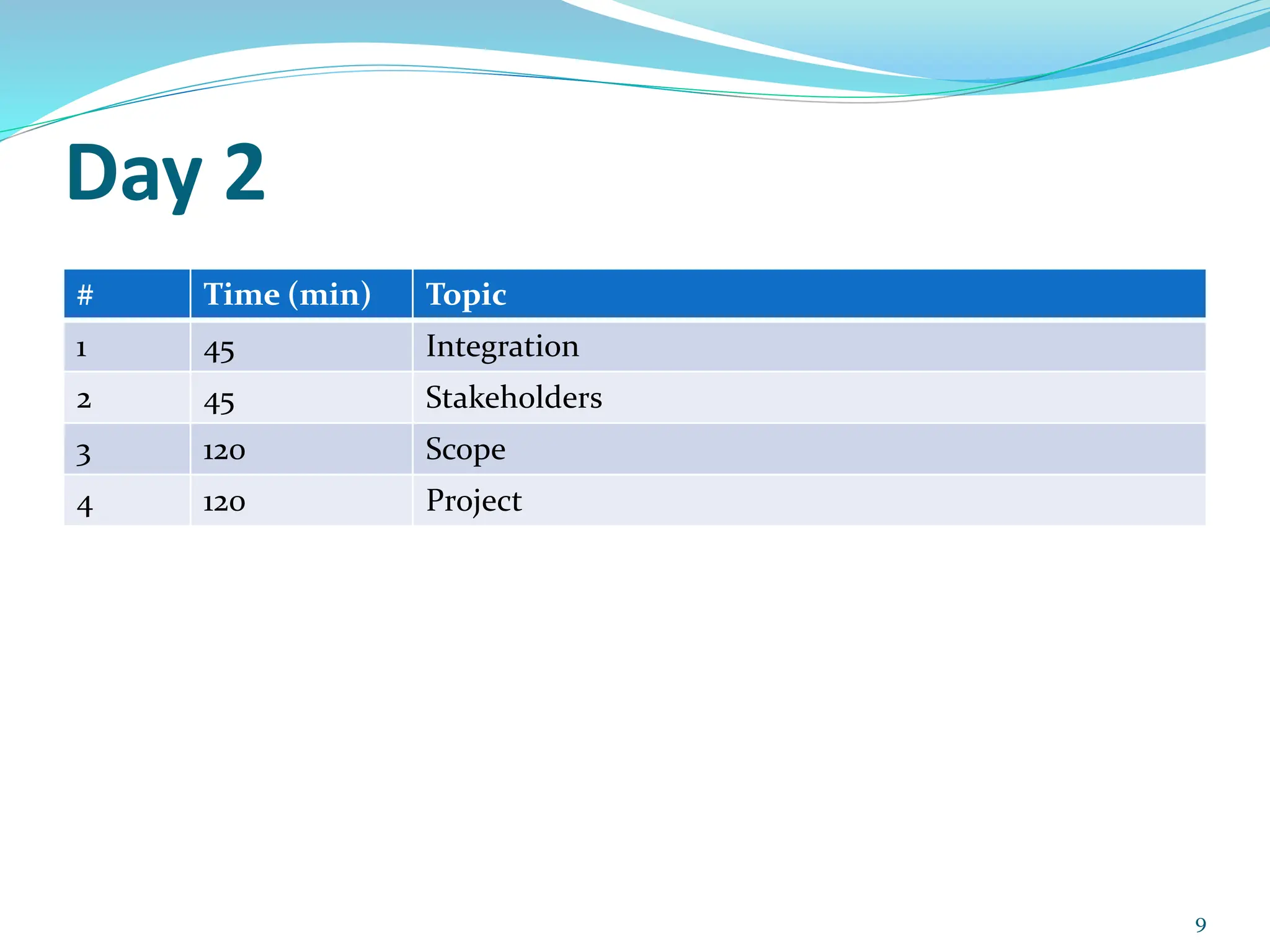
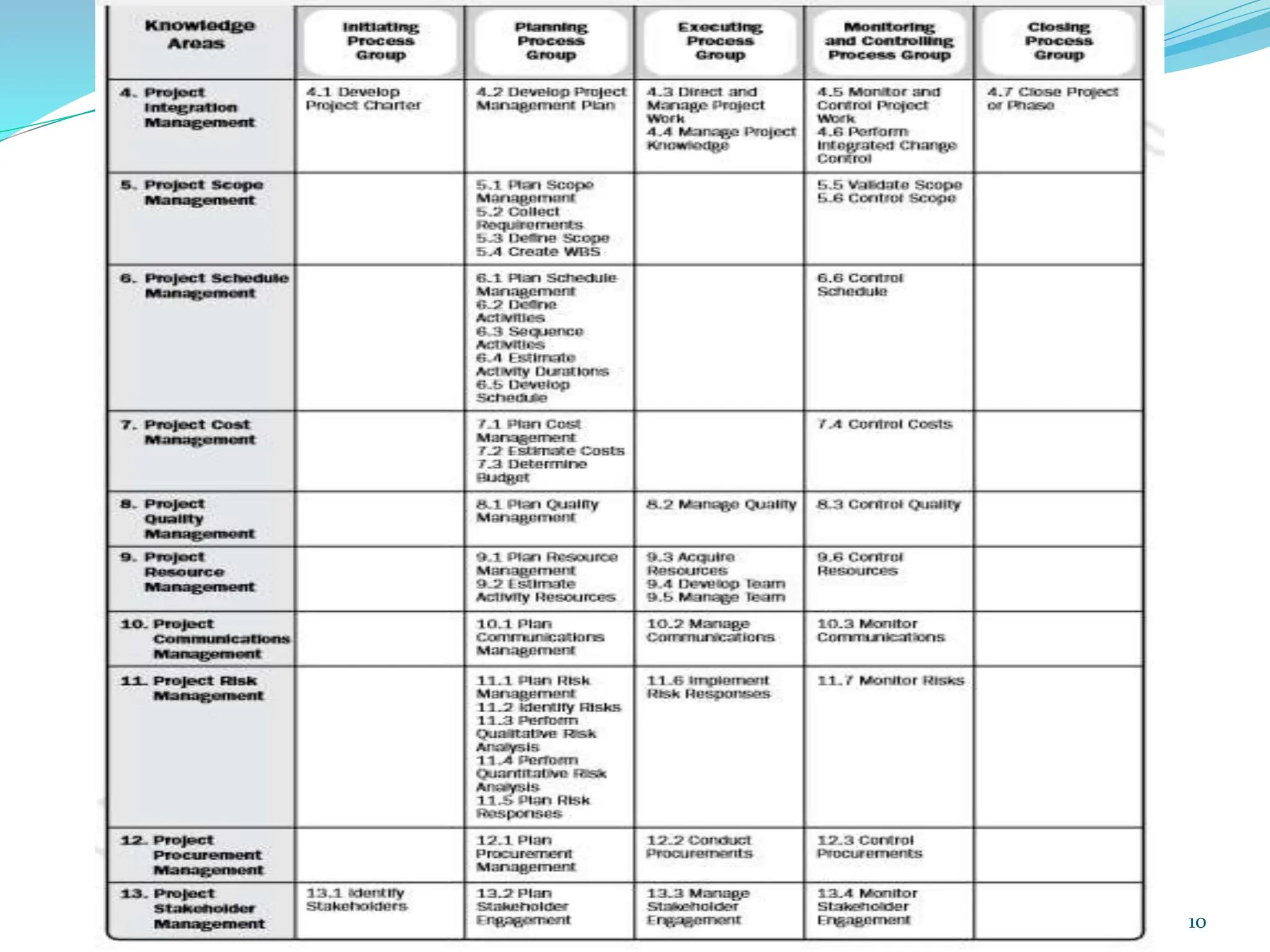
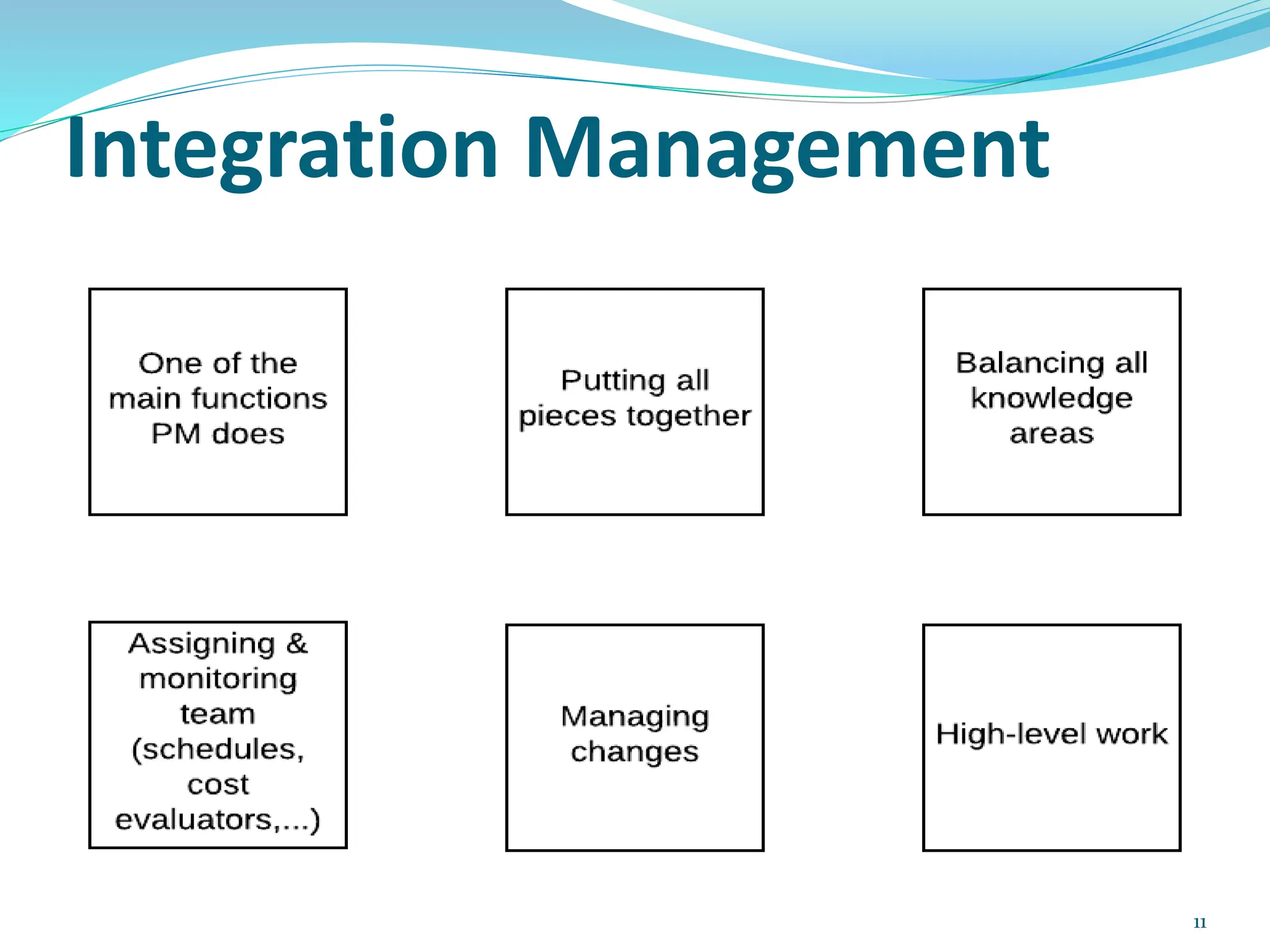
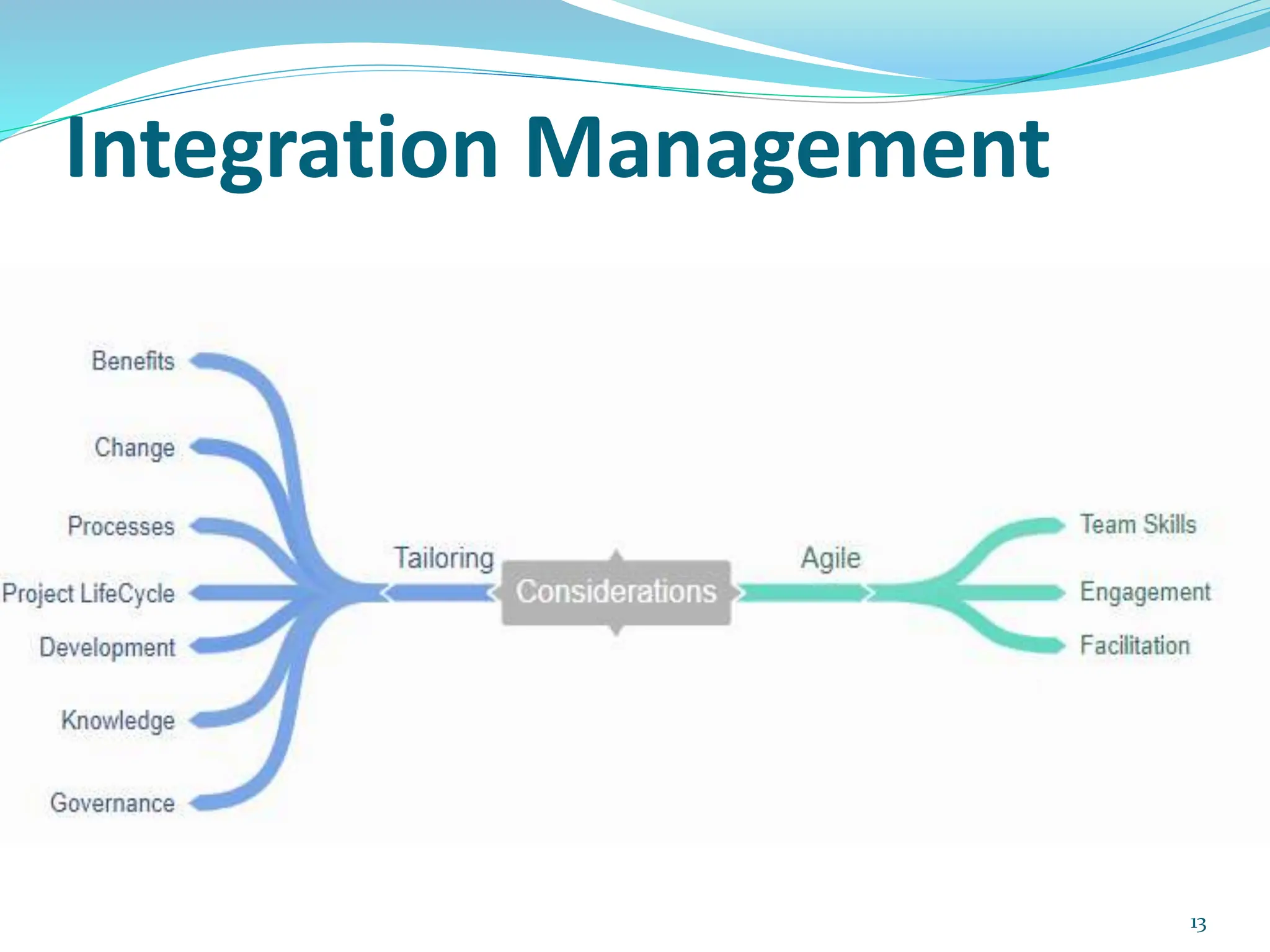
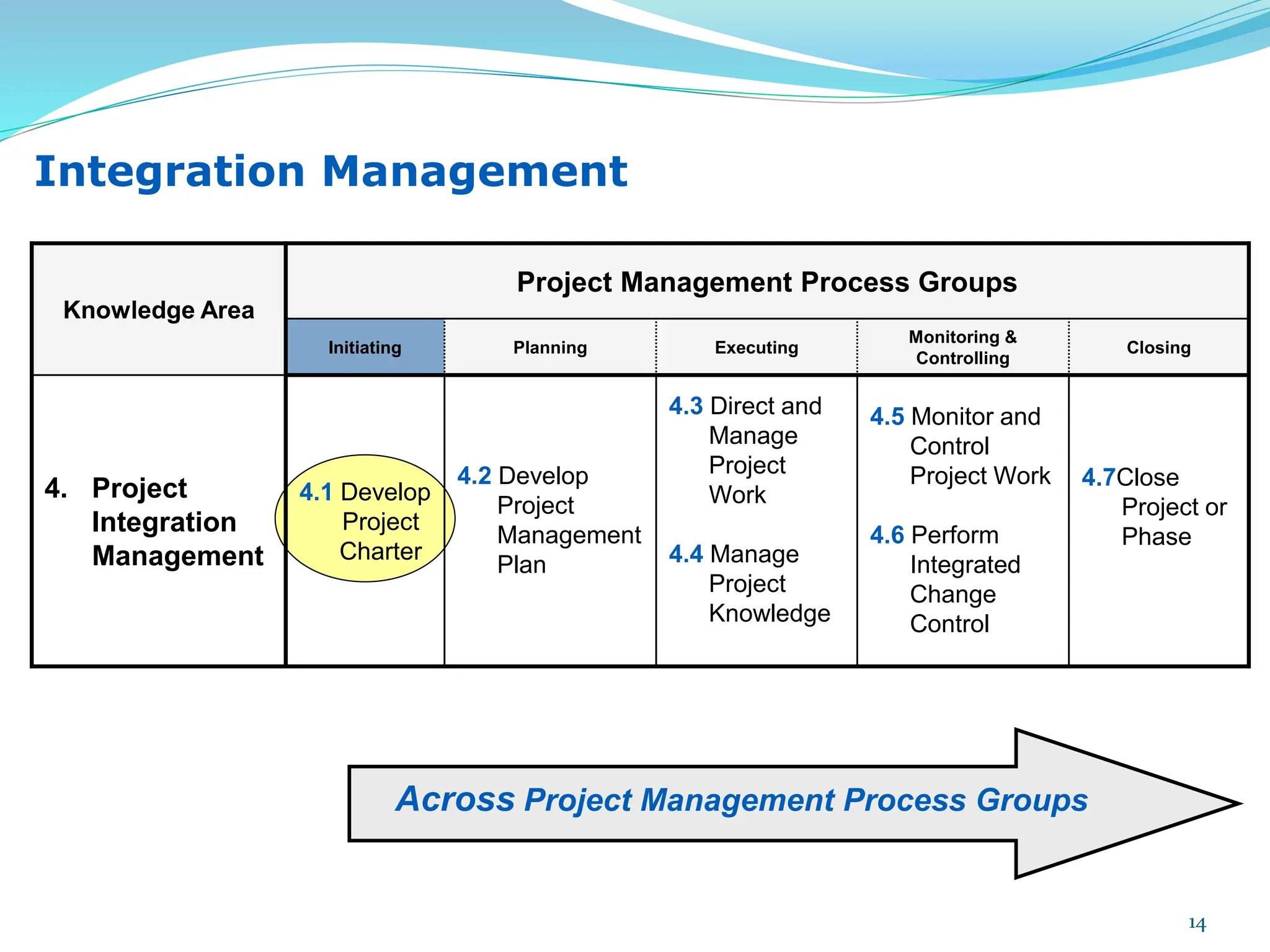
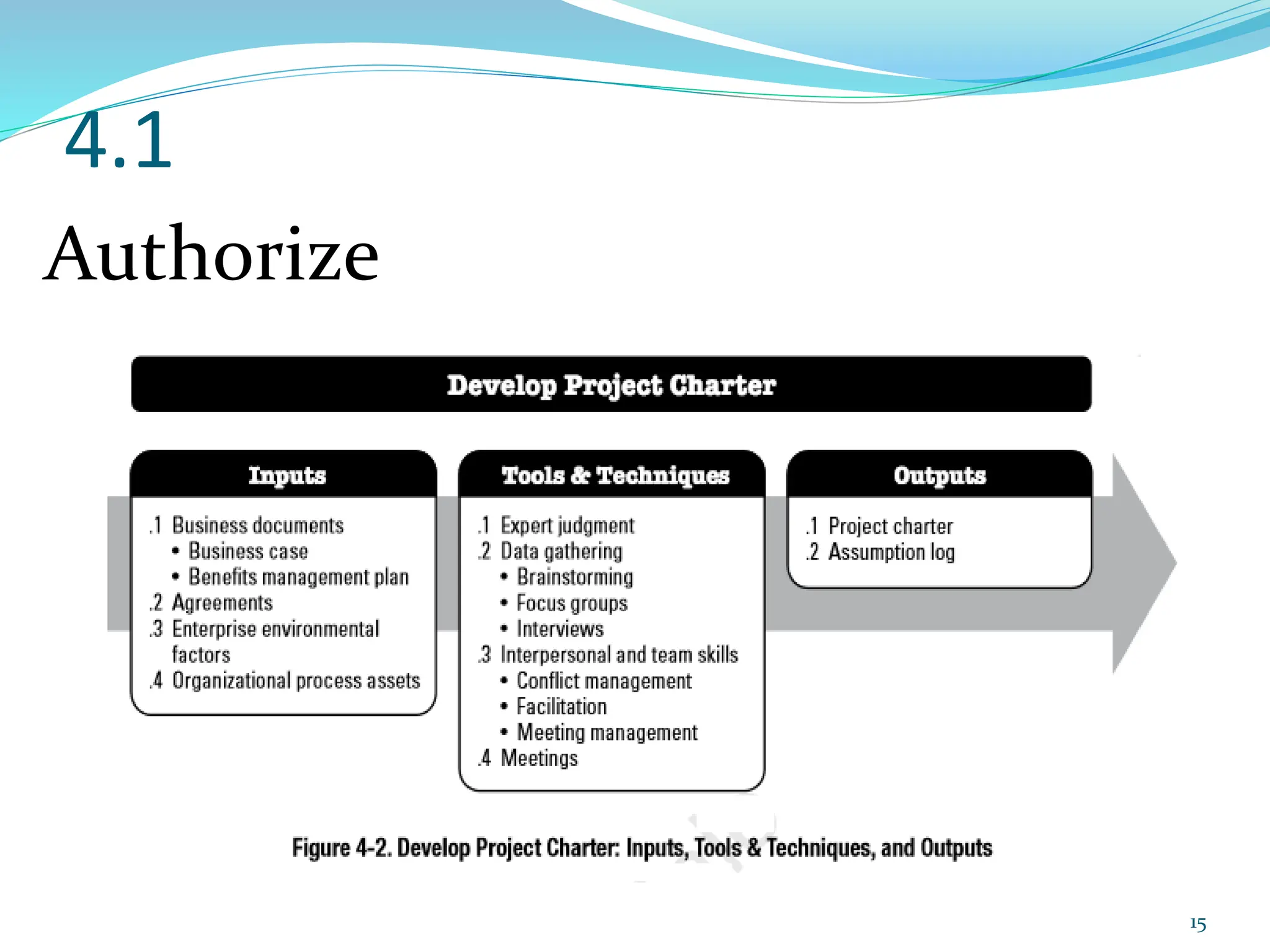
