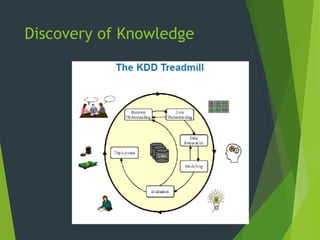
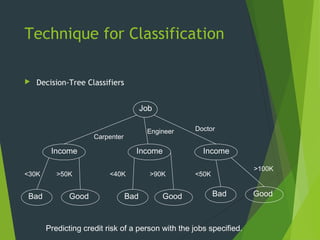
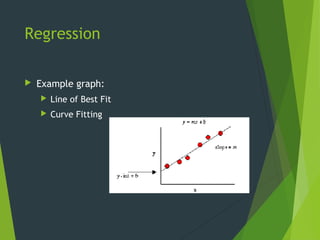
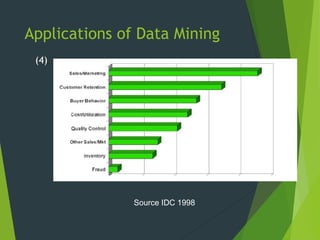
This document discusses data mining techniques including classification, clustering, regression, and association rules. It provides examples of how each technique works and areas where they are applied, such as marketing, risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer care. The advantages of data mining are that it provides new knowledge from existing data that can improve products, services and profits. However, privacy is a concern when linking multiple data sources to gain a wide range of information about individuals.