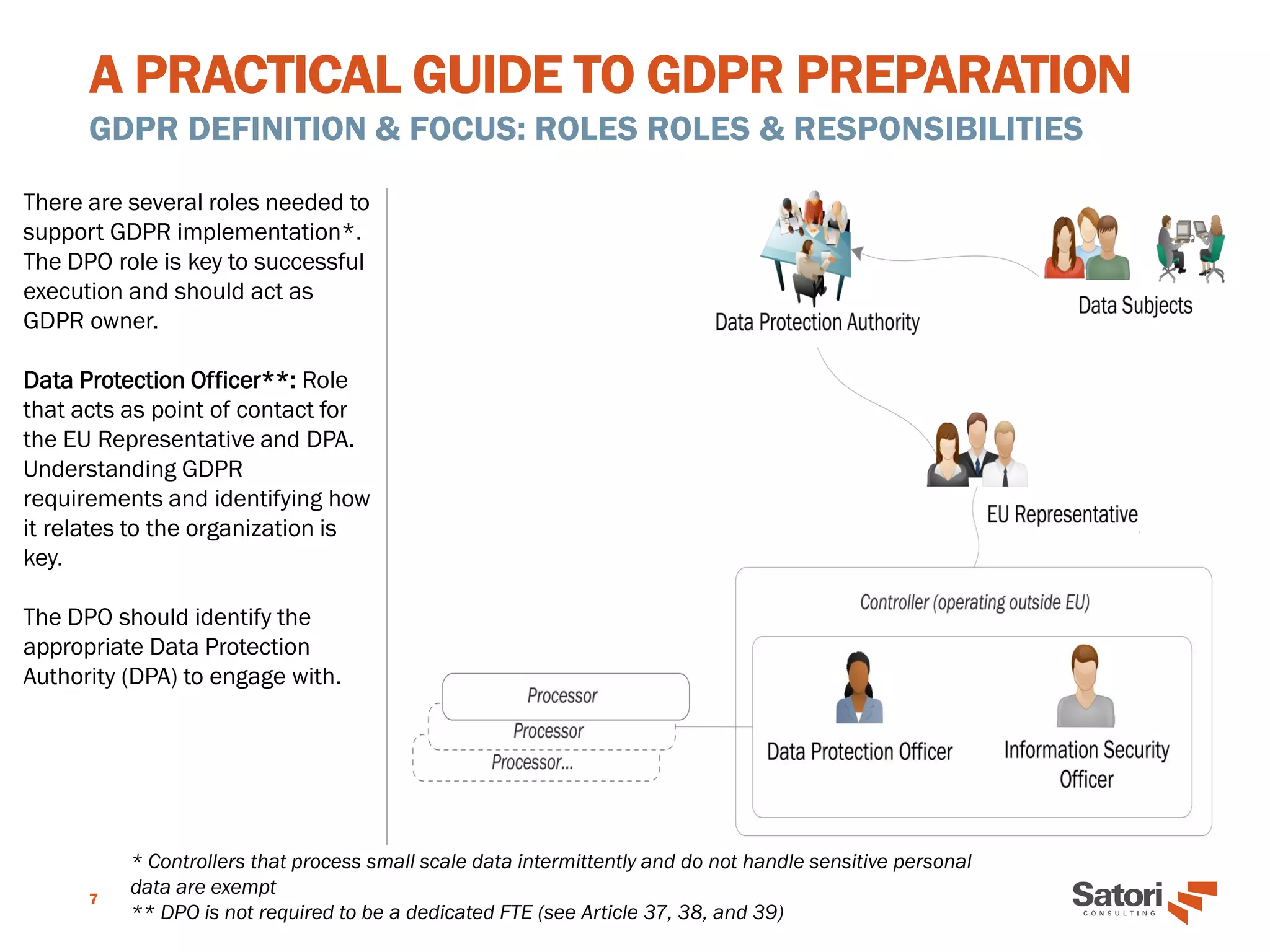
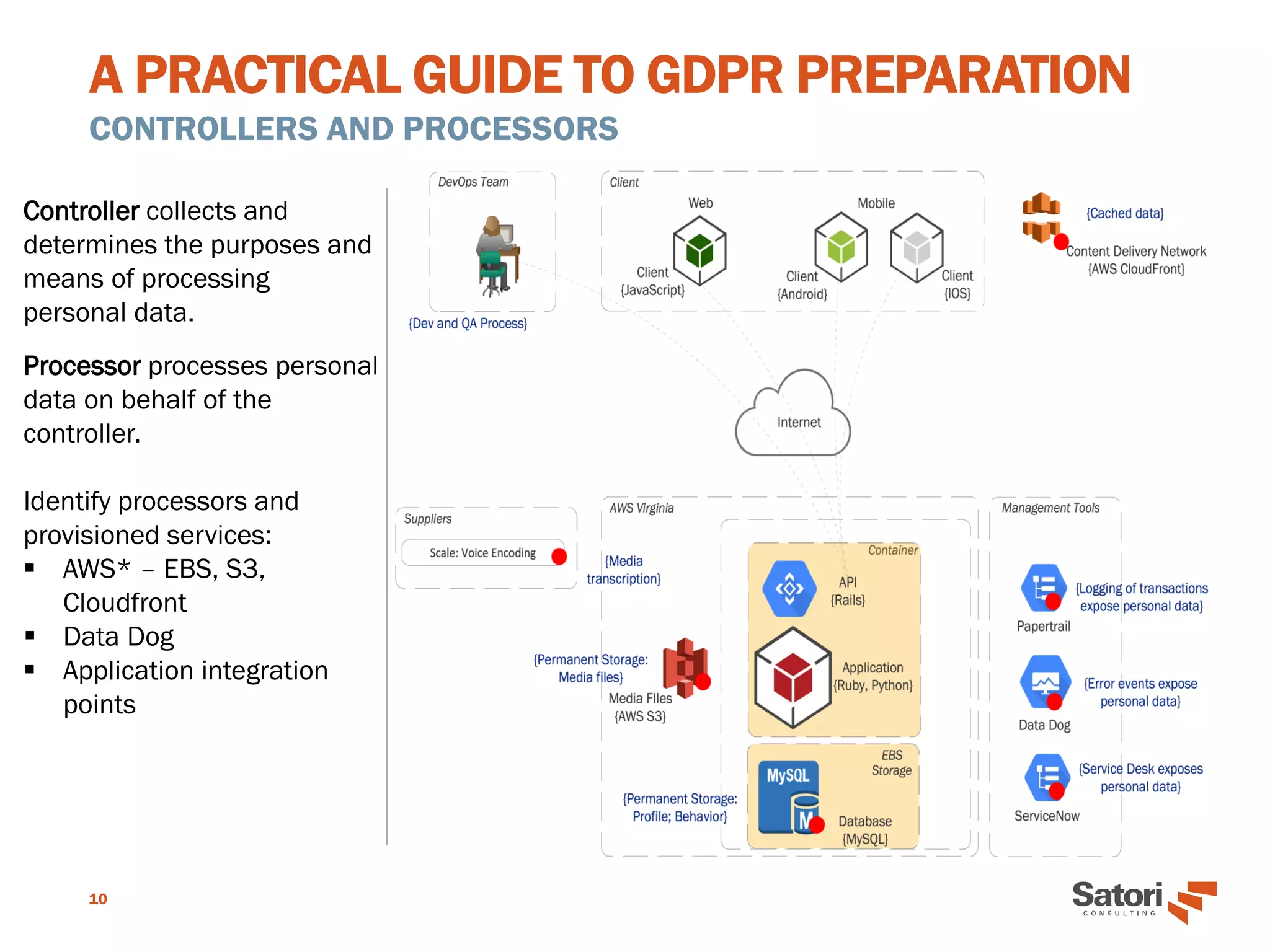
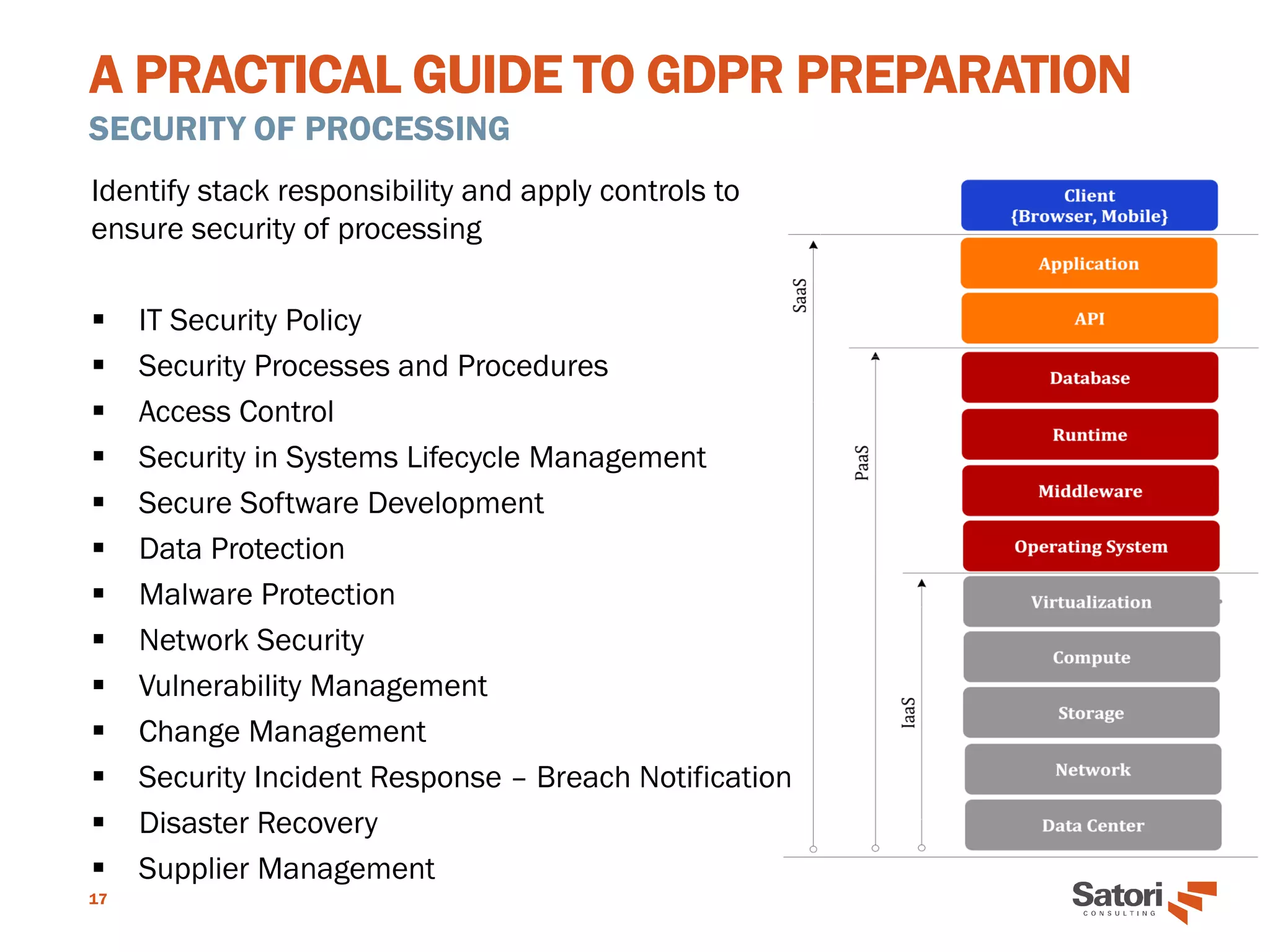
