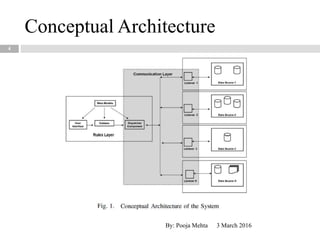
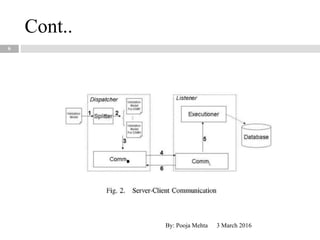
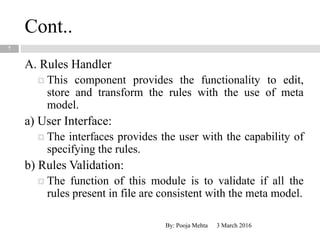
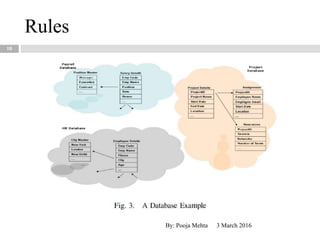
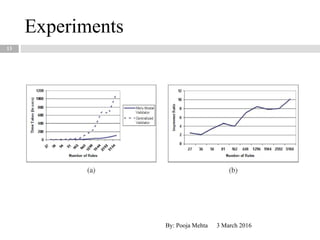
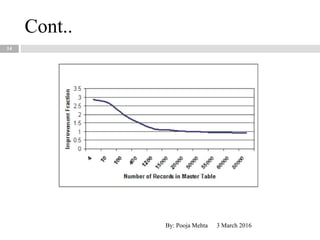
This document proposes a metadata-driven and rule-based system for validating data across multiple data sources for business continuity planning purposes. The system has three main components - a rules handler to manage validation rules, a communication handler to distribute rules and collect results, and a data sources handler where validation is performed. The conceptual architecture is distributed with rules objects sent to each data source and results returned to a central dispatcher. The system was tested on real data sets and proved to be adaptable, faster than centralized validation, scalable, and protects sensitive data.