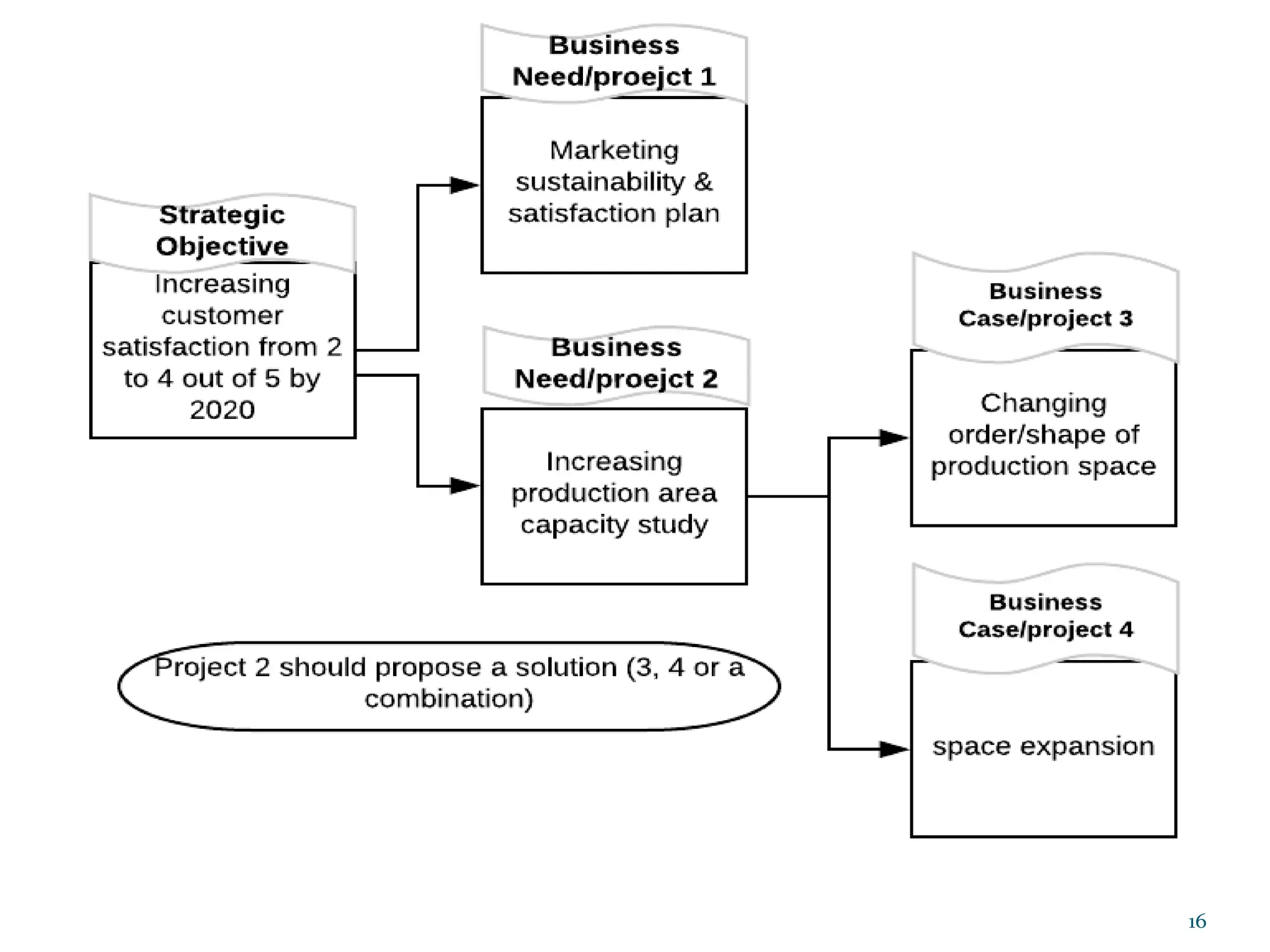
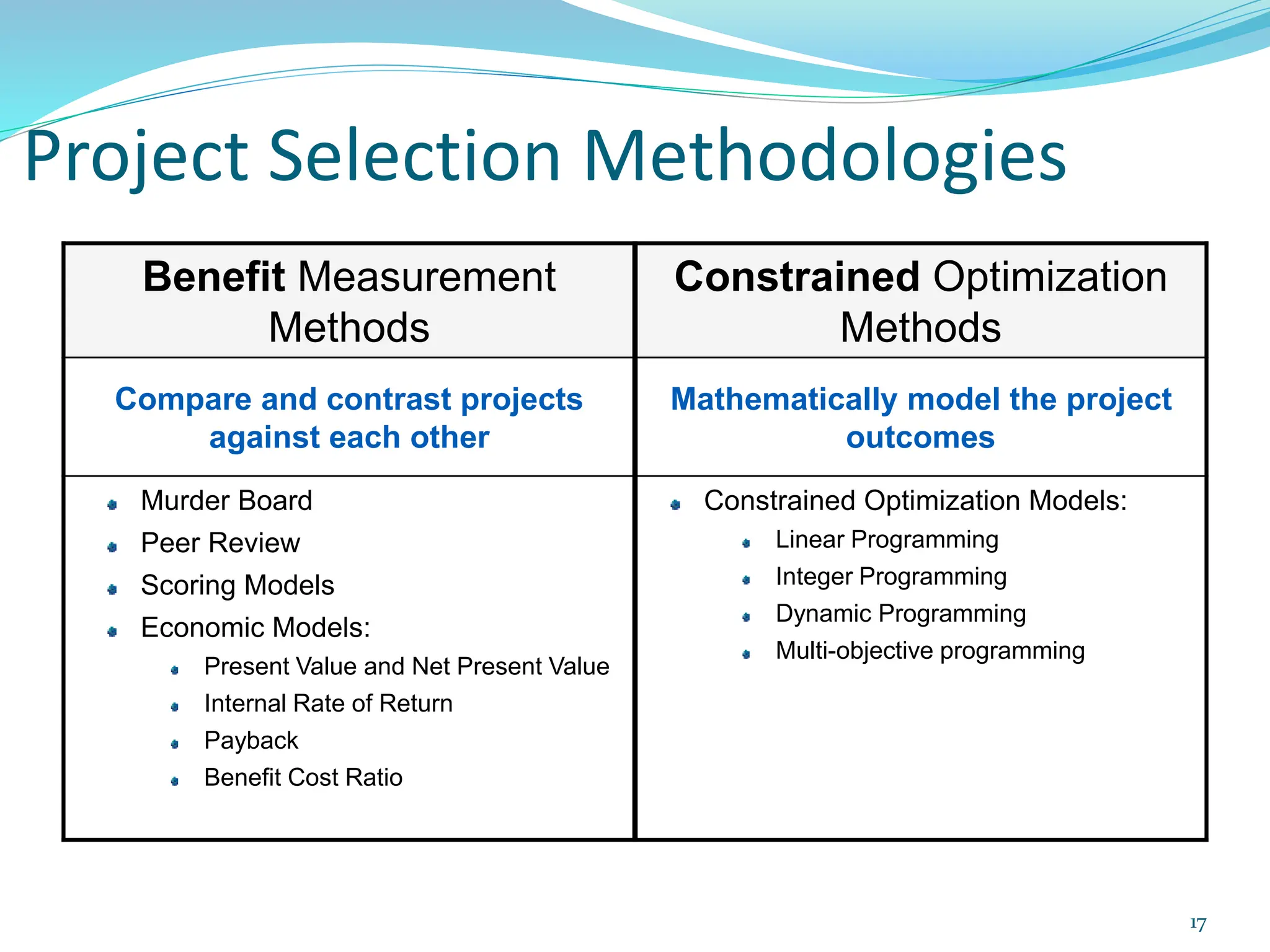
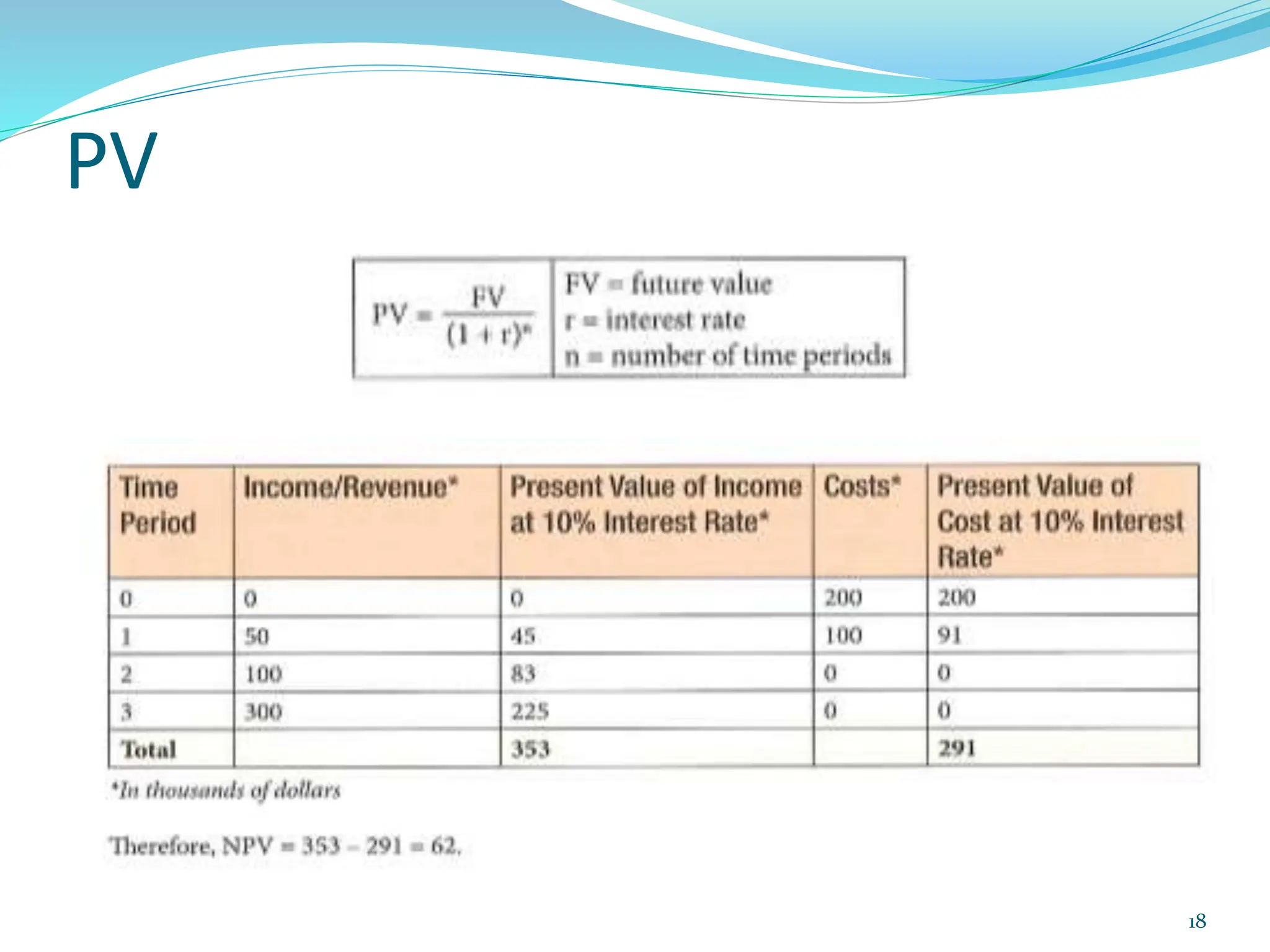
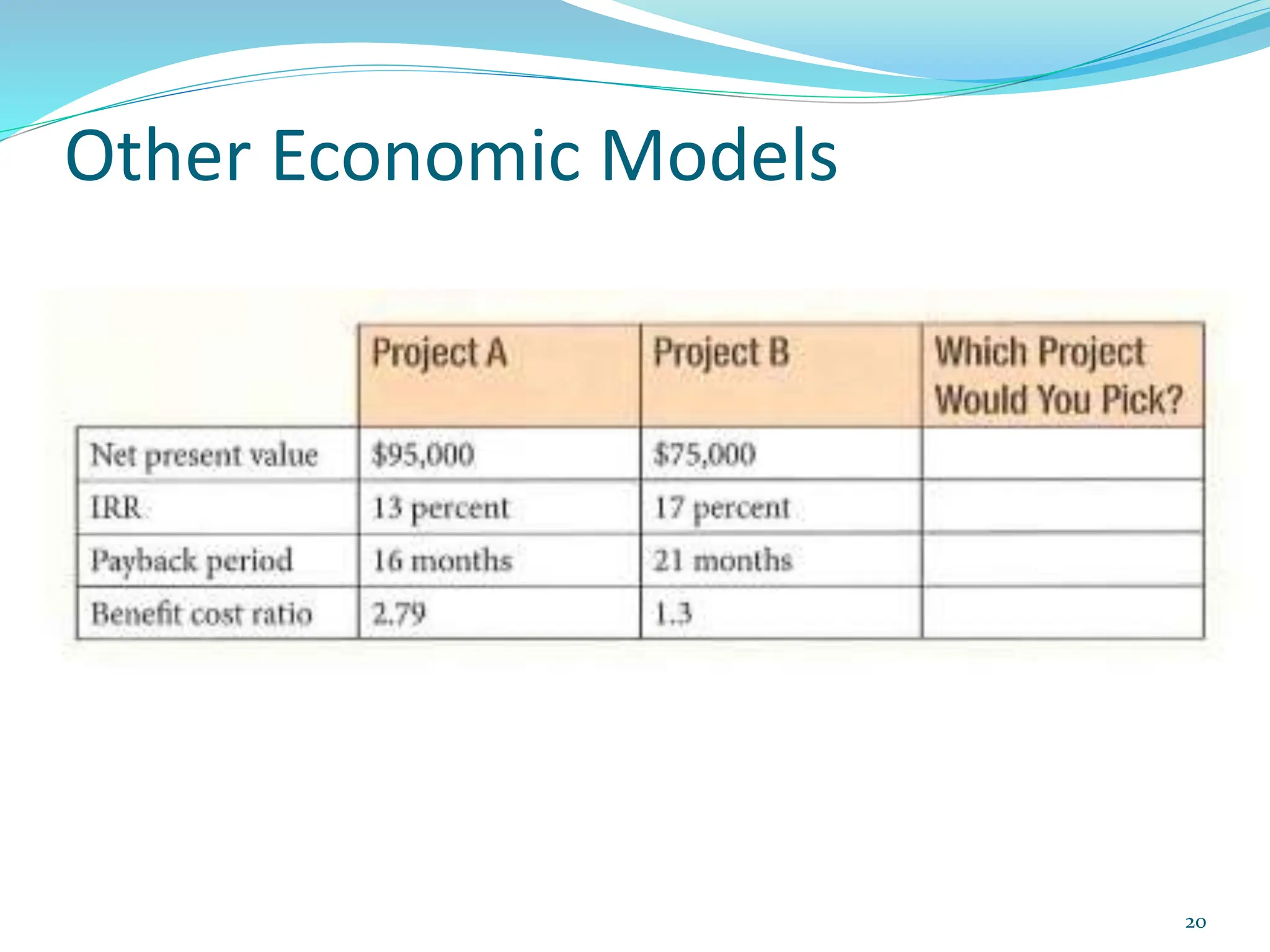
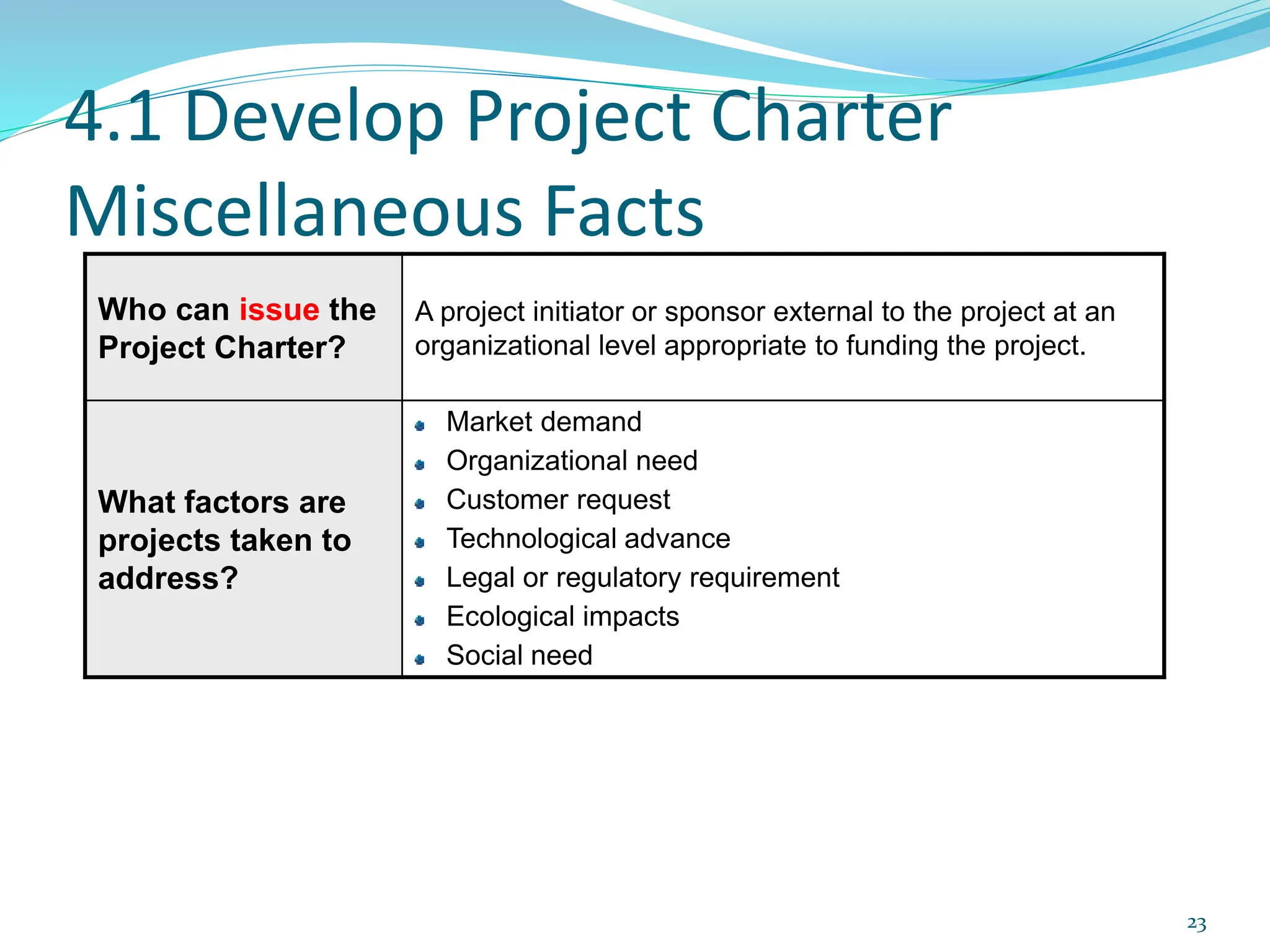
