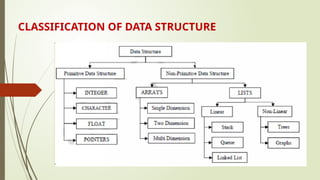
The document introduces data structures, defining them as specialized formats for organizing and storing data in memory, classified into primitive and non-primitive types. Primitive data structures, such as integers and characters, are directly operated on by machine instructions, while non-primitive structures, like arrays and linked lists, are derived from primitives and can be linear or non-linear. Common operations on these data structures include creation, selection, and deletion.