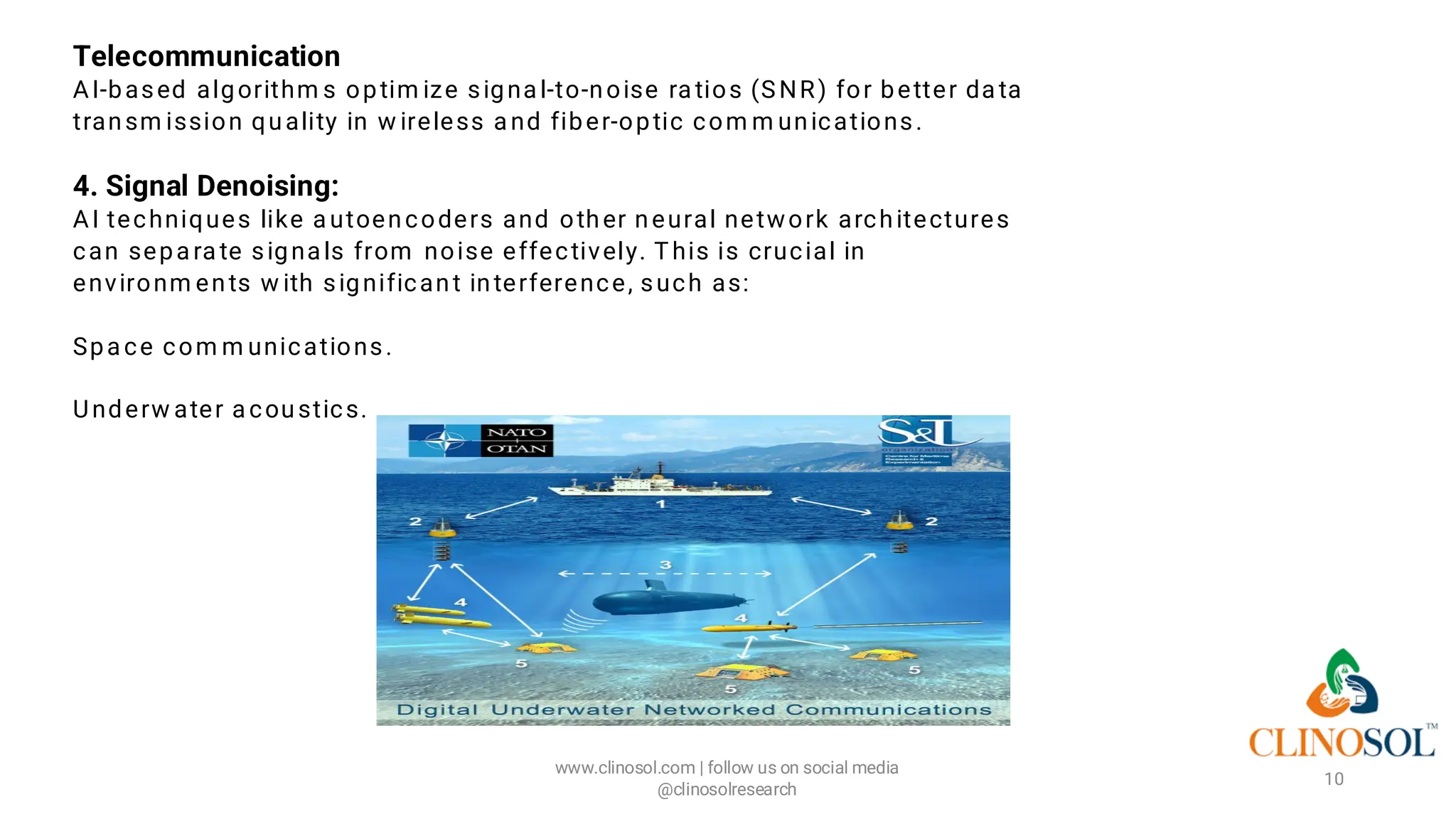
The document discusses the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing signal detection and risk management within modern medical practices. It highlights AI's capabilities in processing information, improving accuracy and efficiency in detecting signals, and aiding in risk identification and mitigation. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of traditional methods and the transformative benefits of integrating AI into these processes.










![Reference:
• M anicka m P , M ariappa n SA, M urugesan SM , H a nsda S, Ka ushik A,
Shinde R, Thipperudra sw am y SP . Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet
of M edica l Things (IoM T) Assisted Biom edical System s for Intelligent
H ealthca re. B iosensors (B asel). 2022 Jul 25;12(8):562. doi:
10.3390/bios12080562. PM ID: 35892459; P M CID: P M C9330886.
• Sghaier W , H ergon E, Desroches A. G estion globa le des risques [G loba l
risk m anagem ent]. Transfus Clin Biol. 2015 Aug;22(3):158-67. French.
doi: 10.1016/j.tra cli.2015.05.007. Epub 2015 Jun 25. P M ID: 26119049.
11/20/2024
www.clinosol.com | follow us on social media
@clinosolresearch
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt2024-241214214402-057e854a/75/The-Role-of-Artificial-Intelligence-in-Signal-Detection-and-Risk-Management-16-2048.jpg)