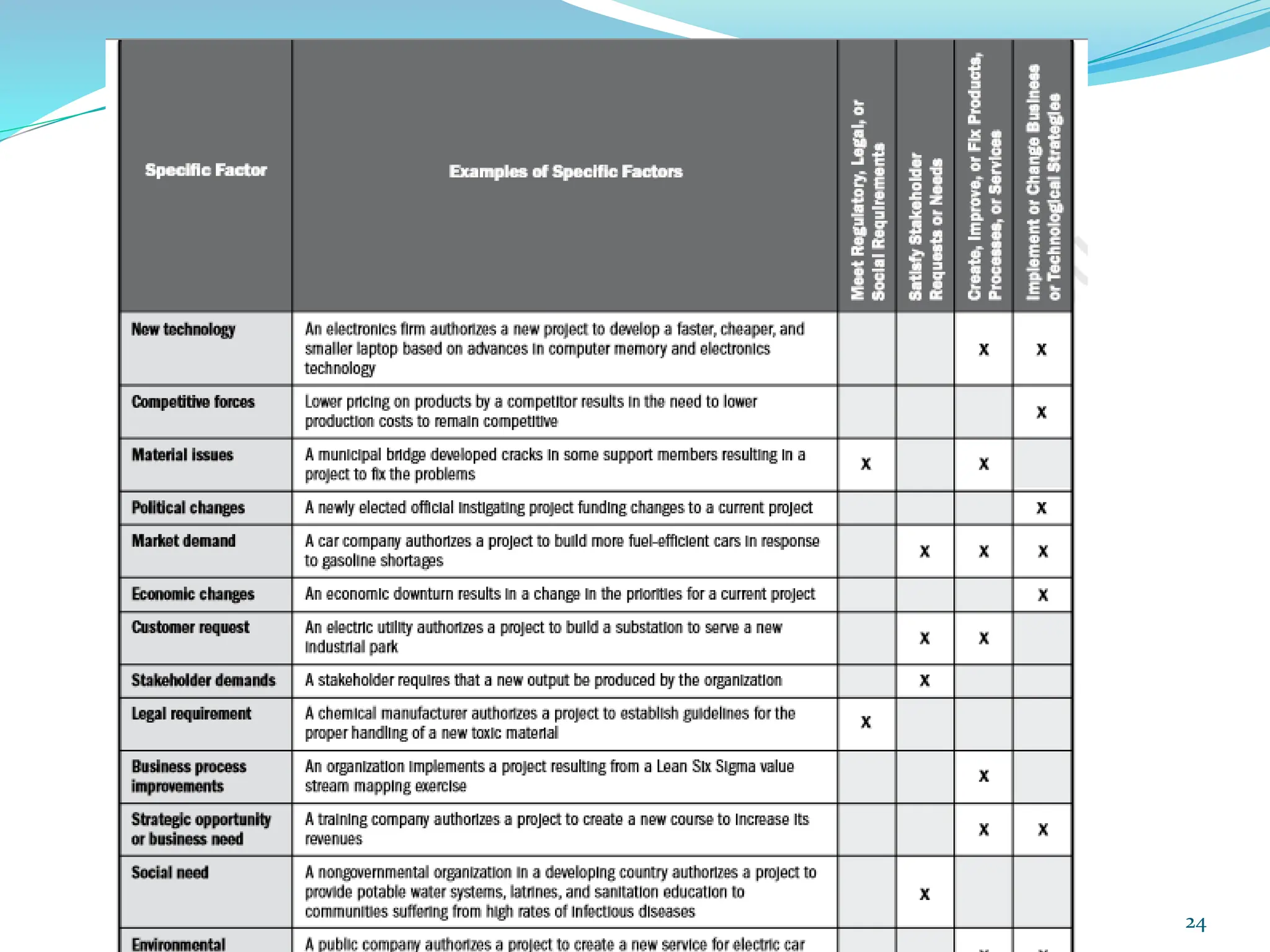
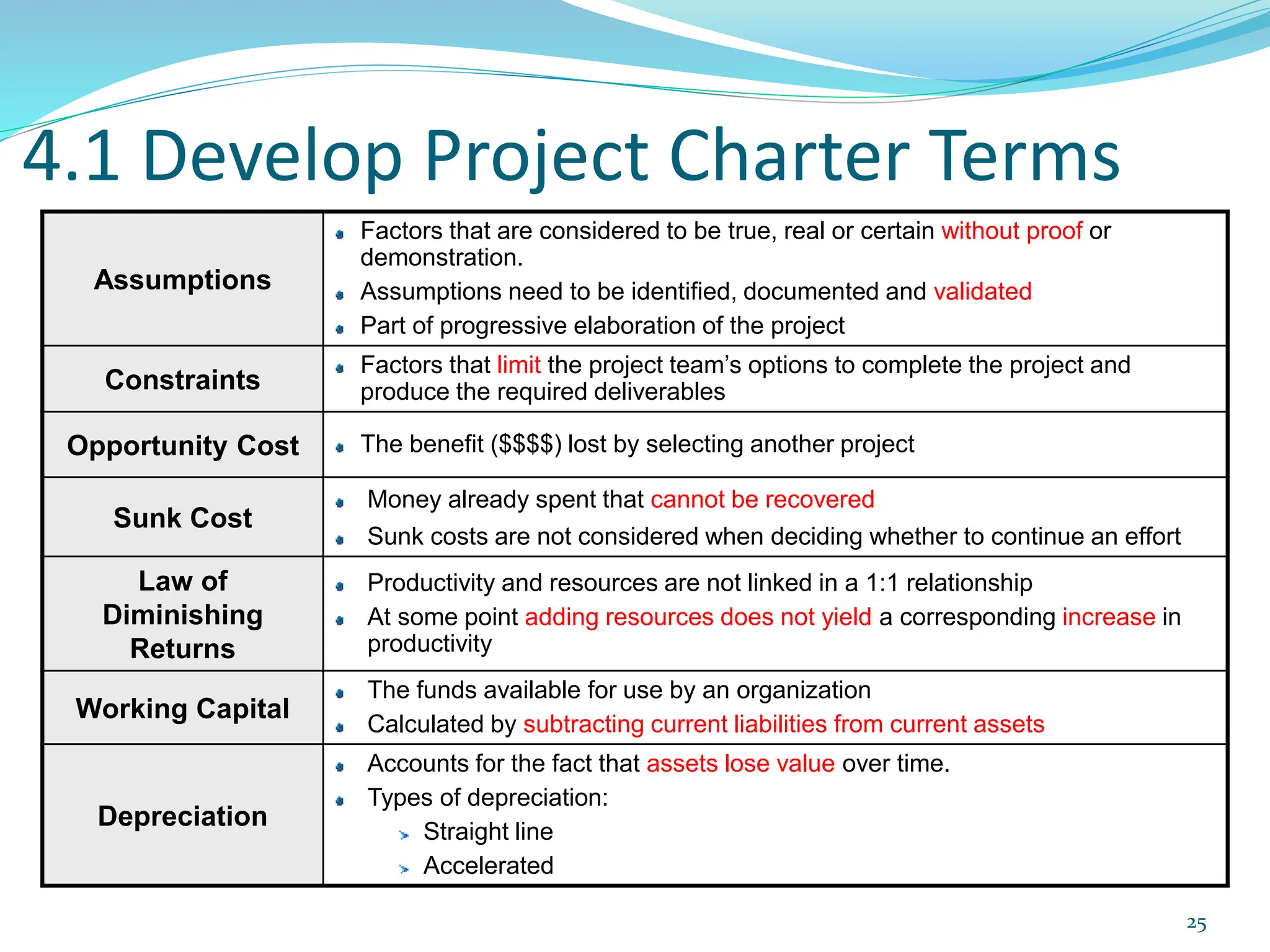
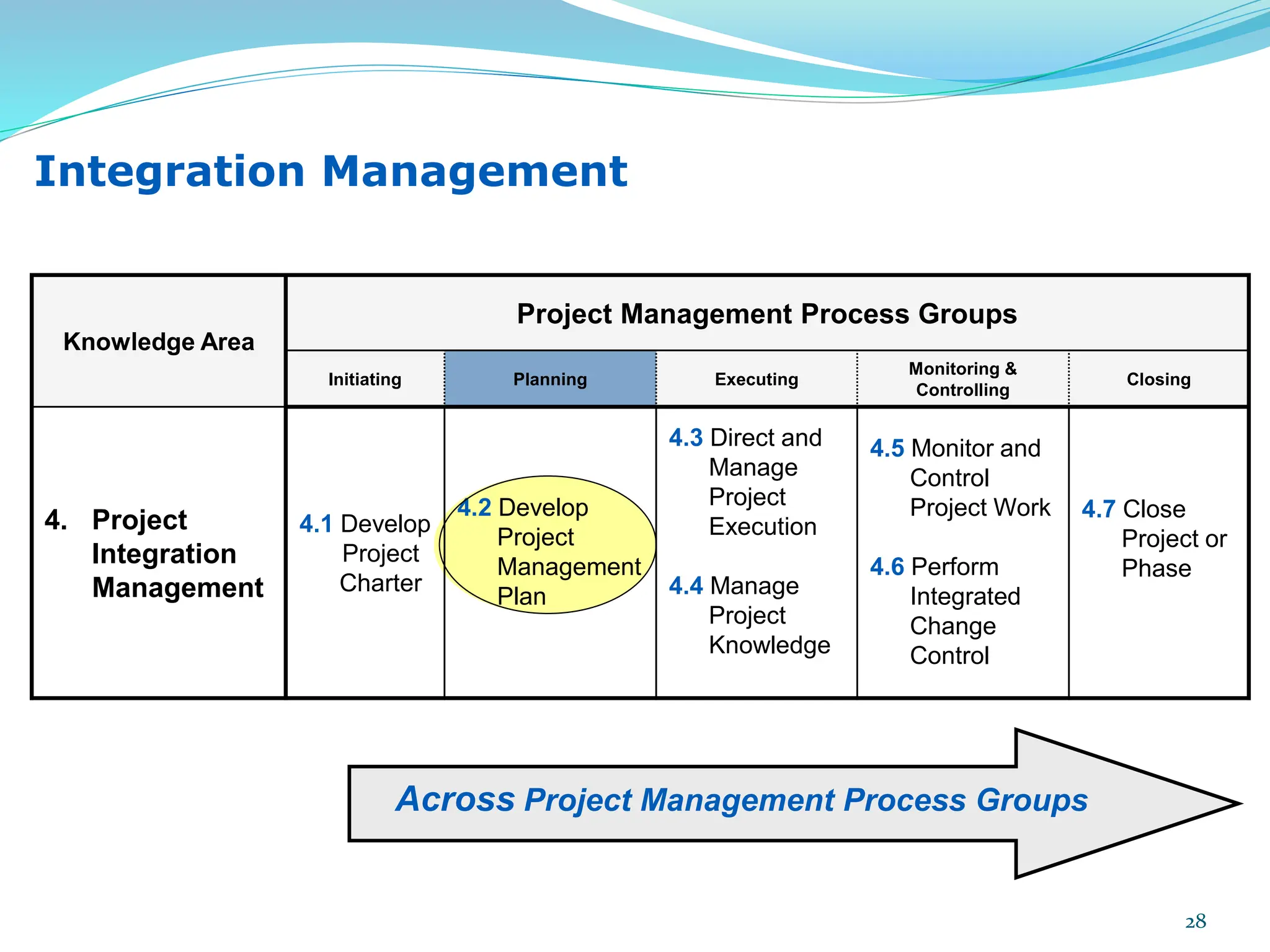
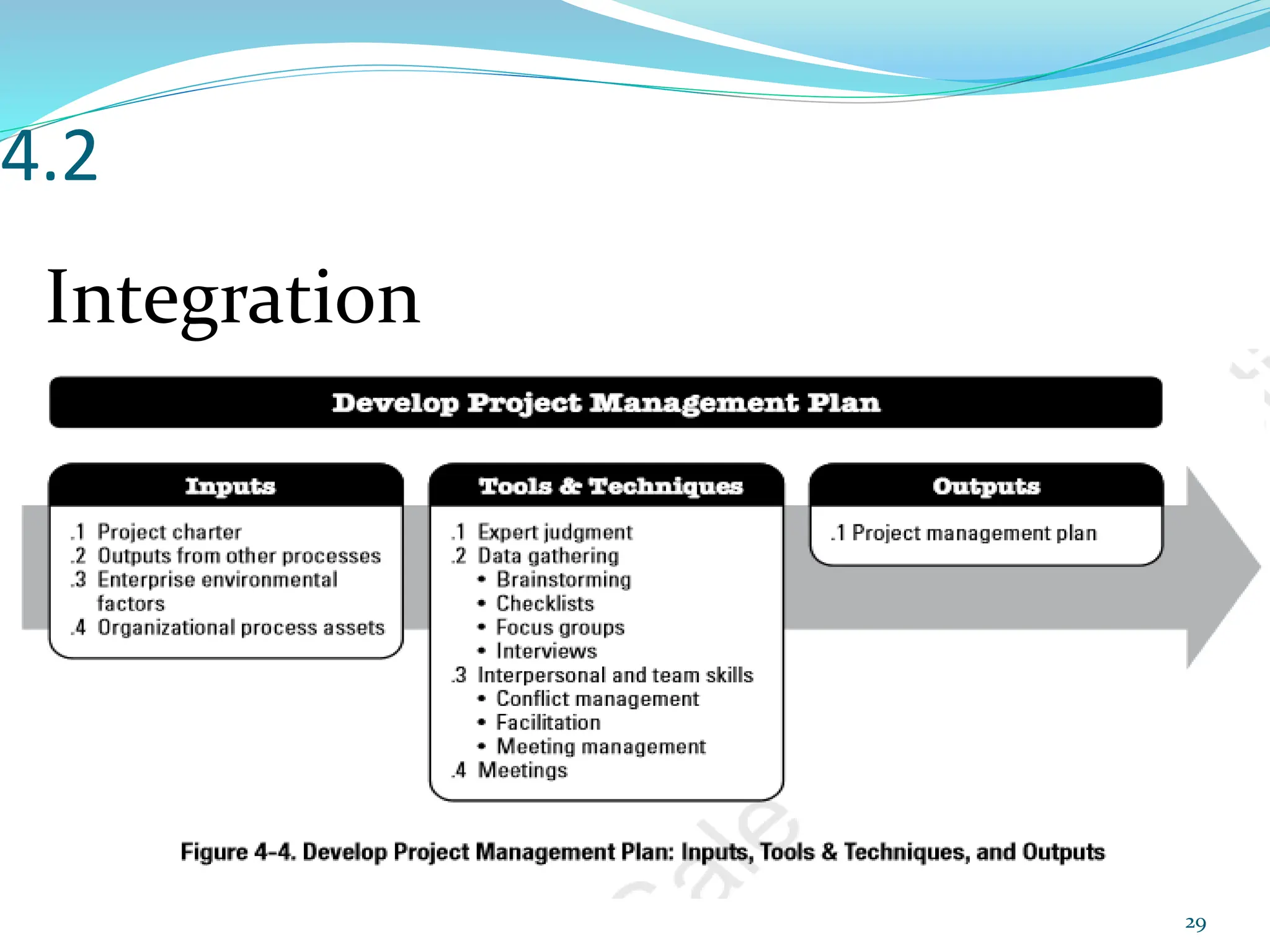
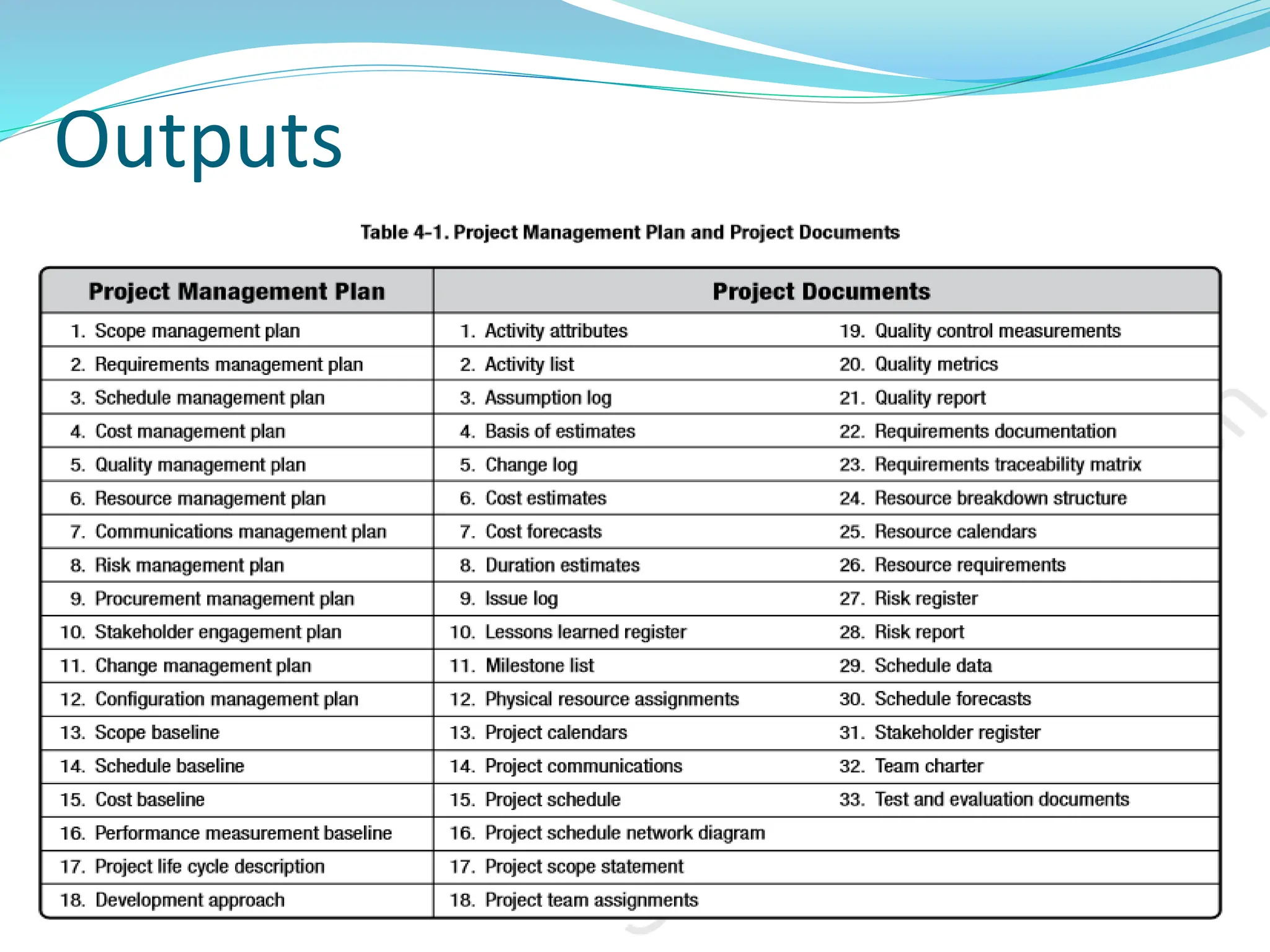
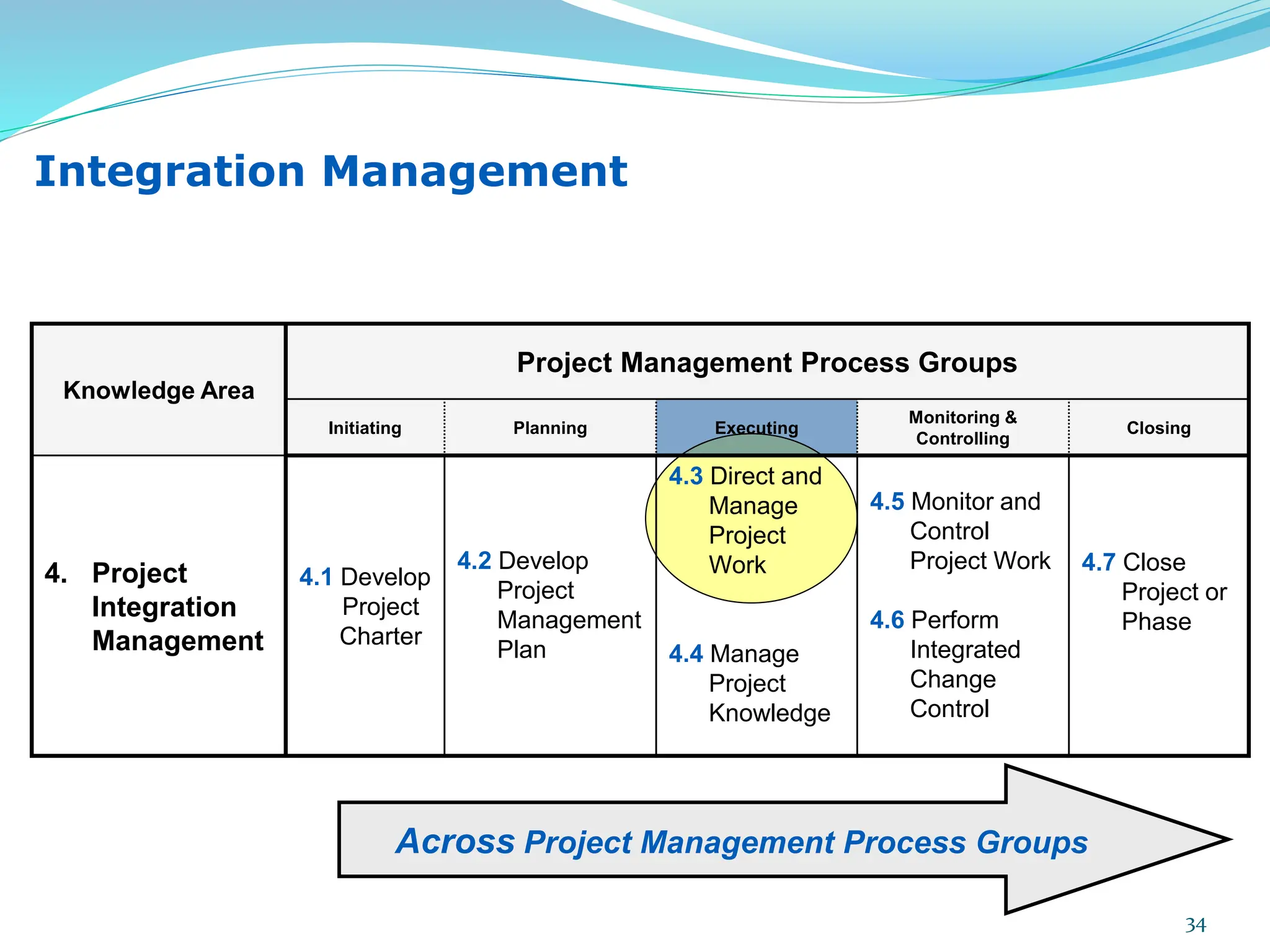
