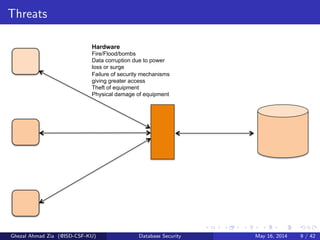
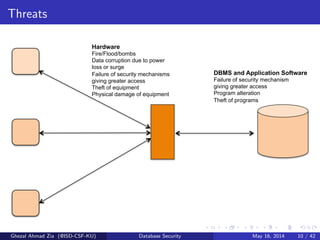
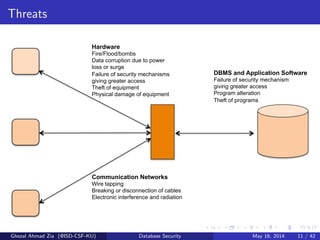
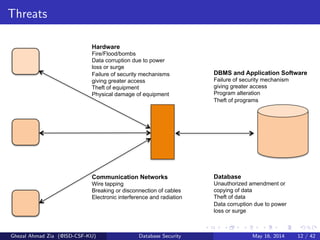
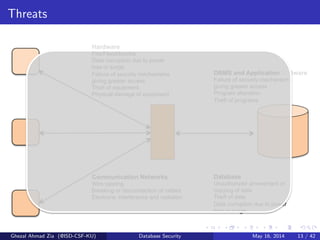
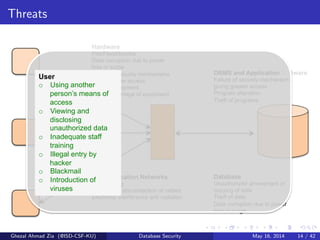
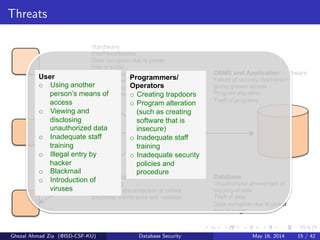
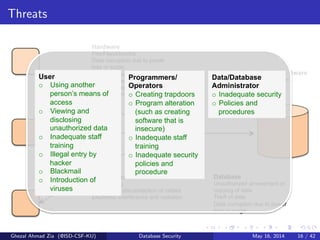
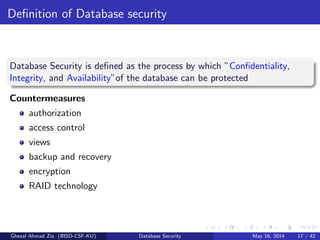
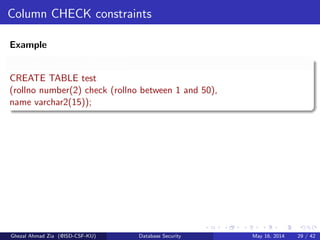
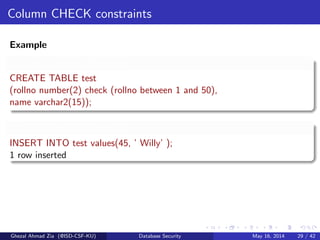
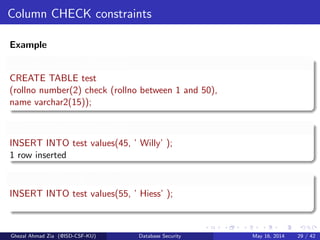
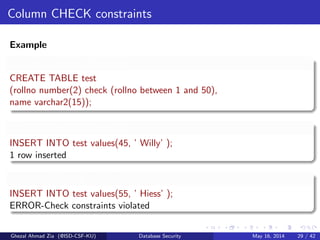
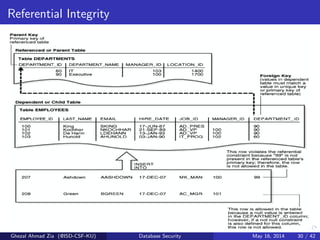
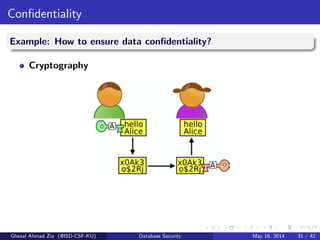
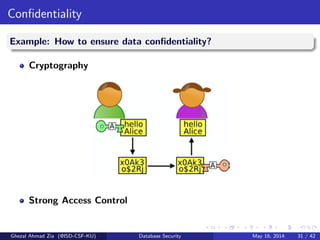
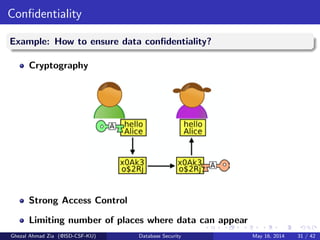
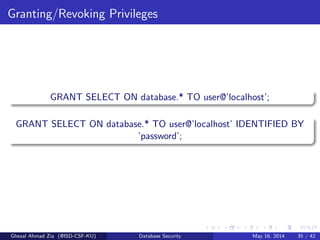
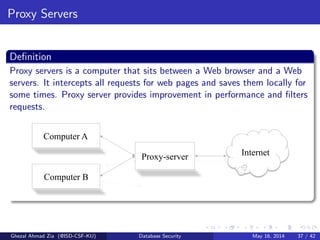
The document discusses database security. It covers main aspects of database security including integrity, confidentiality, and availability. It also discusses access control methods like discretionary access control and mandatory access control. The document lists various threats to database security from hardware, software, networks, users, and programmers/operators. These threats include things like fires, unauthorized data access, data theft, and inadequate security policies.