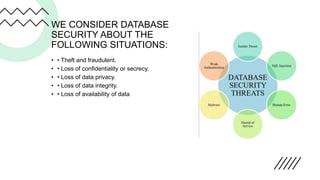
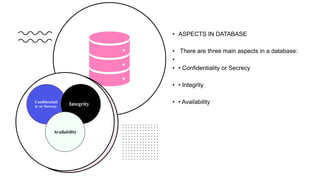
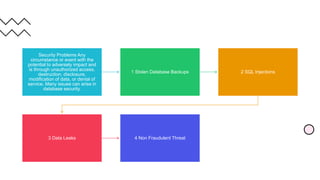
Database security refers to protecting a database from illegitimate use and cyber threats. It aims to secure the data, database management system, and any applications accessing the database from intrusion, misuse of data, and damage. There are three main aspects of database security - confidentiality or secrecy to protect from unauthorized users, integrity to ensure authorized users can only perform allowed actions, and availability to prevent unplanned downtime and ensure data recovery. Common security threats include stolen database backups containing sensitive data, SQL injections allowing hackers to alter records, data leaks releasing private information, and non-fraudulent threats like human errors, hardware bugs, or natural disasters. Methods of securing databases include authorization with privileges and views, encryption, authentication with passwords