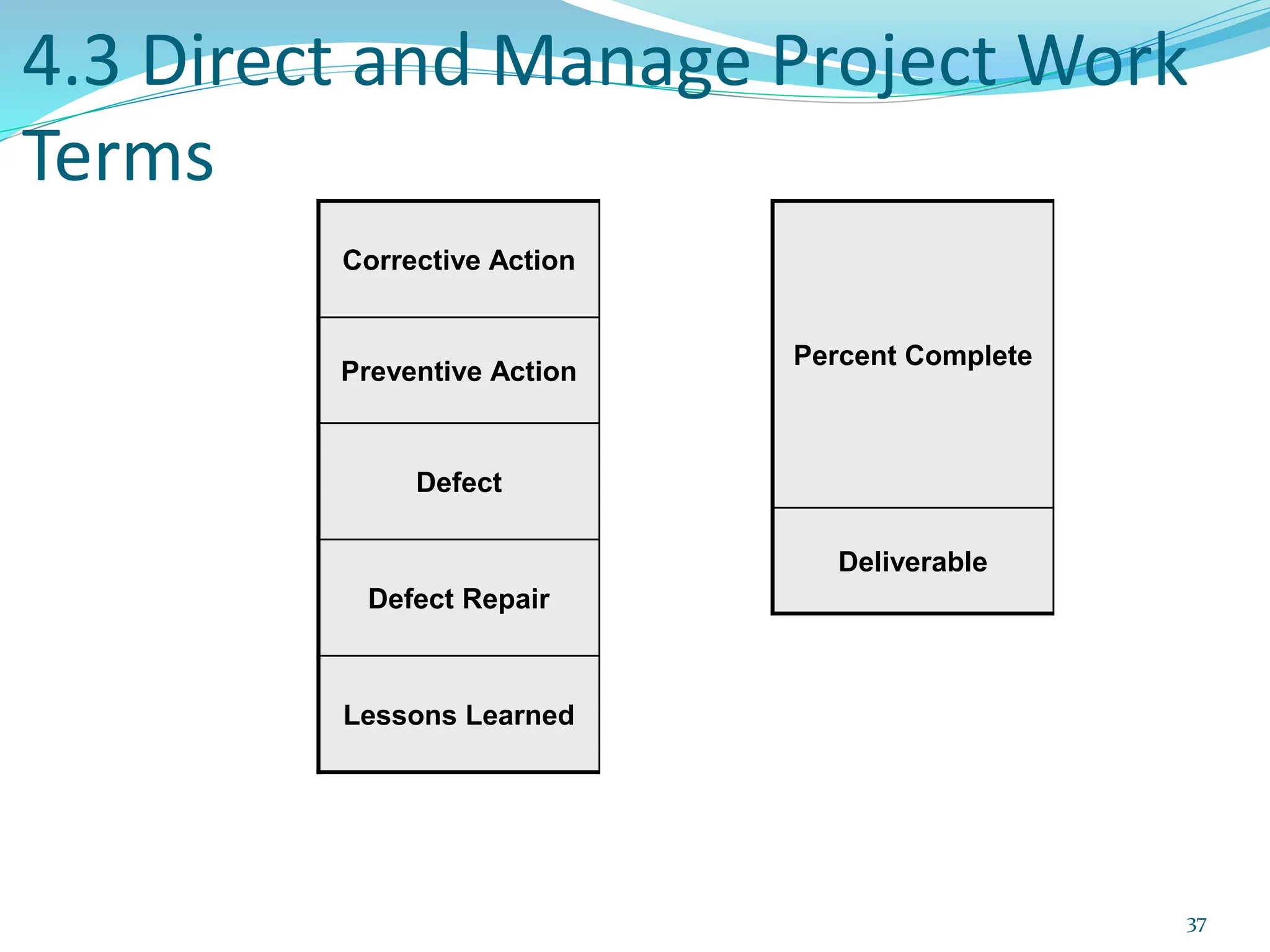
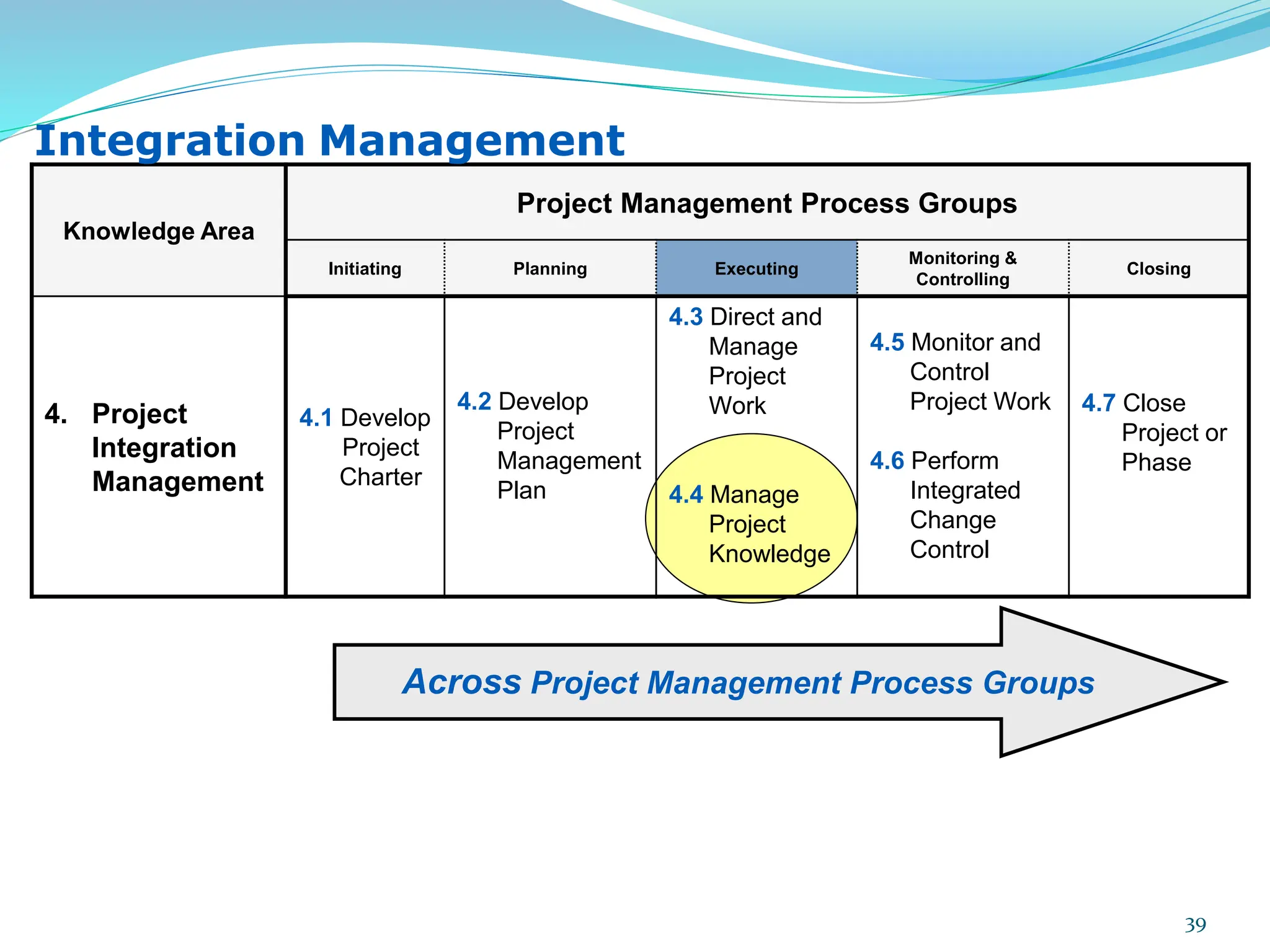
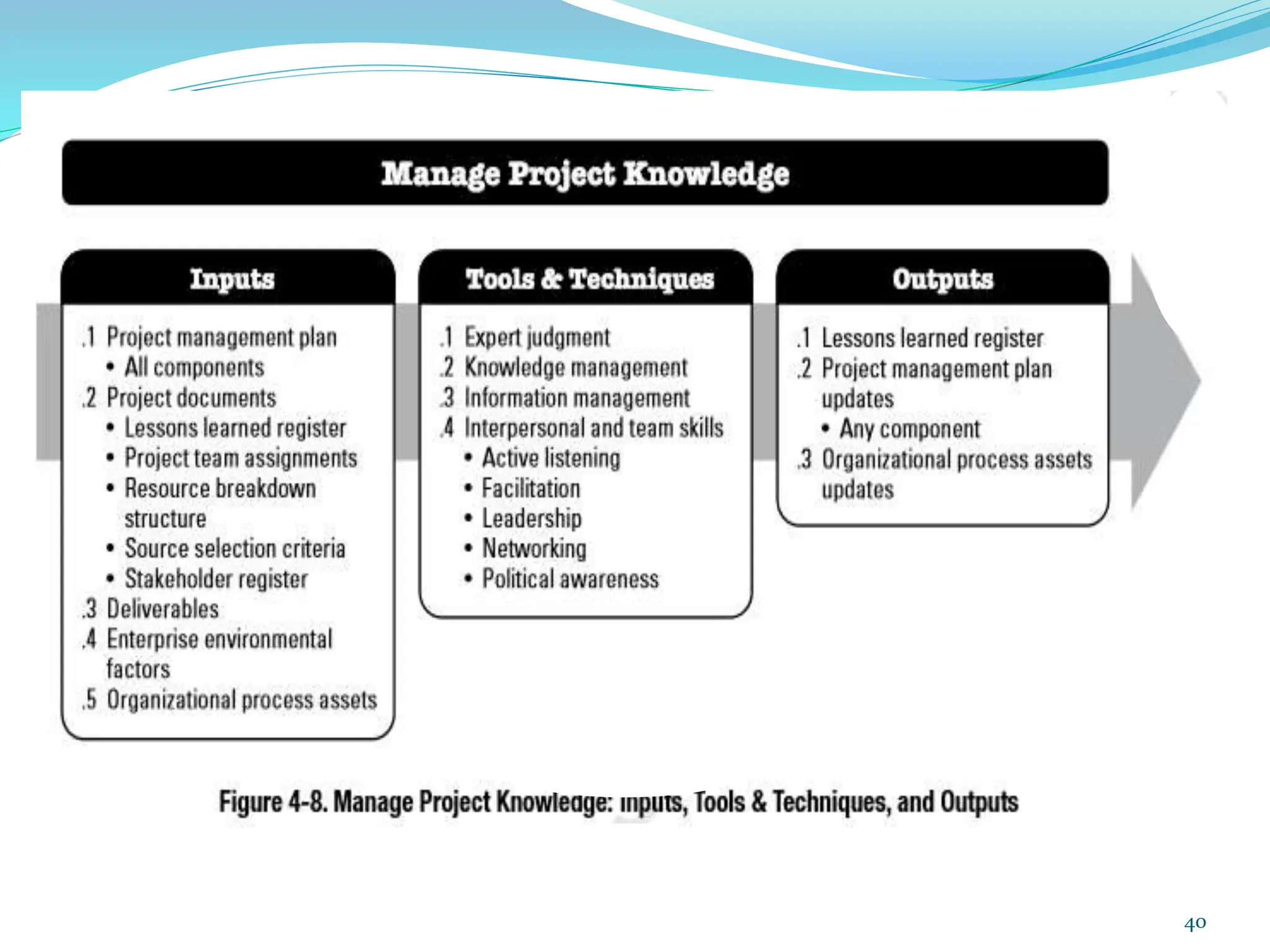
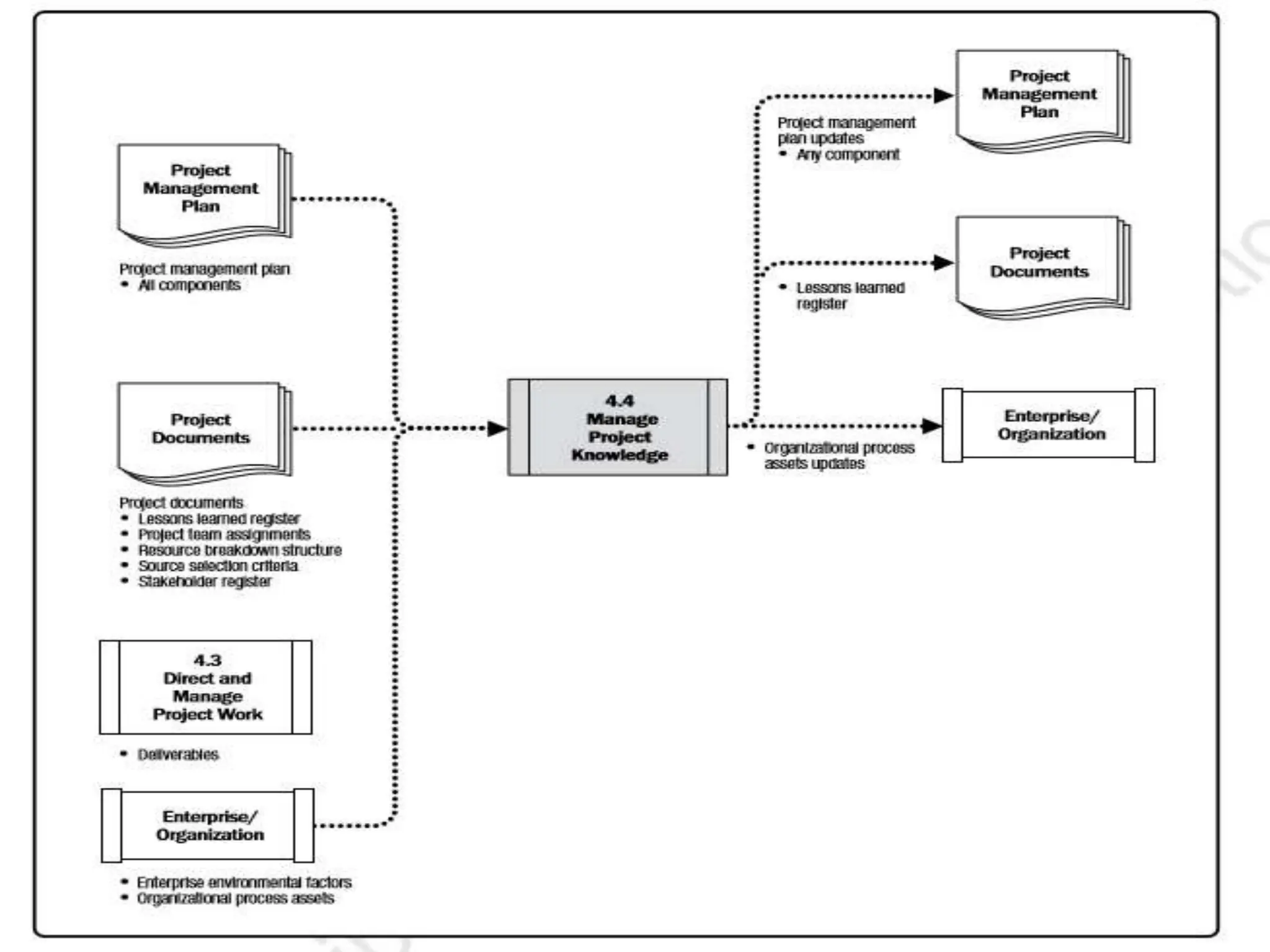
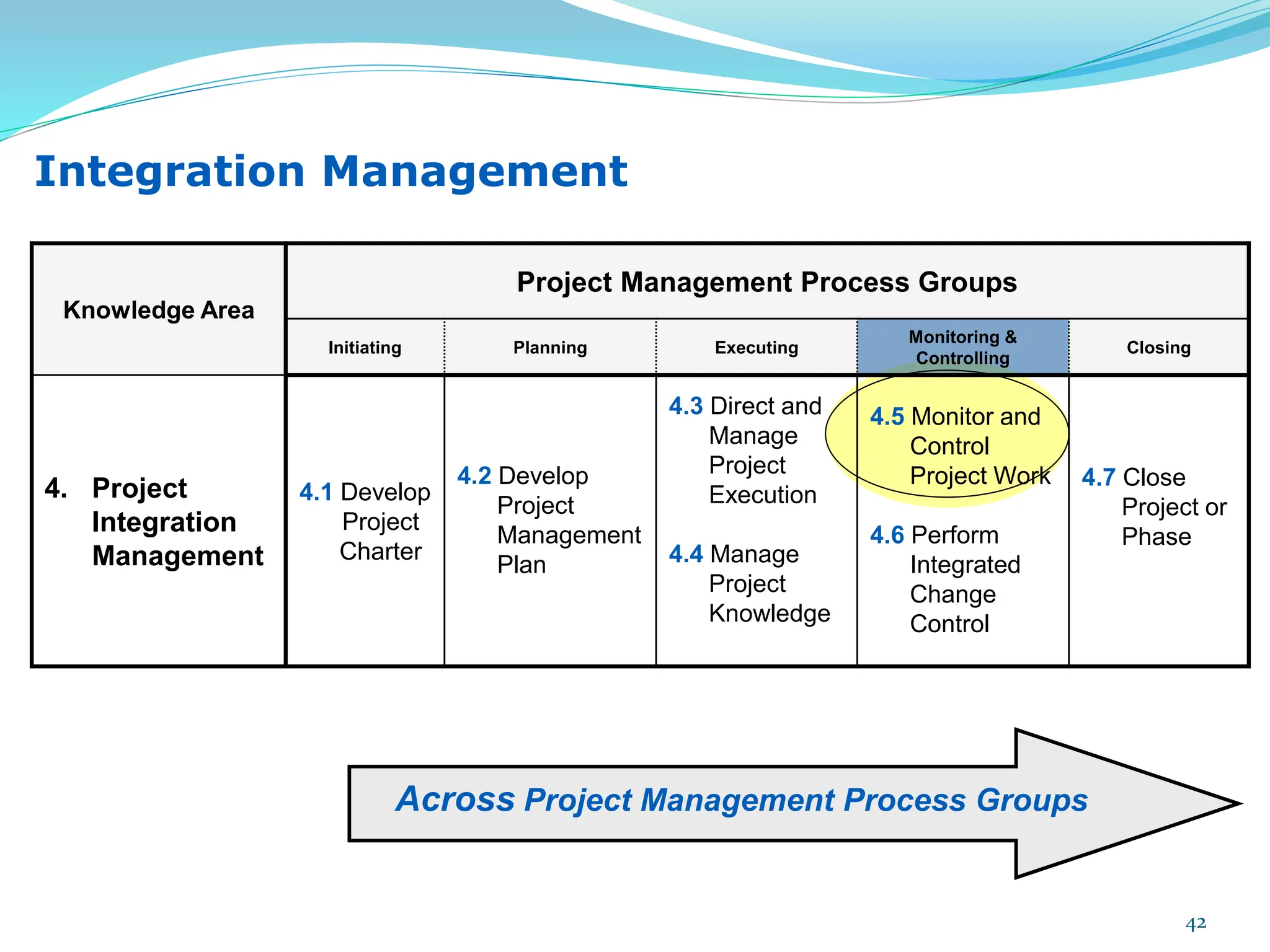
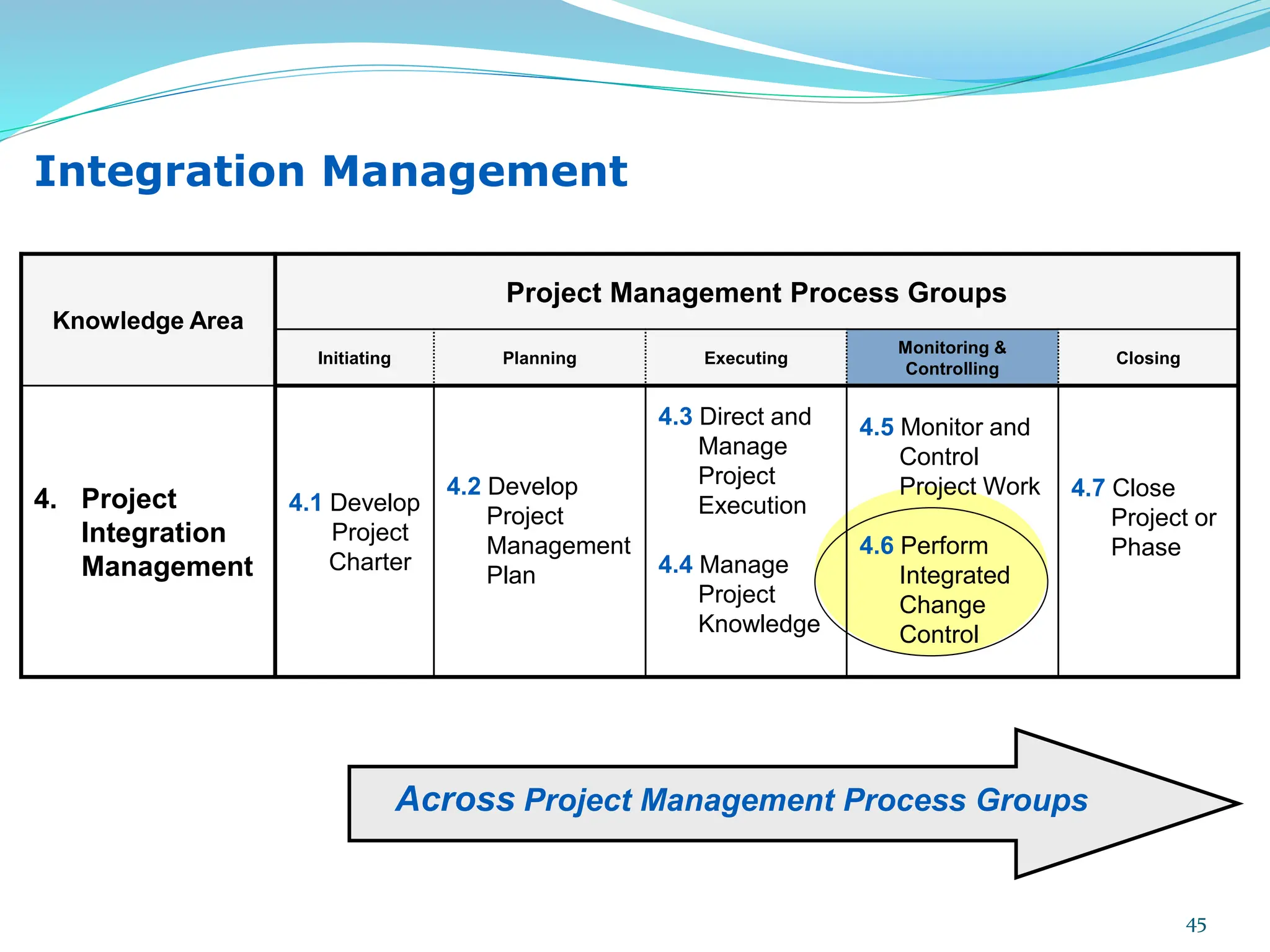
