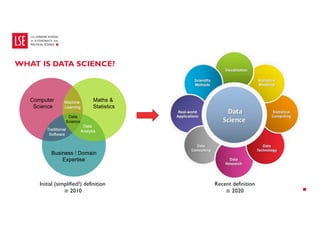
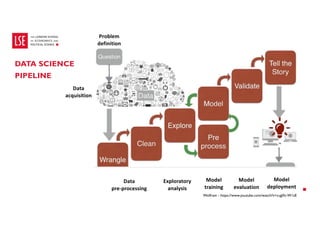
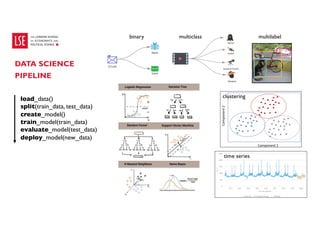
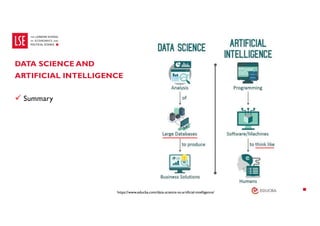
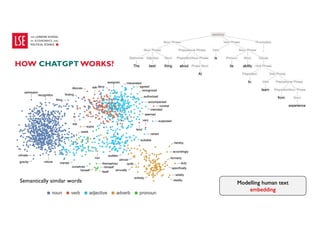
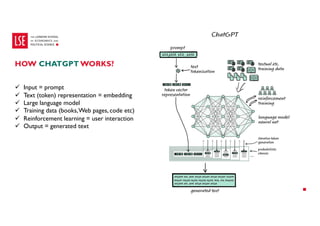
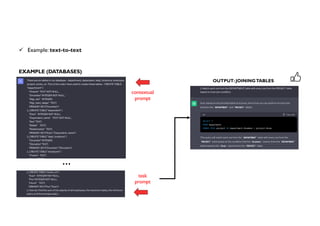
Data science and artificial intelligence (AI) were discussed. Data science involves collecting and analyzing data to solve problems and can be defined as the science of extracting knowledge from data. AI involves creating intelligent machines and can be defined as machines performing tasks normally requiring human intelligence. Examples of AI applications and different types of AI systems like narrow AI, general AI, and super AI were provided. Generative AI tools that can generate text, images, and other media were also discussed along with factors affecting their performance and considerations around using them.