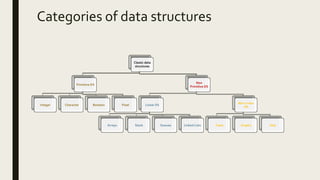
Data structures provide a way to organize and store data so that it can be used efficiently. They allow data to be processed, structured, and presented in a meaningful way to solve problems like slow searching of large datasets, limited processor speeds, and multiple simultaneous requests. Common data structures include linear structures like arrays, stacks, queues and linked lists, and non-linear structures like trees and graphs. Operations on data structures include traversing, searching, insertion, deletion, sorting, and merging.