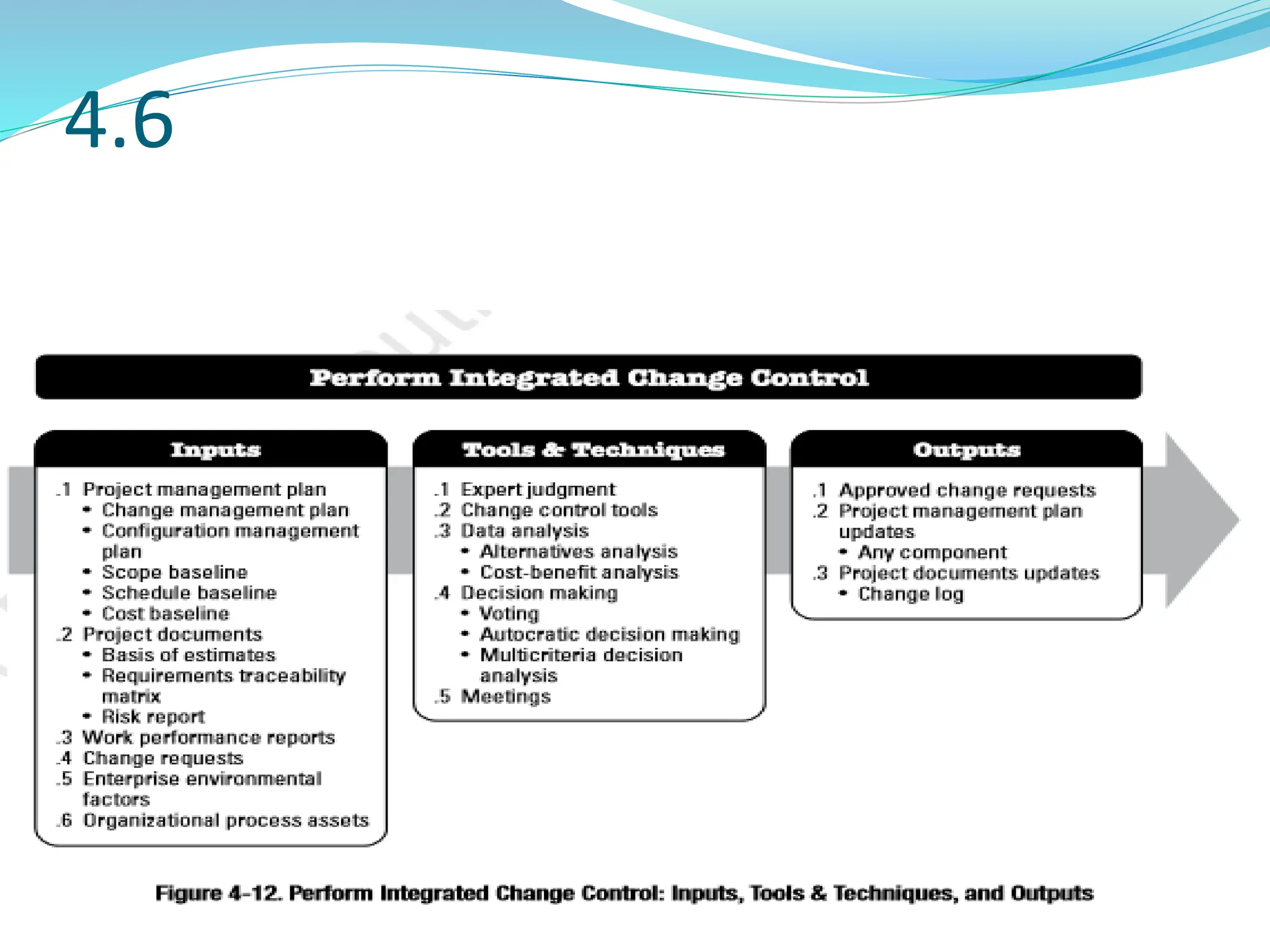
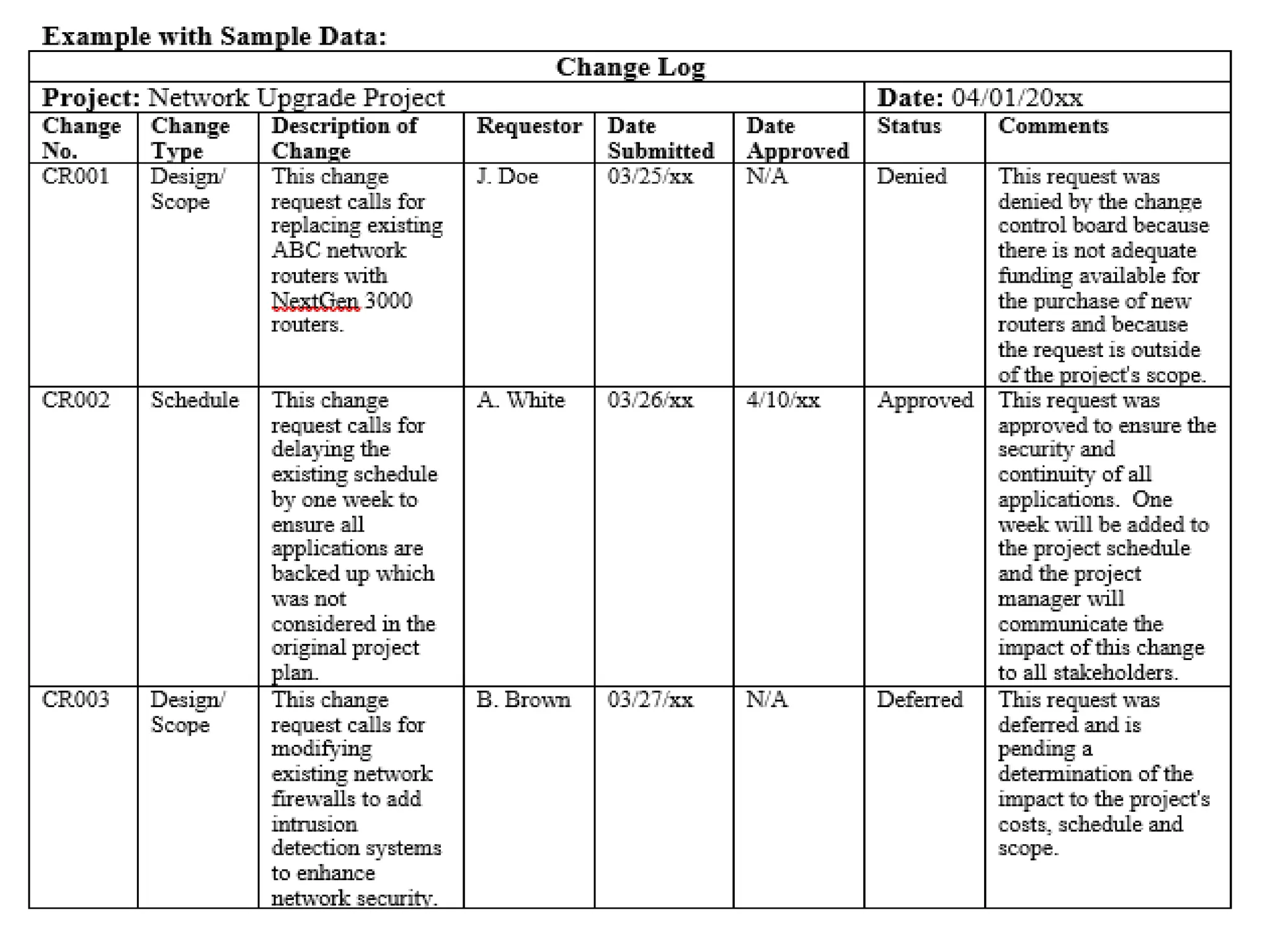
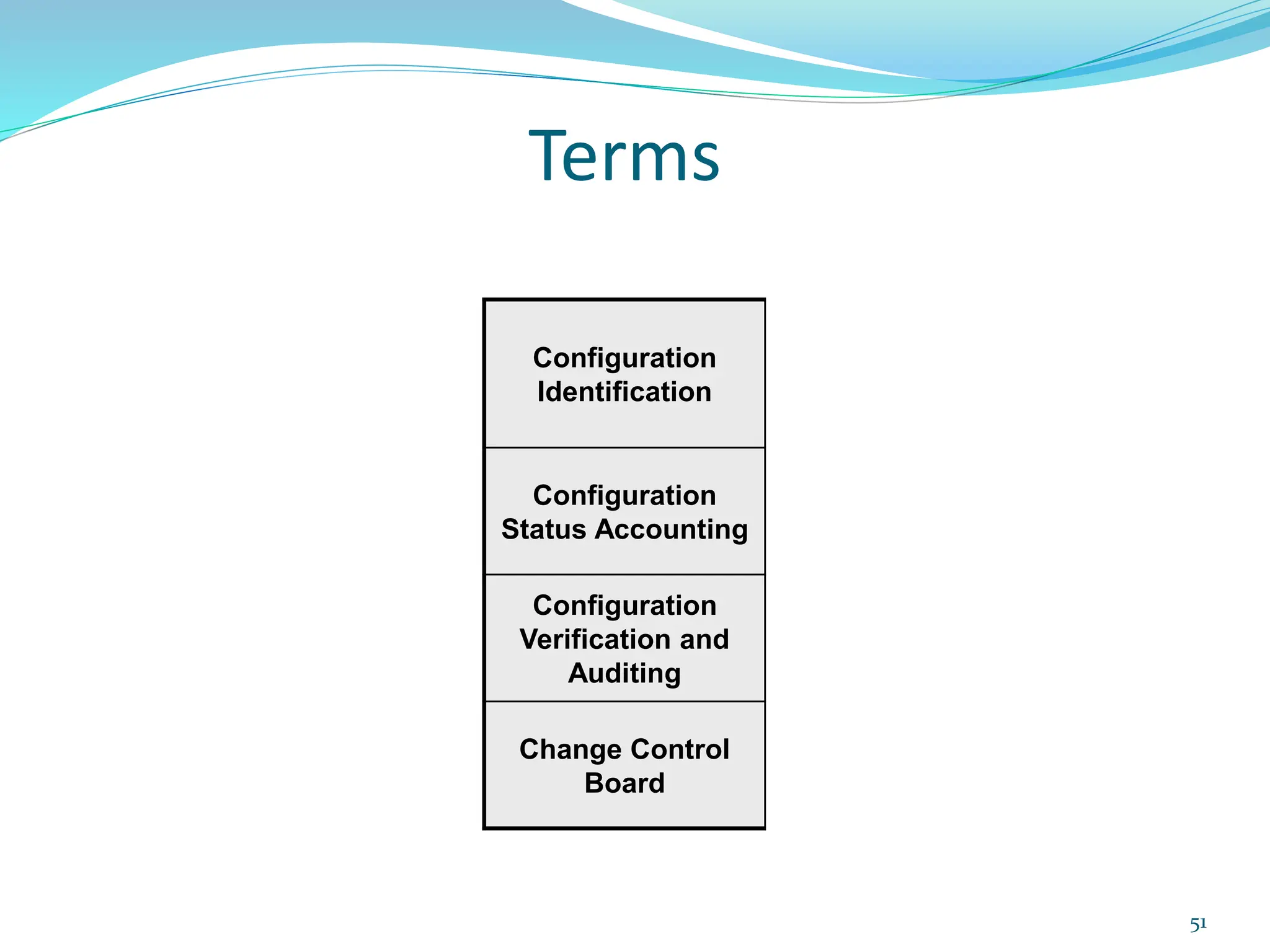
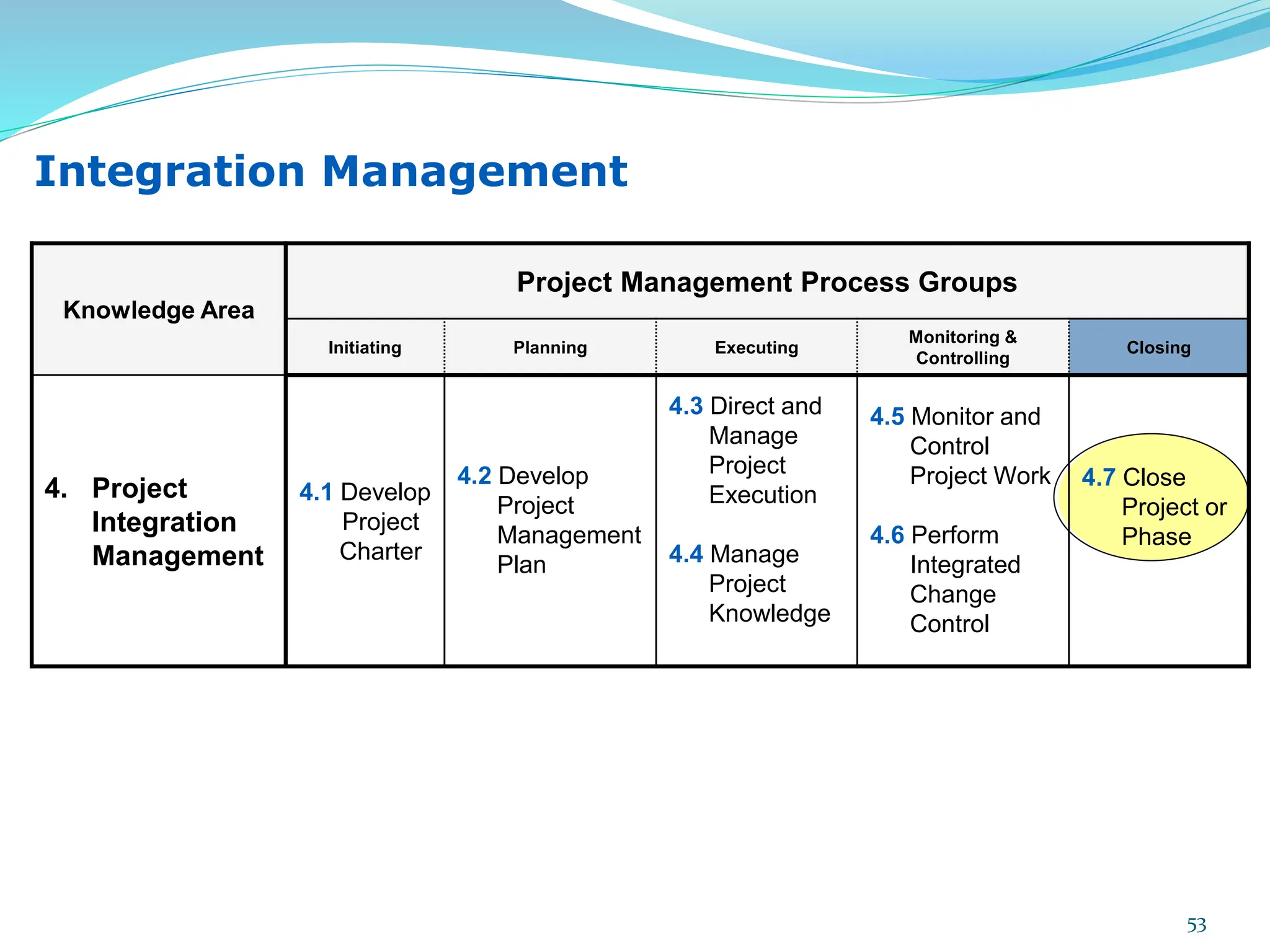
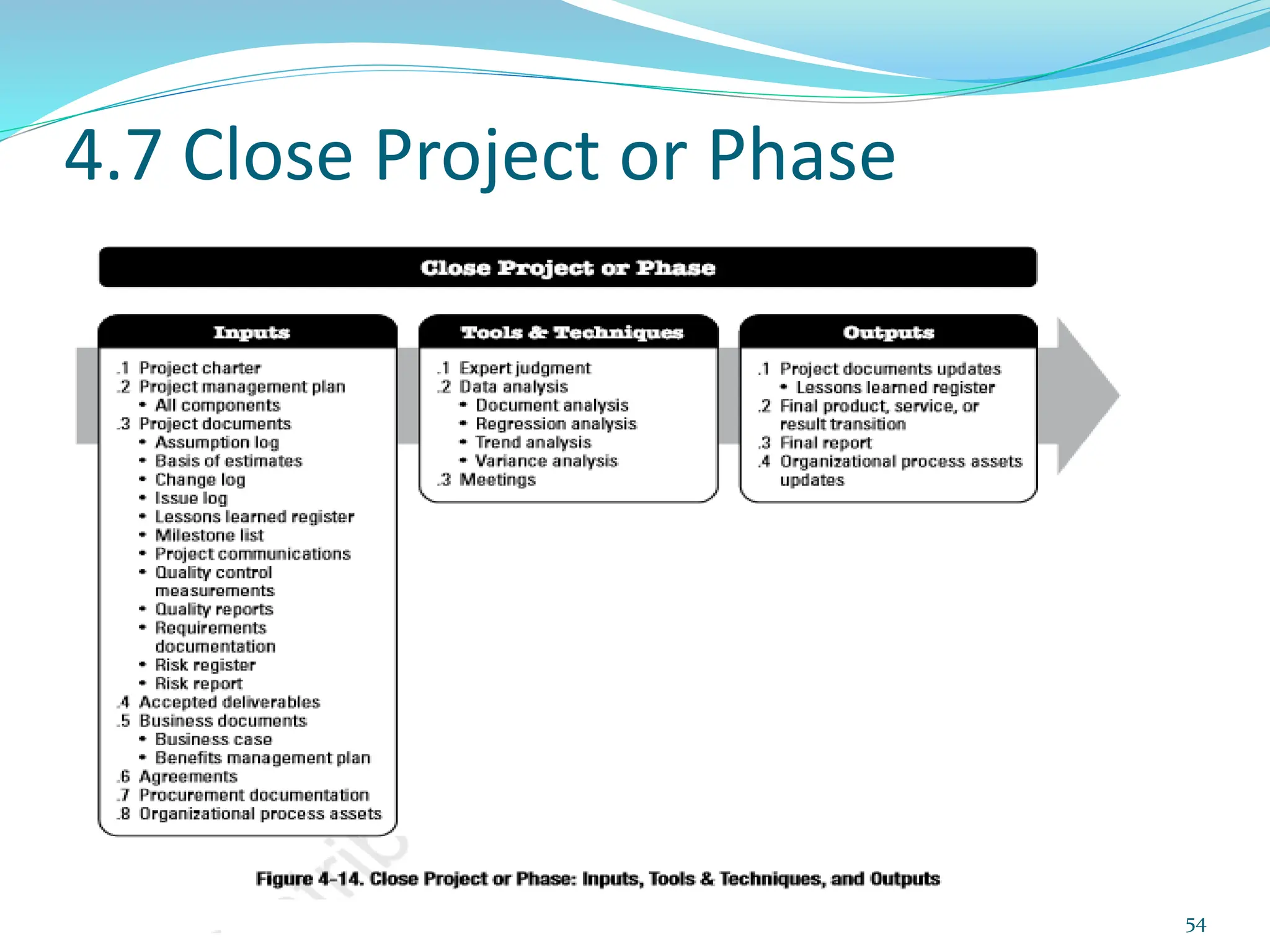
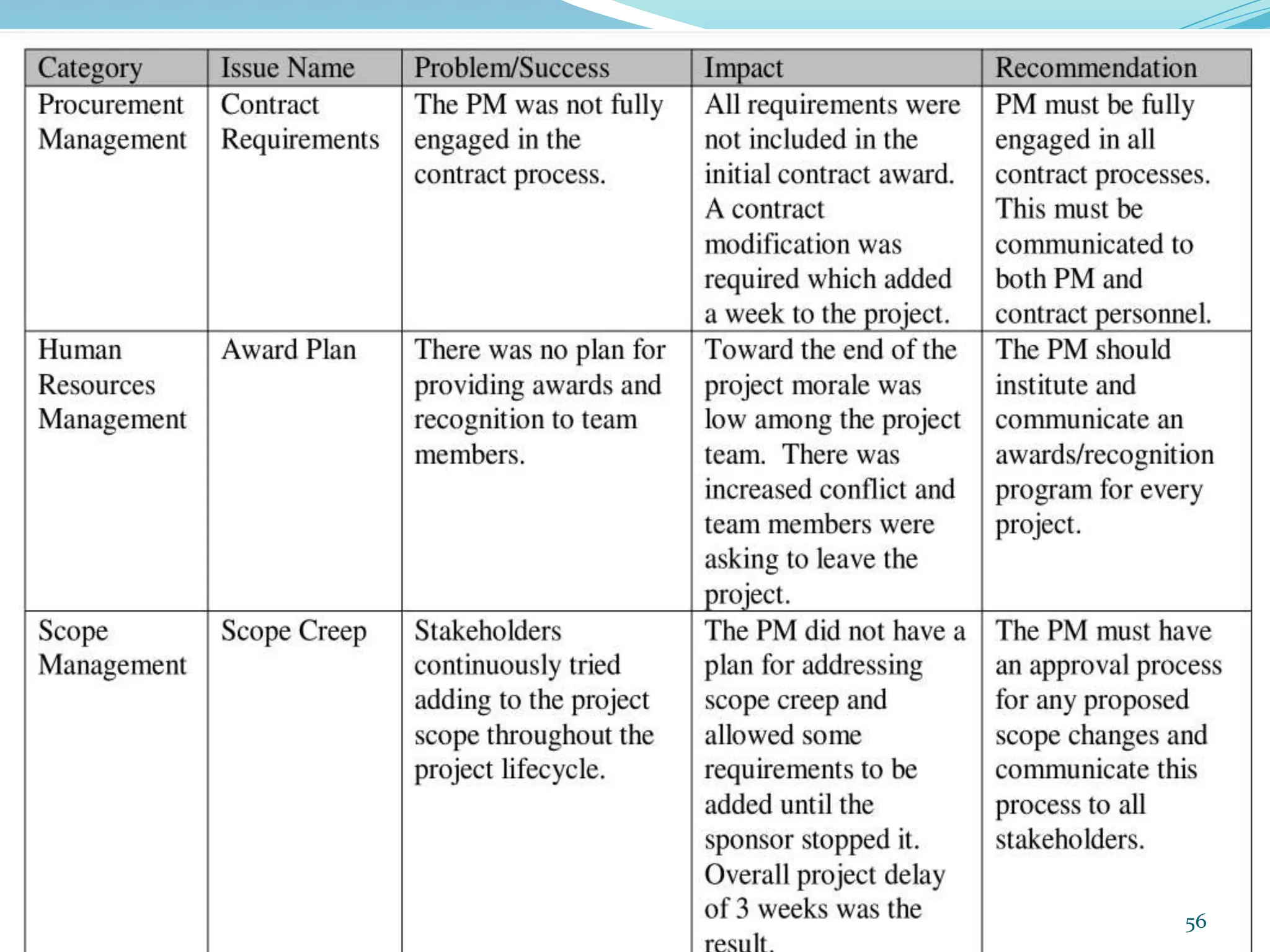
