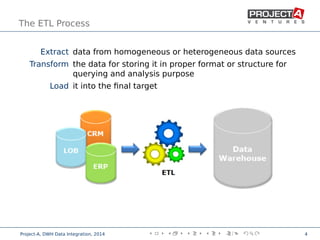
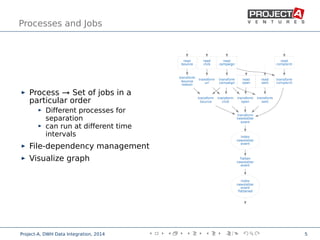
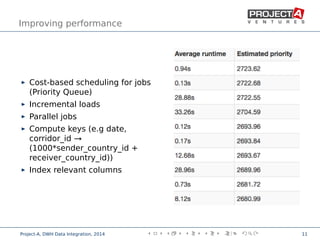
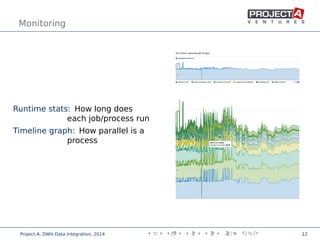
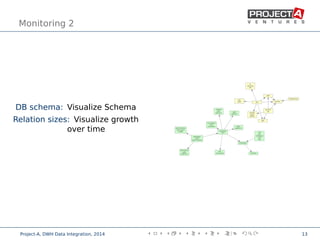
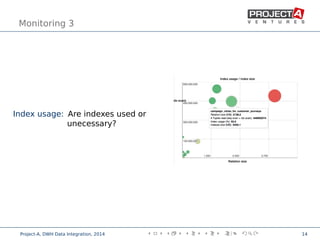
Data integration combines data from disparate sources into a data warehouse using extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes. It involves discovering, cleaning, monitoring, transforming, and delivering data from various sources. Ensuring data quality is critical through checks, constraints, and consistency tests. Performance is improved through cost-based job scheduling, incremental loads, parallelization, indexing, and compute keys. The process is monitored through runtime statistics, timelines, schema and relation sizes, and index usage.