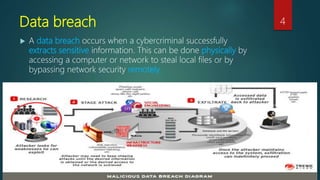
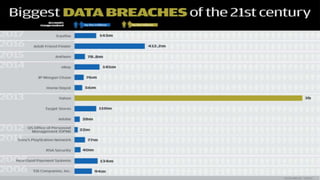
The document discusses database security and common database attacks. It outlines six types of database attacks: excessive privileges that allow inappropriate access to data; privilege abuse where legitimate access is used for unauthorized purposes; platform vulnerabilities that are exploited to gain access; SQL injection that allows sending unauthorized queries; denial of service techniques that compromise availability; and database protocol vulnerabilities. The document emphasizes implementing proper access controls, monitoring, and encryption of backups to mitigate these attacks.