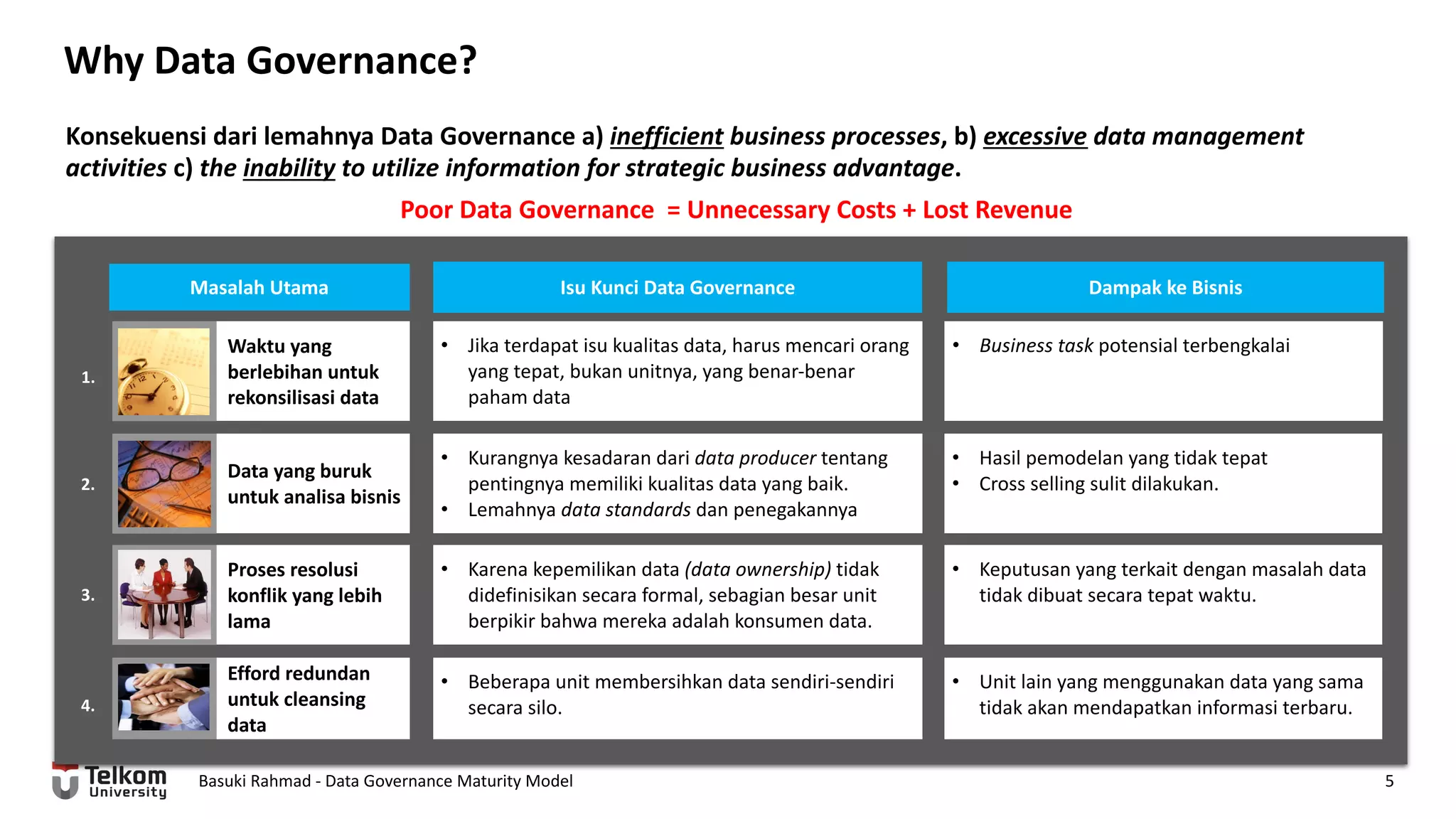