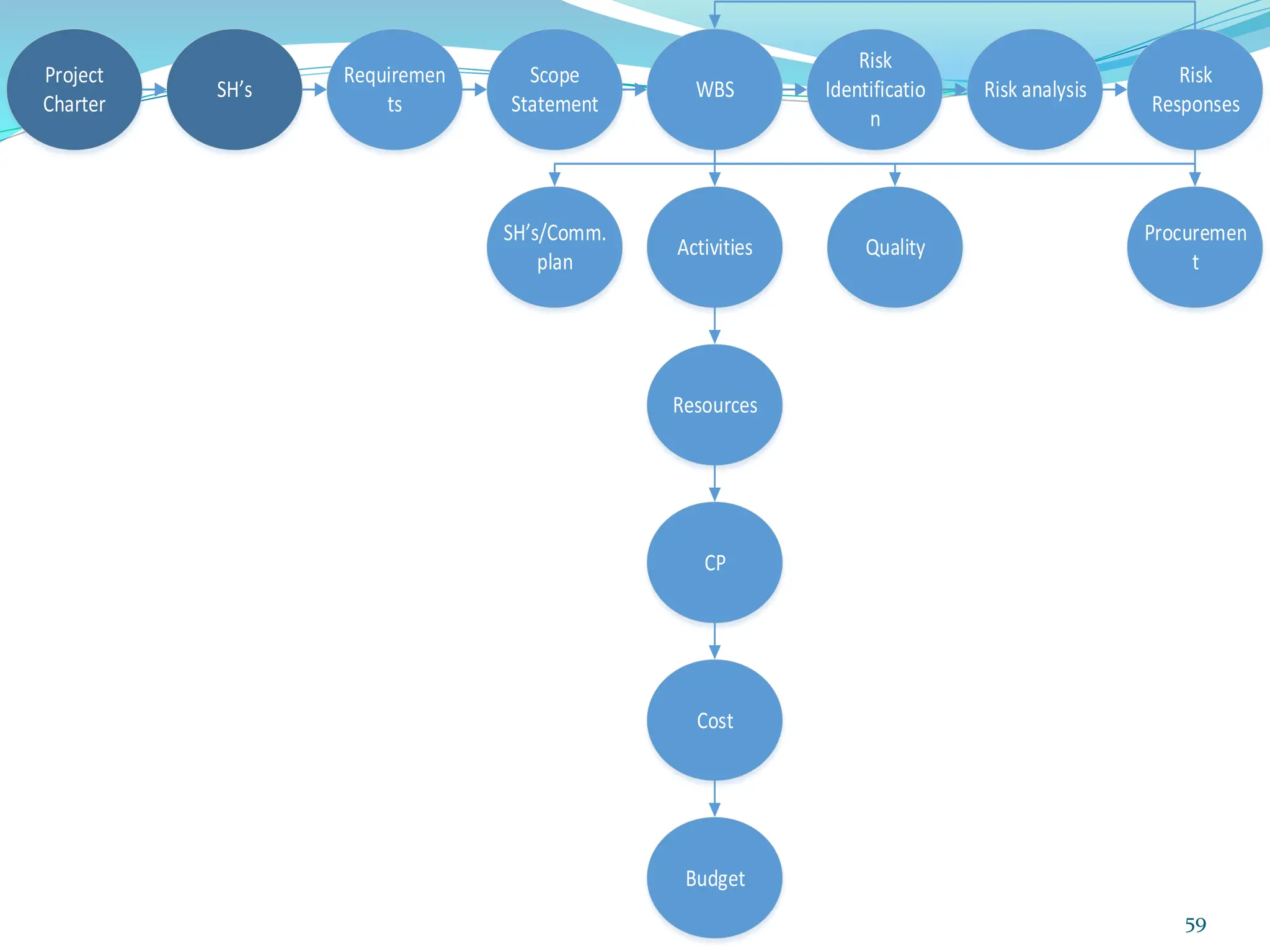
This document provides an overview of an upcoming project management training course. It outlines the vision, goals, resources, audience, evaluation process, and course structure. The course structure lists the topics that will be covered each day, including integration management, stakeholders, scope, schedule, cost, quality, risk, procurement, ethics, Agile, and exam preparation. Sample project charter examples and integration management concepts are also discussed in detail throughout various slides. The document aims to inform participants about what to expect from the training to help them become certified in project management.