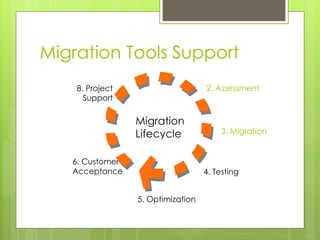
This document summarizes the key aspects and process of migrating an Oracle database to SQL Server 2008/2012. It discusses the major components being migrated - schema, data, applications. The major steps are analysis, migration, testing and deployment. It then focuses on using Microsoft's SQL Server Migration Assistant (SSMA) for Oracle tool to migrate the schema, business logic, data types and validate the migrated data.