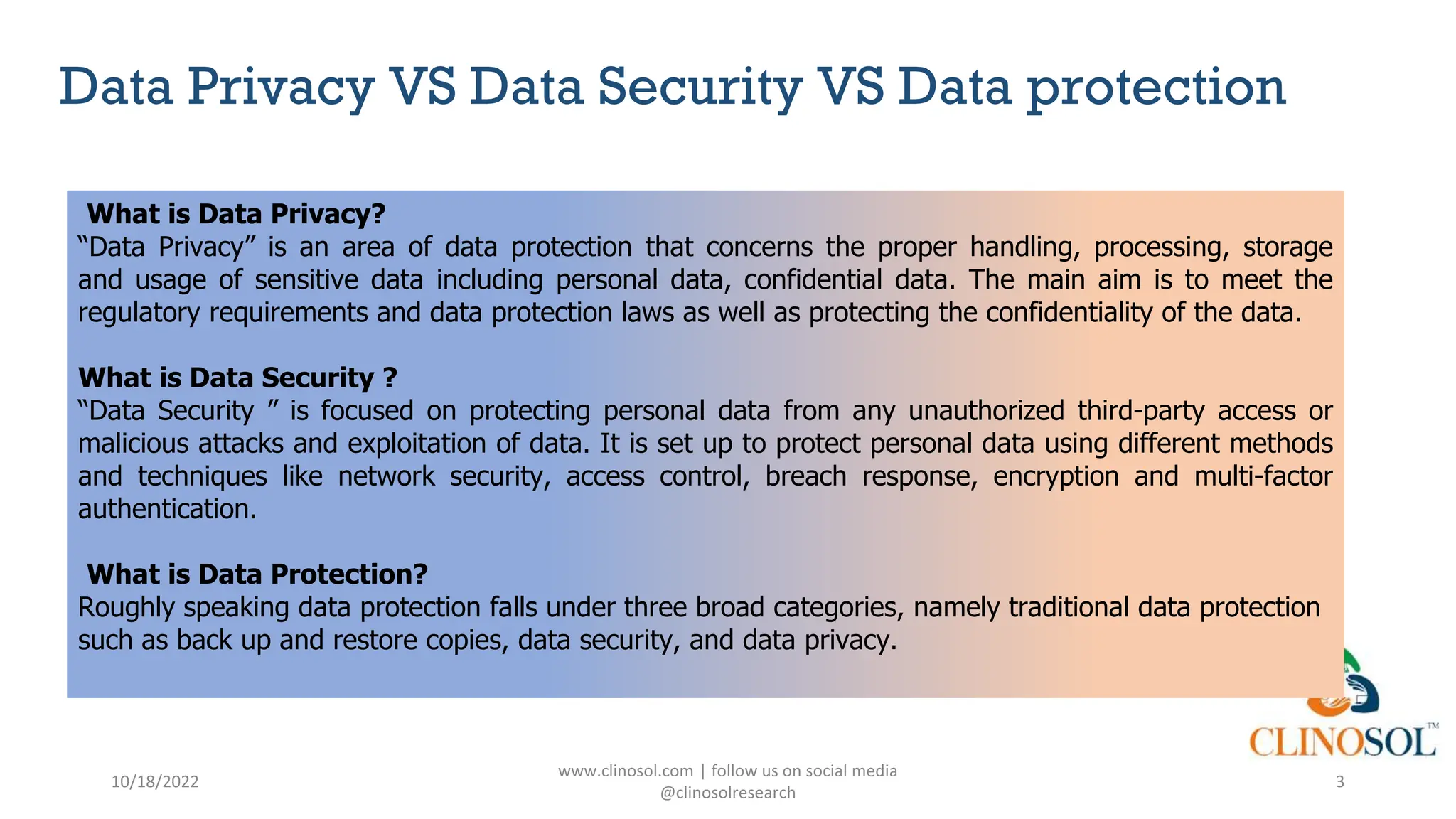
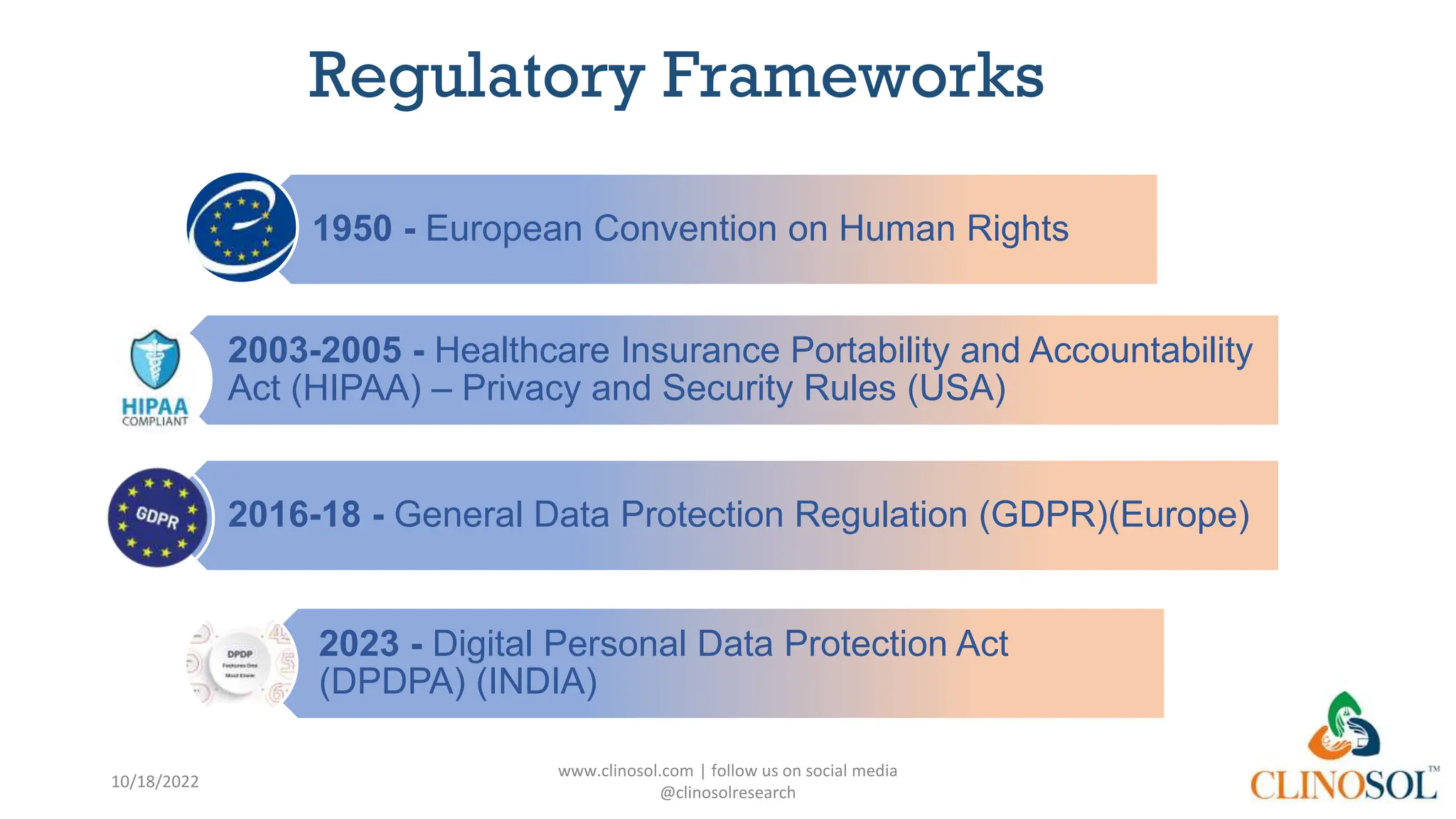
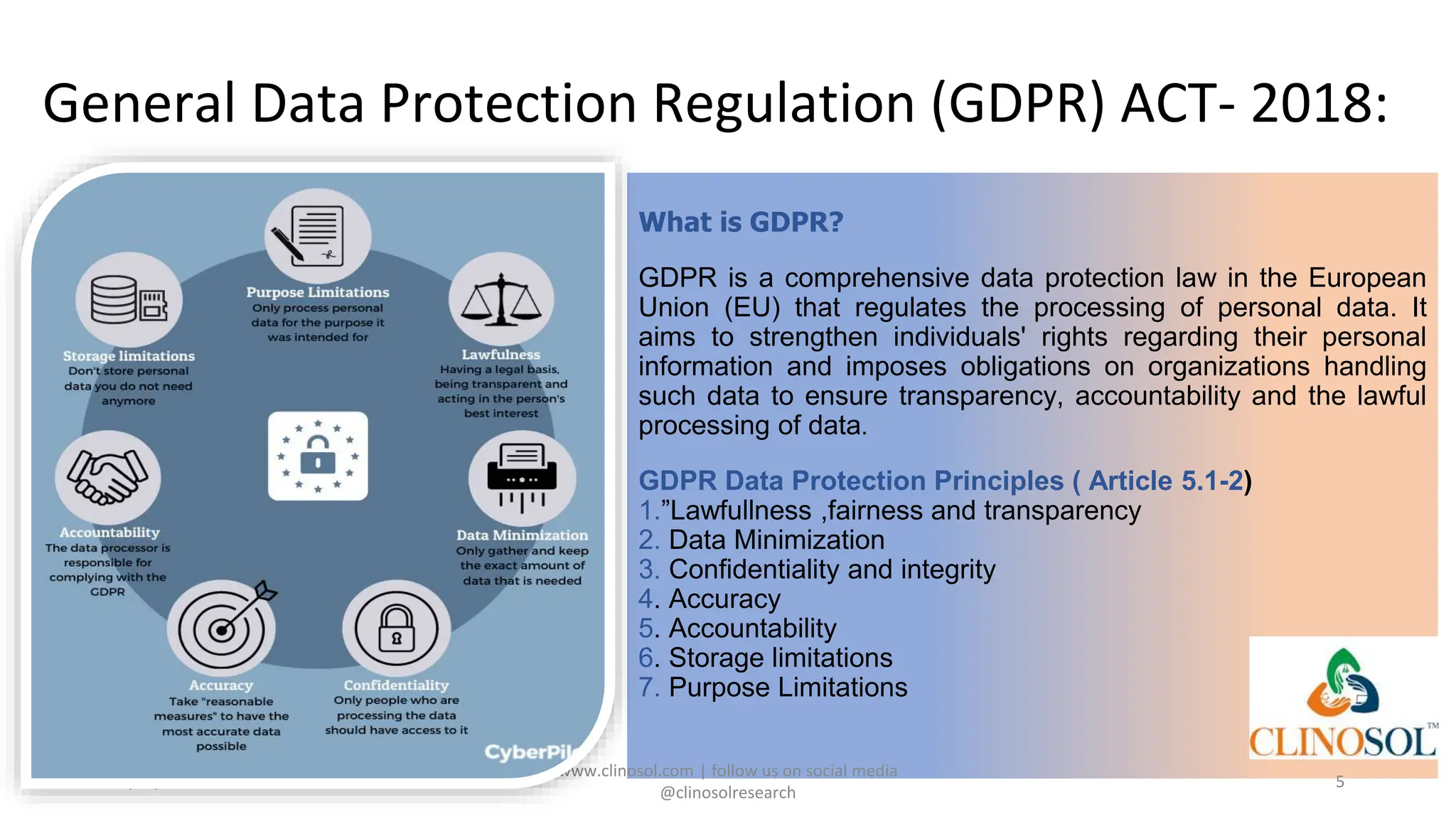