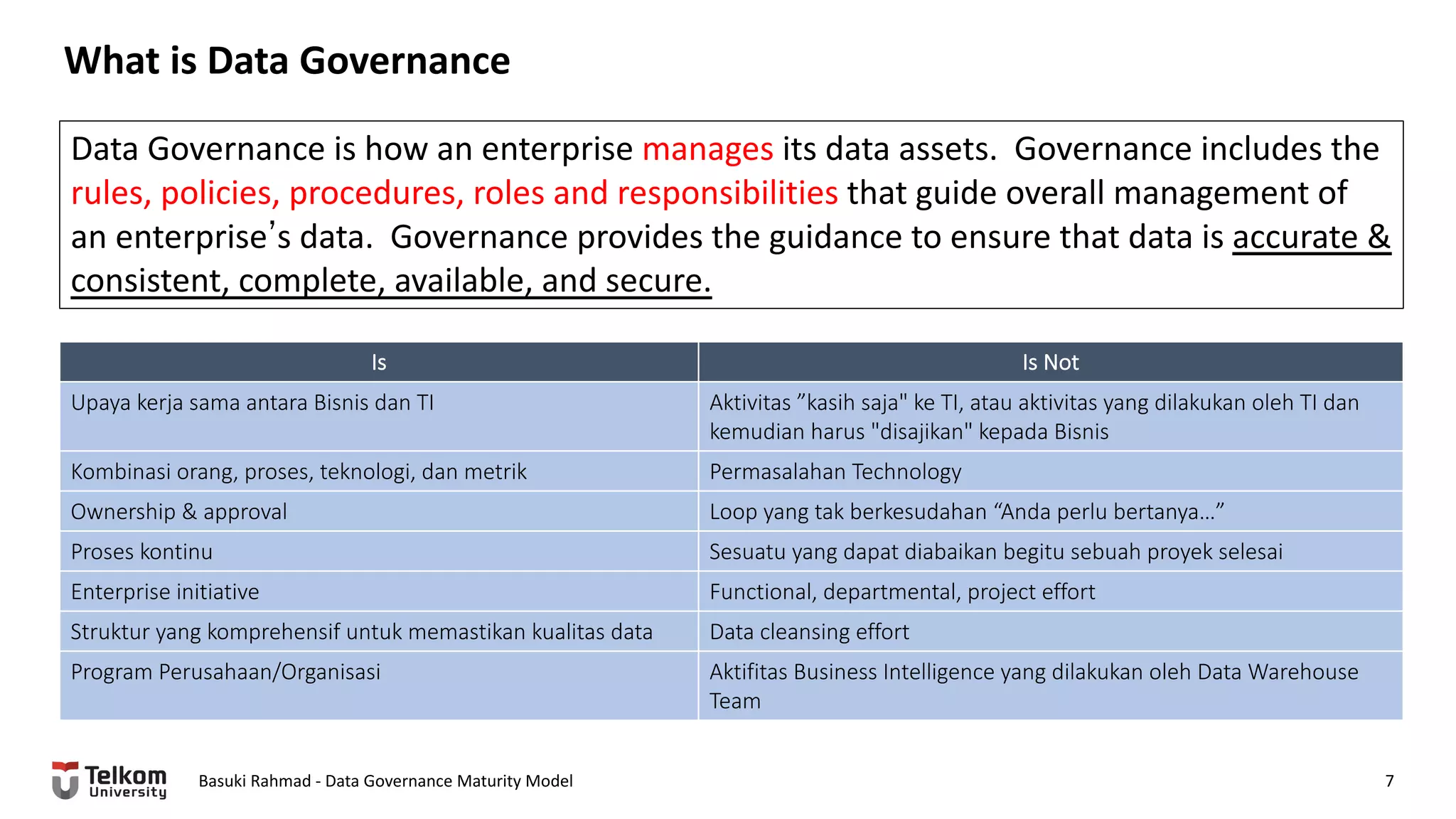
