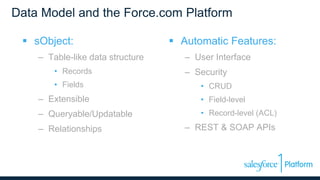
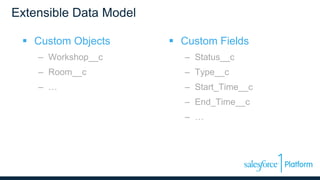
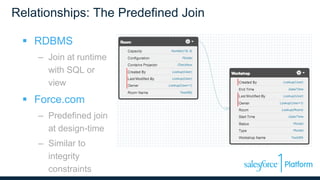
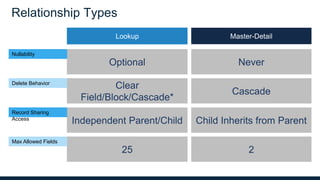
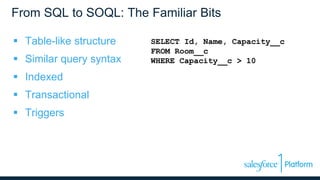
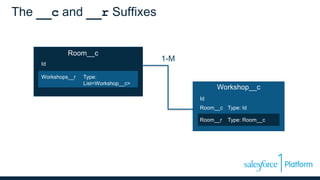
The webinar discusses data models, relationships, and SOQL (Salesforce Object Query Language) on the Force.com platform, including comparisons with relational databases. It emphasizes the importance of understanding predefined joins and relationship types within the platform, along with the unique features of SOQL compared to SQL. Additionally, the presentation covers various querying techniques and best practices for effective data design in Salesforce.













![Relationship Query: Child to Parent
SELECT Id, Name, Room__c,
Room__r.Id,
Room__r.Capacity__c
FROM Workshop__c
WHERE Status__c = ’Open’
[
{
"Id": "a0145000000aBf4AAE",
"Name": "Yoga for Beginners",
"Room__c": "a00vn000000dU3dAAE",
"Room__r": {
"Id": "a00vn000000dU3dAAE",
"Capacity__c": 10
}
},
{
"Id": "a0145000000aBf4AAE",
"Name": "Yoga for Beginners",
"Room__c": "",
"Room__r": ""
}, ...
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamodelrelationshipssoql1-140407100547-phpapp02/85/Salesforce1-Platform-Data-Model-Relationships-and-Queries-Webinar-20-320.jpg)
![Relationship Query: Parent to Child
SELECT Id, Name,
(SELECT Id, Status__c
FROM Workshops__r)
FROM Room__c
WHERE Capacity__c > 10
[
{
"Id": "a00vn000000dU3dAAE",
"Name": "Salon 1 West",
"Workshops__r": [
{
"Id": "a0145000000aBf4AAE",
"Status__c": "Open"
},
{
"Id": "a0145000000aBd4AAE",
"Status__c": "Full"
}
]
}, ...
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamodelrelationshipssoql1-140407100547-phpapp02/85/Salesforce1-Platform-Data-Model-Relationships-and-Queries-Webinar-21-320.jpg)
![Querying for Intersection
Select Id, Name,
Room__r.Name,
Room__r.Capacity__c
FROM Workshop__c
WHERE
Room__r.Capacity__c > 8
[
{
"Id": "a0145000000aBf4AAE",
"Name": "Yoga for Beginners",
"Room__c": "a00vn000000dU3dAAE",
"Room__r": {
"Id": "a00vn000000dU3dAAE",
"Capacity__c": 10
}
},
{...},
...
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamodelrelationshipssoql1-140407100547-phpapp02/85/Salesforce1-Platform-Data-Model-Relationships-and-Queries-Webinar-22-320.jpg)
![Aggregate Queries
SELECT
COUNT(Id) rmCount,
MAX(Capacity__c) maxRmCap,
Configuration__c
FROM Room__c
GROUP BY Configuration__c
[
{
"rmCount": 4,
"maxRmCap": 6,
"Configuration__c": "Classroom"
},
{
"rmCount": 2,
"maxRmCap": 10,
"Configuration__c": "Theatre"
},
...
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamodelrelationshipssoql1-140407100547-phpapp02/85/Salesforce1-Platform-Data-Model-Relationships-and-Queries-Webinar-23-320.jpg)