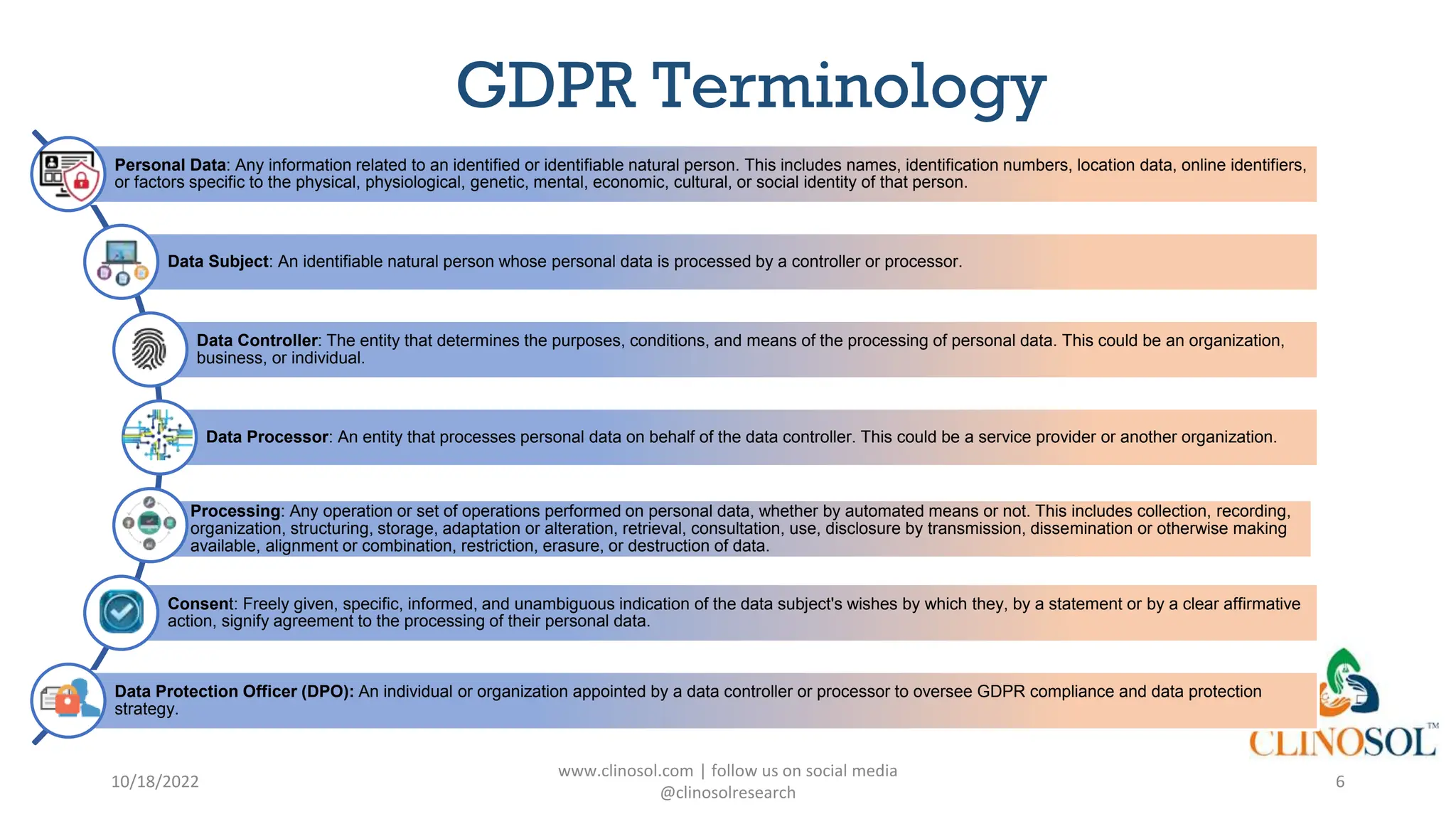
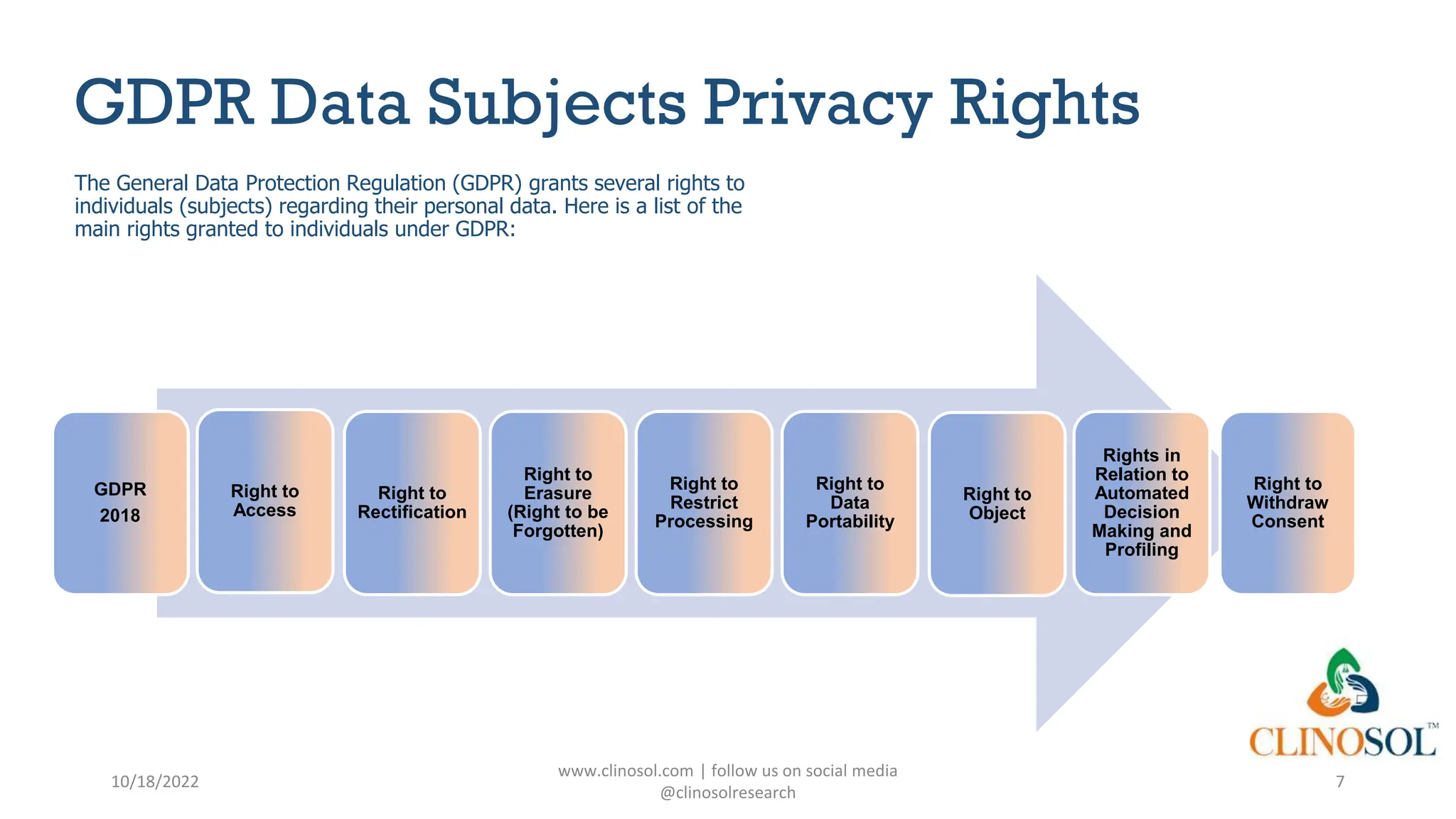
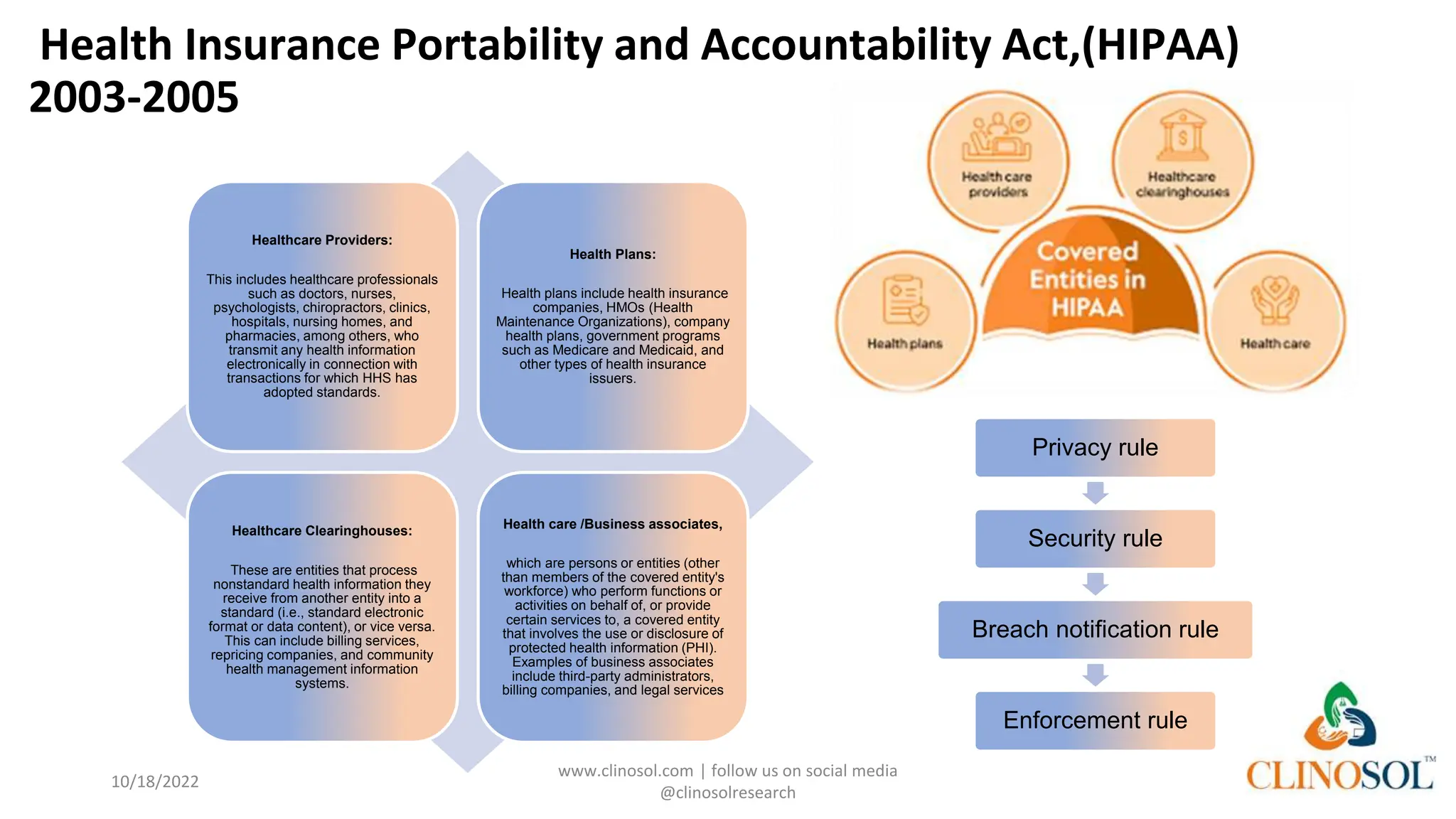
