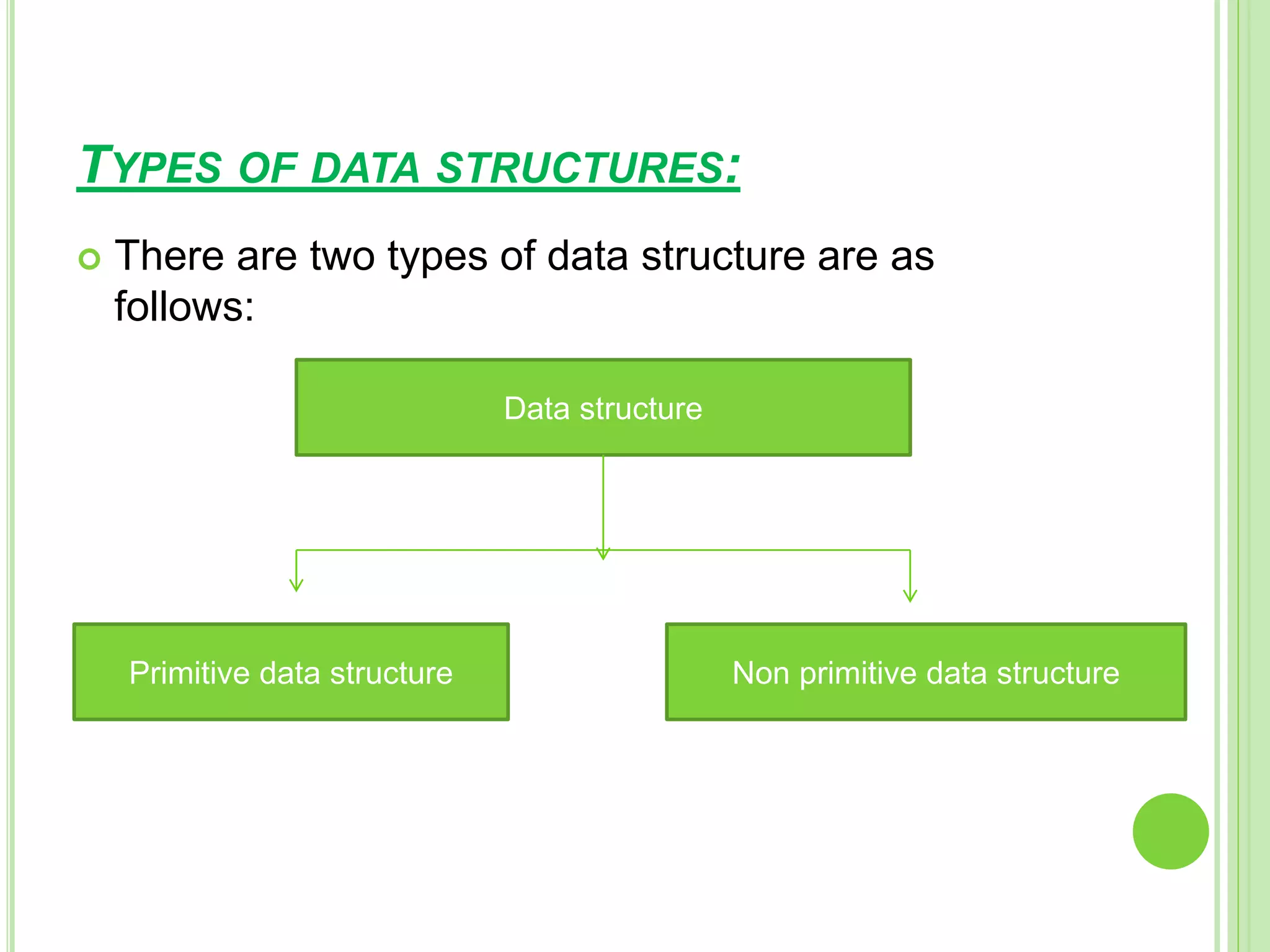
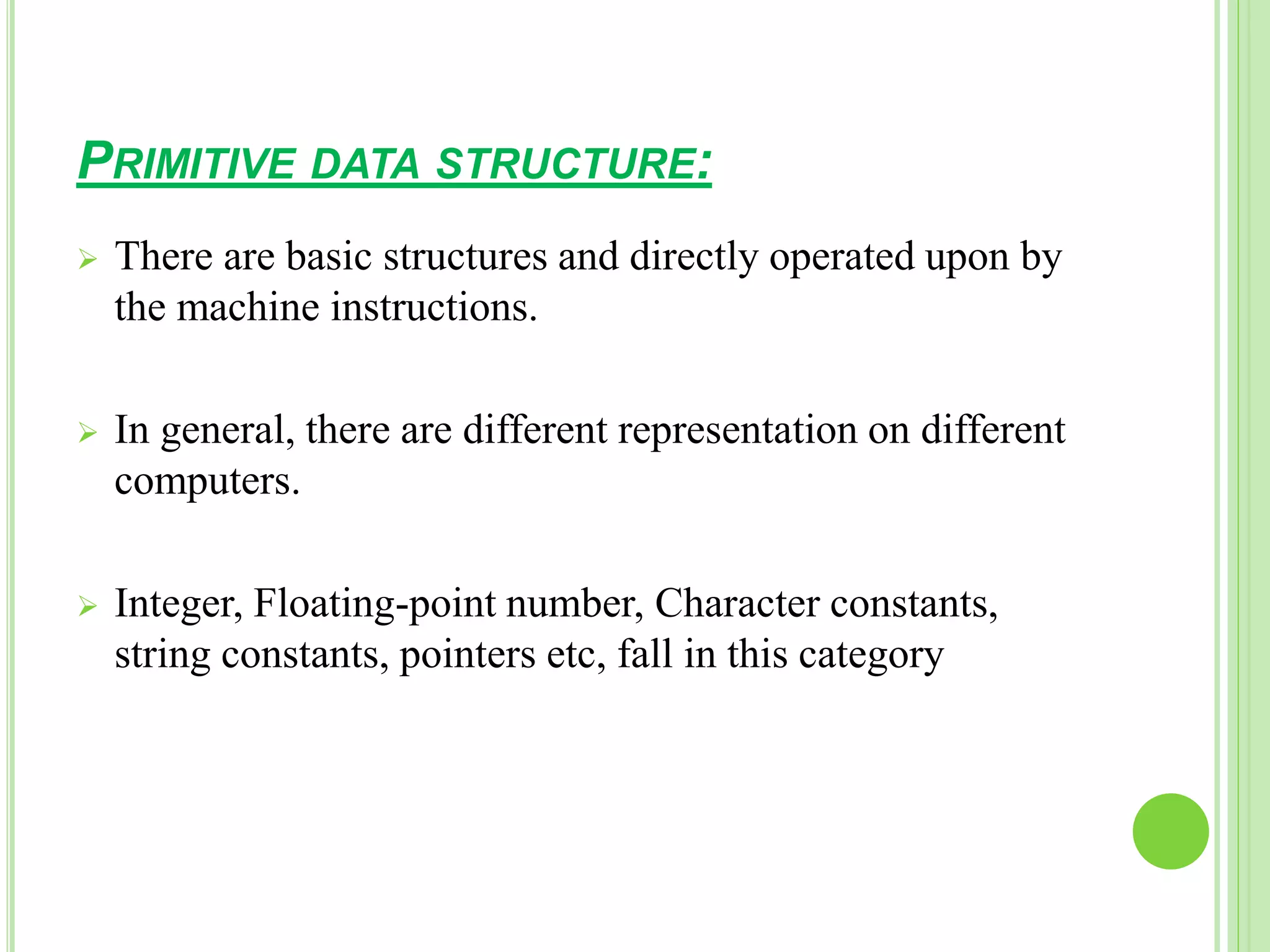
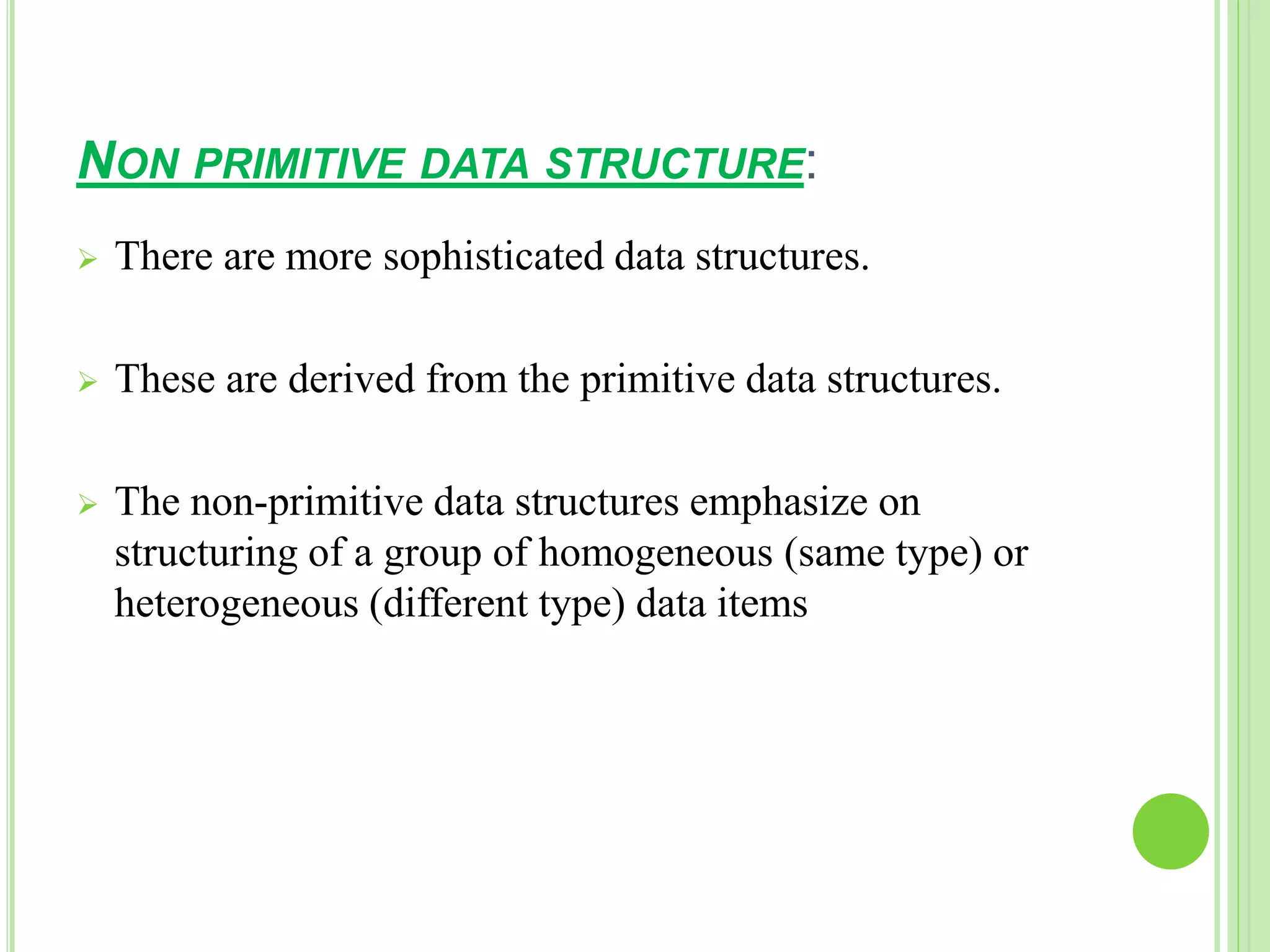
This document discusses data structures and their importance in program design. It defines a data structure as a specialized format for organizing and storing data for a specific purpose. The document outlines different types of data structures, including primitive structures like integers and characters that are directly operated on by the machine, and non-primitive structures like arrays, records, tables, and trees that are built from primitive structures. It also lists some common operations on data structures such as creation, selection, updating, searching, sorting, and deleting.