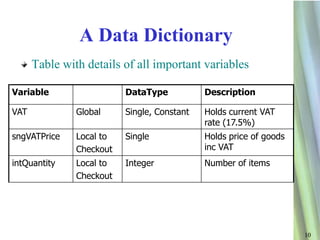
This document provides an overview of the software design documentation process. It discusses the stages of the software development lifecycle including identifying requirements, designing, developing, testing, and evaluating. It then focuses on the design documentation, including creating a requirements specification, screen designs, a process specification using techniques like flowcharts and pseudocode, and a data dictionary. The goal is to plan the solution to identified problems and produce formal documentation of the program design.