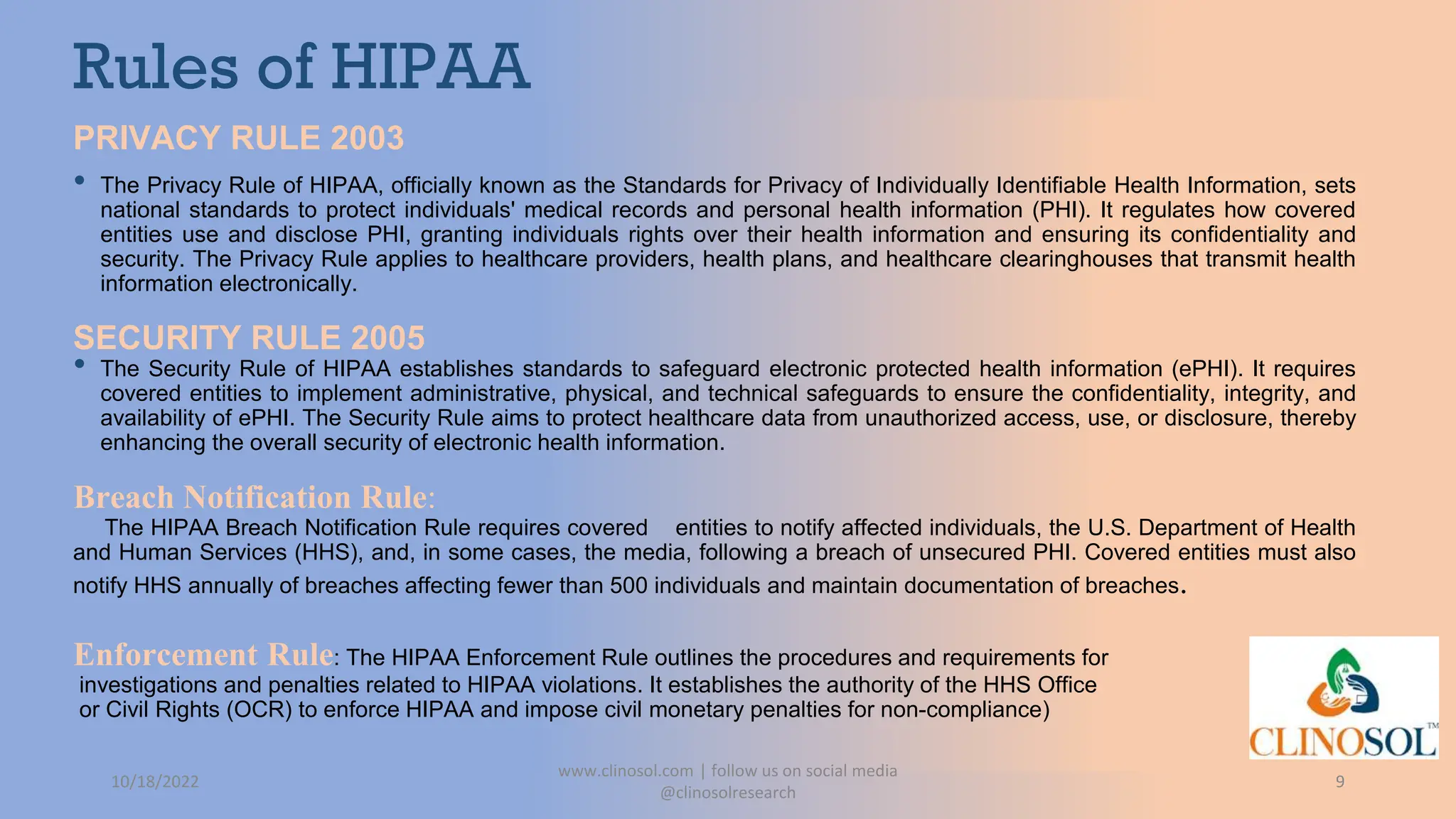
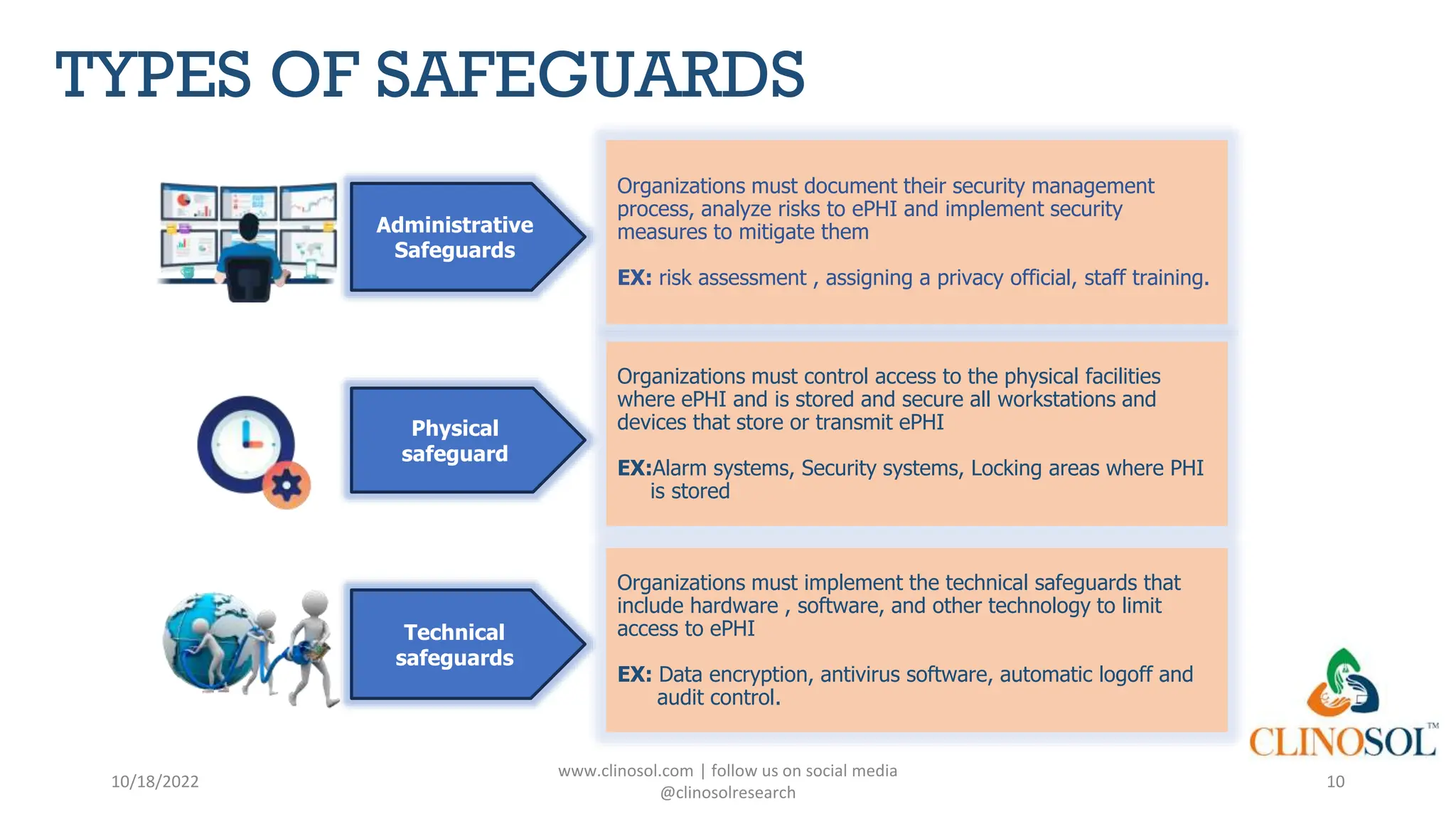
