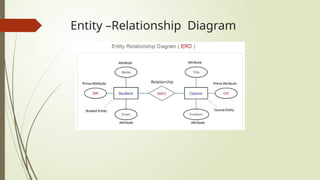
The document provides an overview of Database Management Systems (DBMS), explaining their purpose and types, such as relational and NoSQL DBMS. It covers key database terminologies, including tables, entities, attributes, primary and foreign keys, and relationships, while also highlighting the advantages of using a DBMS like data redundancy reduction and improved security. Ultimately, it emphasizes the structuring and efficient management of data within a database.