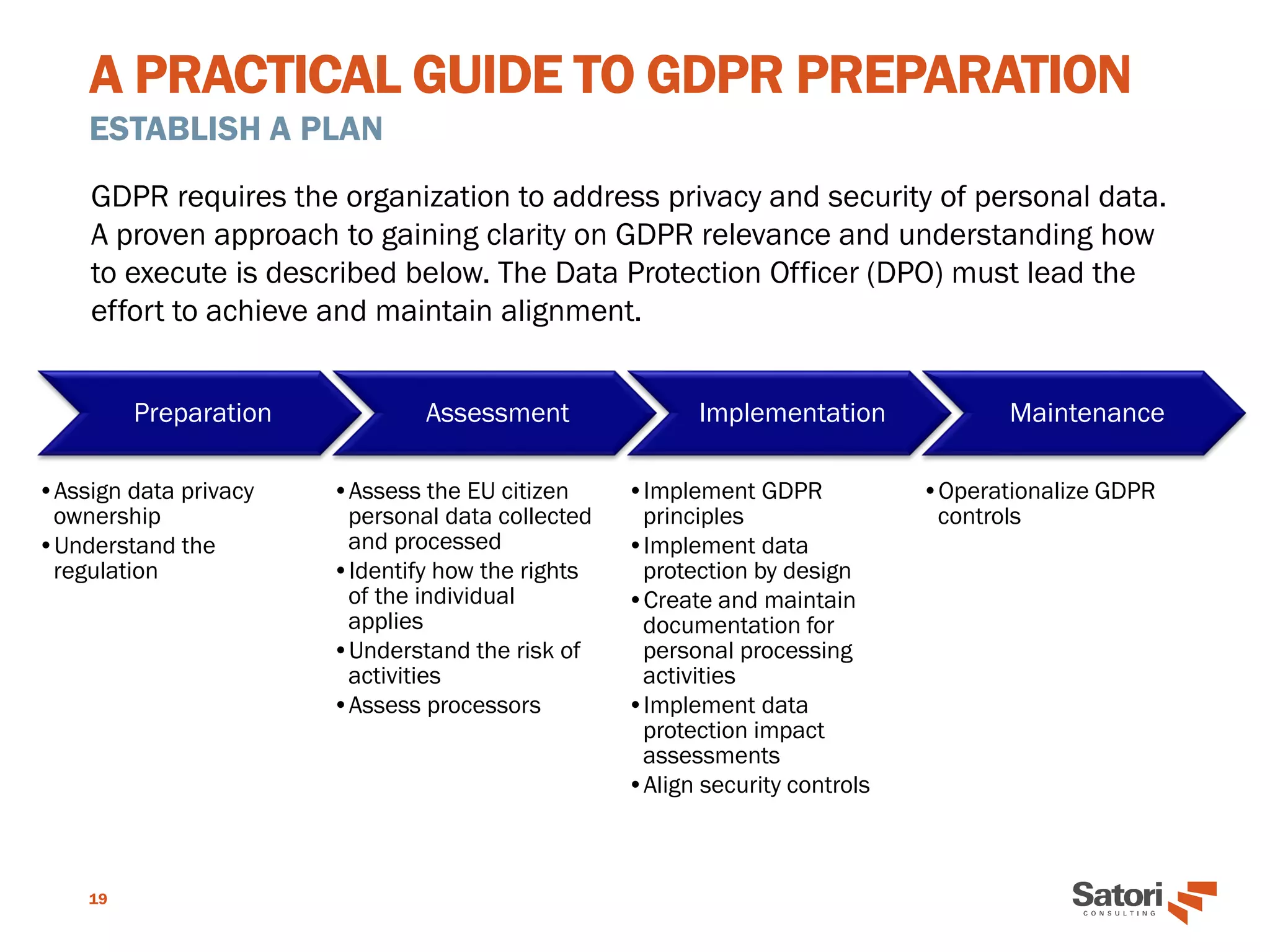
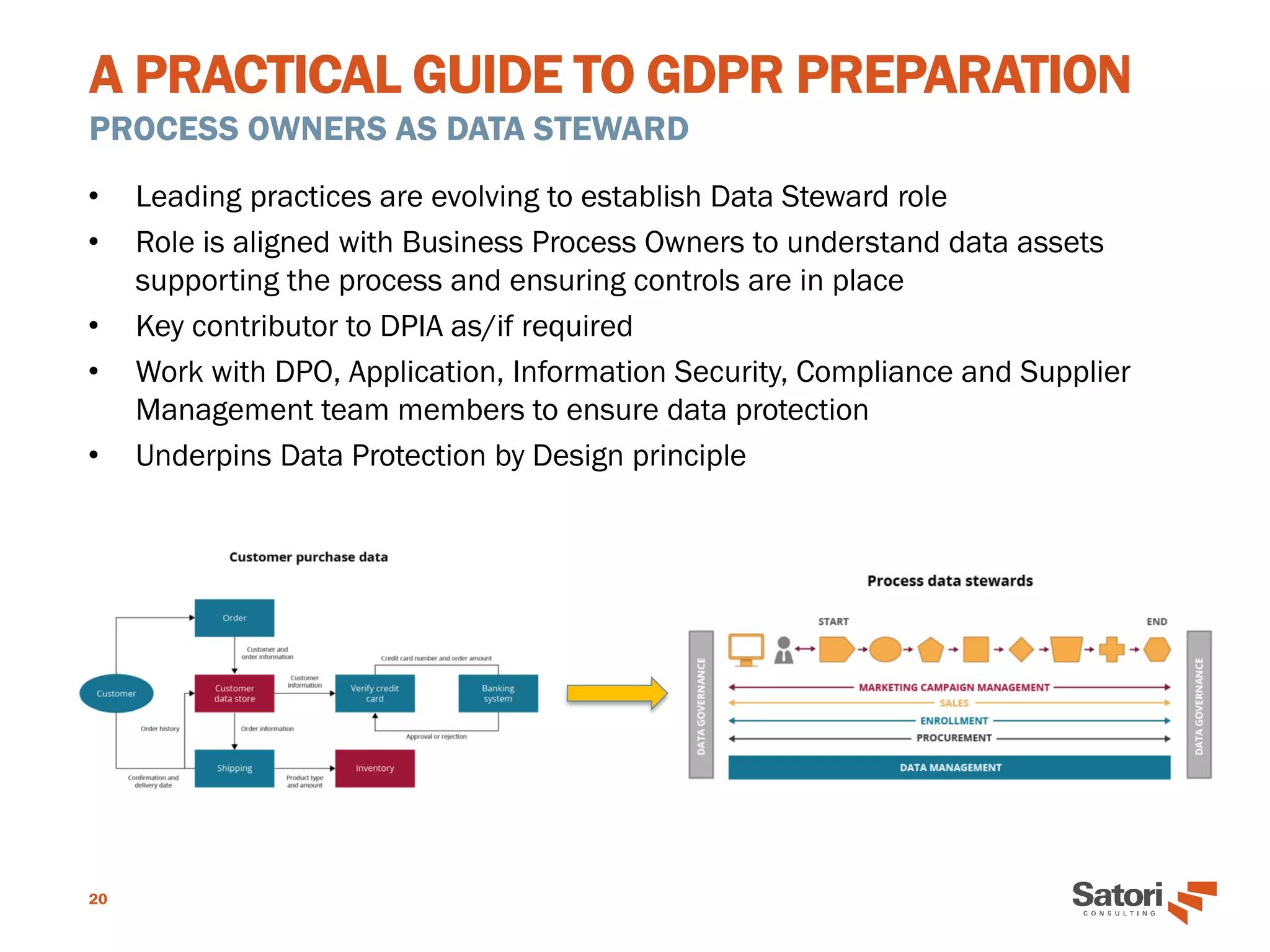
This document serves as a practical guide for organizations preparing to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), outlining its significance and core concepts. Key roles, such as the Data Protection Officer (DPO), responsibilities for data controllers and processors, and essential principles for GDPR readiness are detailed. The guide emphasizes the importance of data protection by design, security measures, and the necessity for documentation and assessment to ensure compliance.