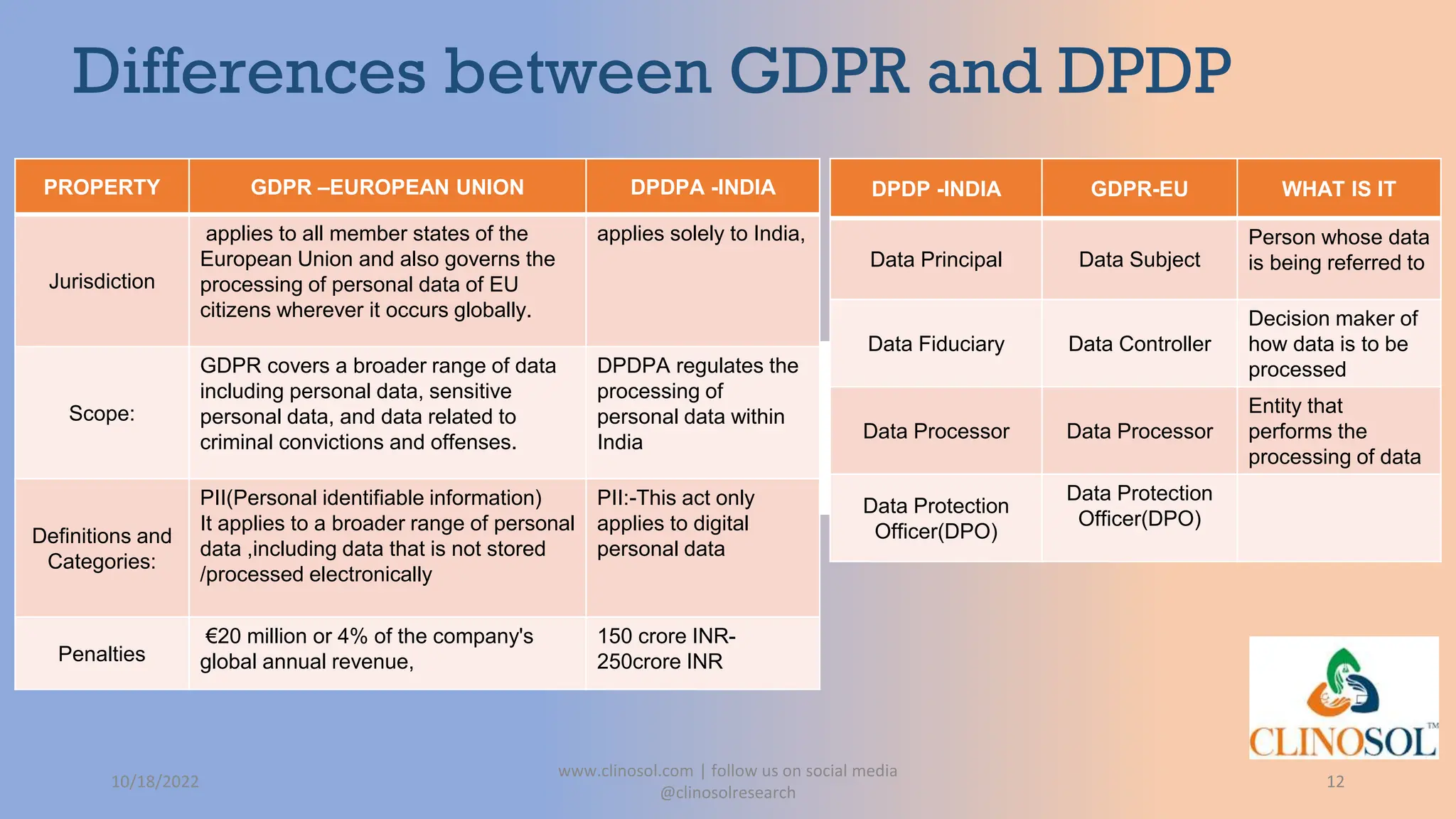
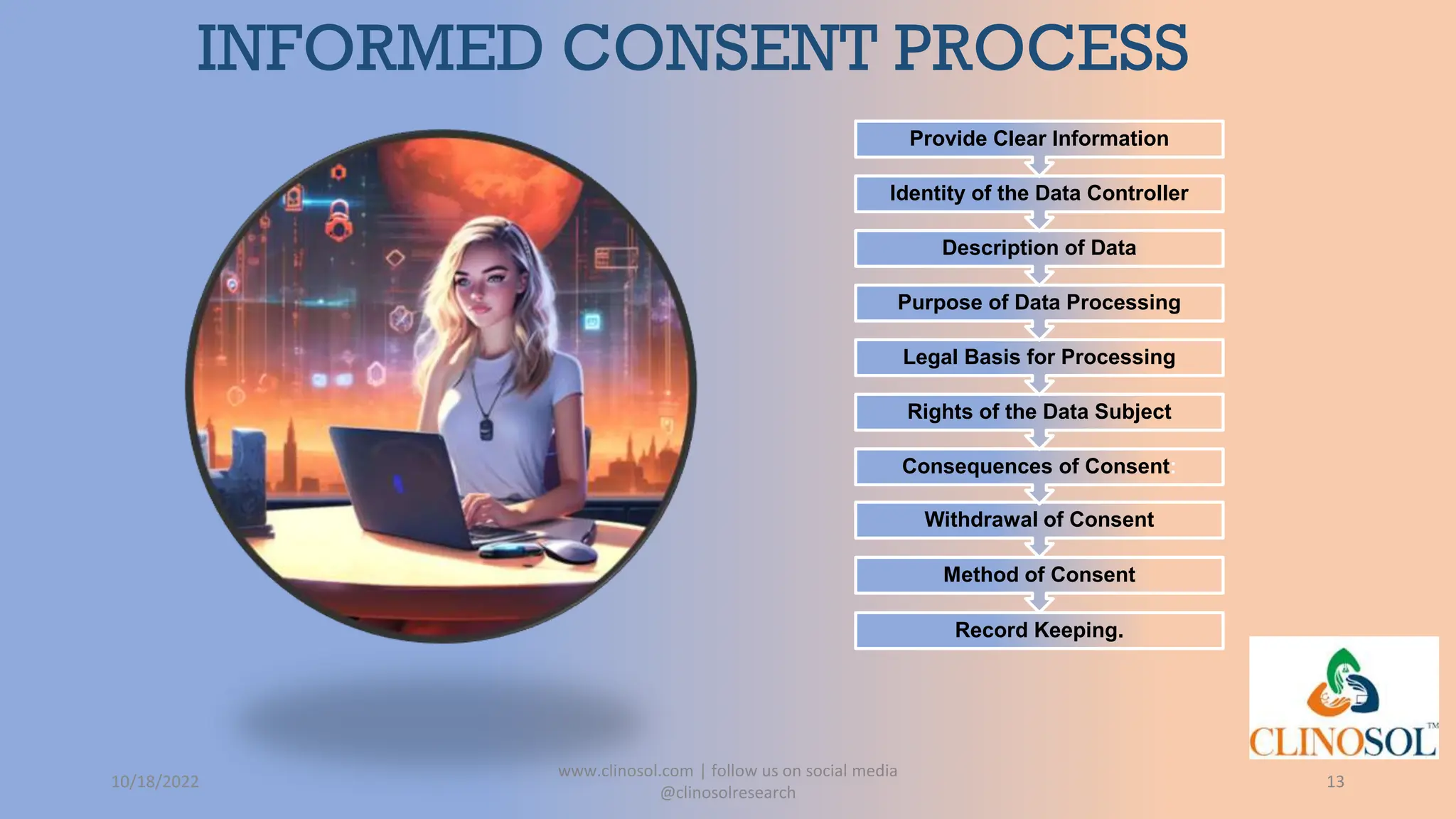
The document provides an overview of data privacy and consent management in clinical research, emphasizing regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and the upcoming DPDPA in India. It discusses concepts of data privacy, security, and protection, as well as the informed consent process and strategies for effective management. Additionally, it highlights emerging trends in data privacy technology and emphasizes the need for clear communication and respect for participant autonomy.