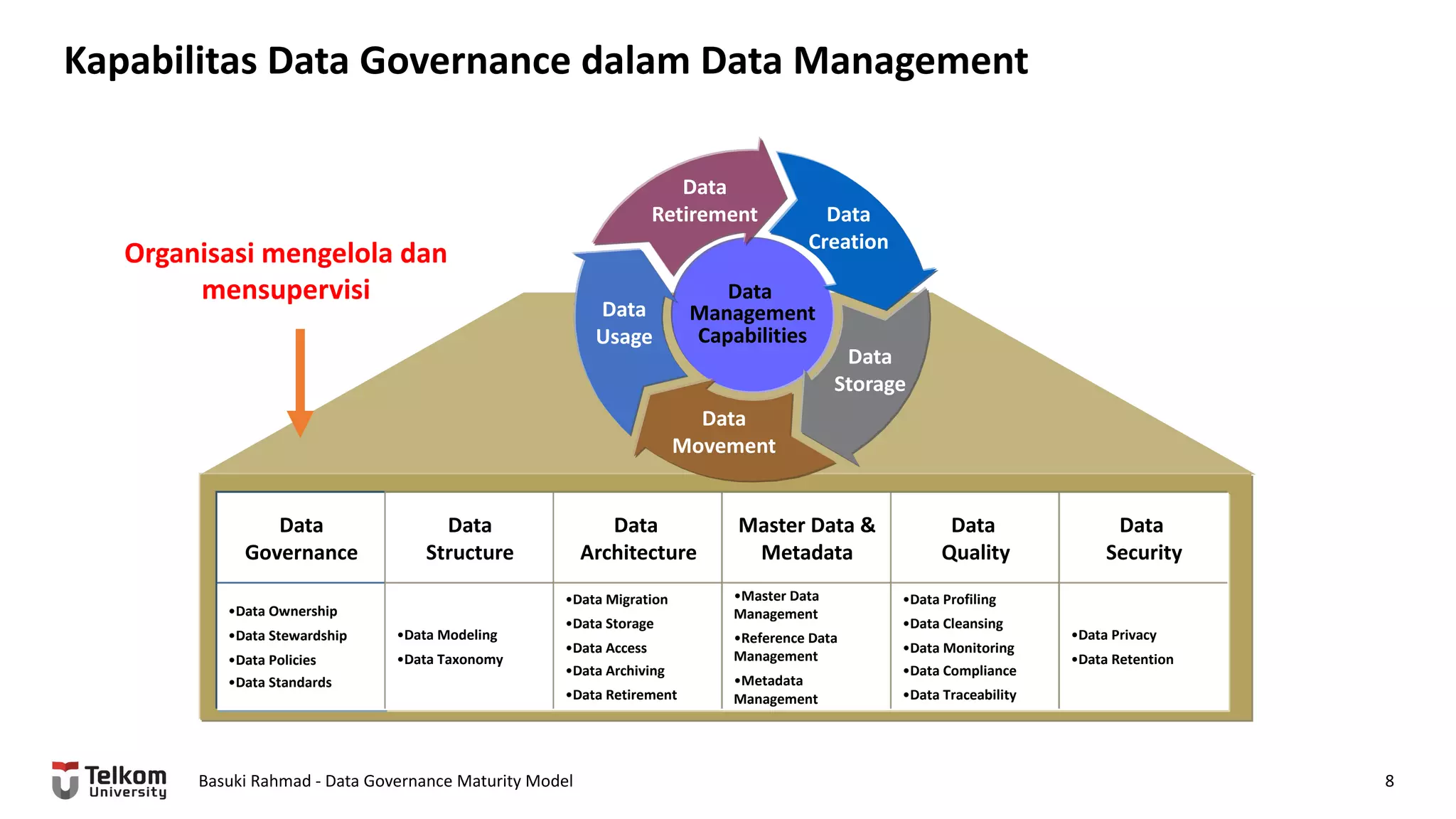
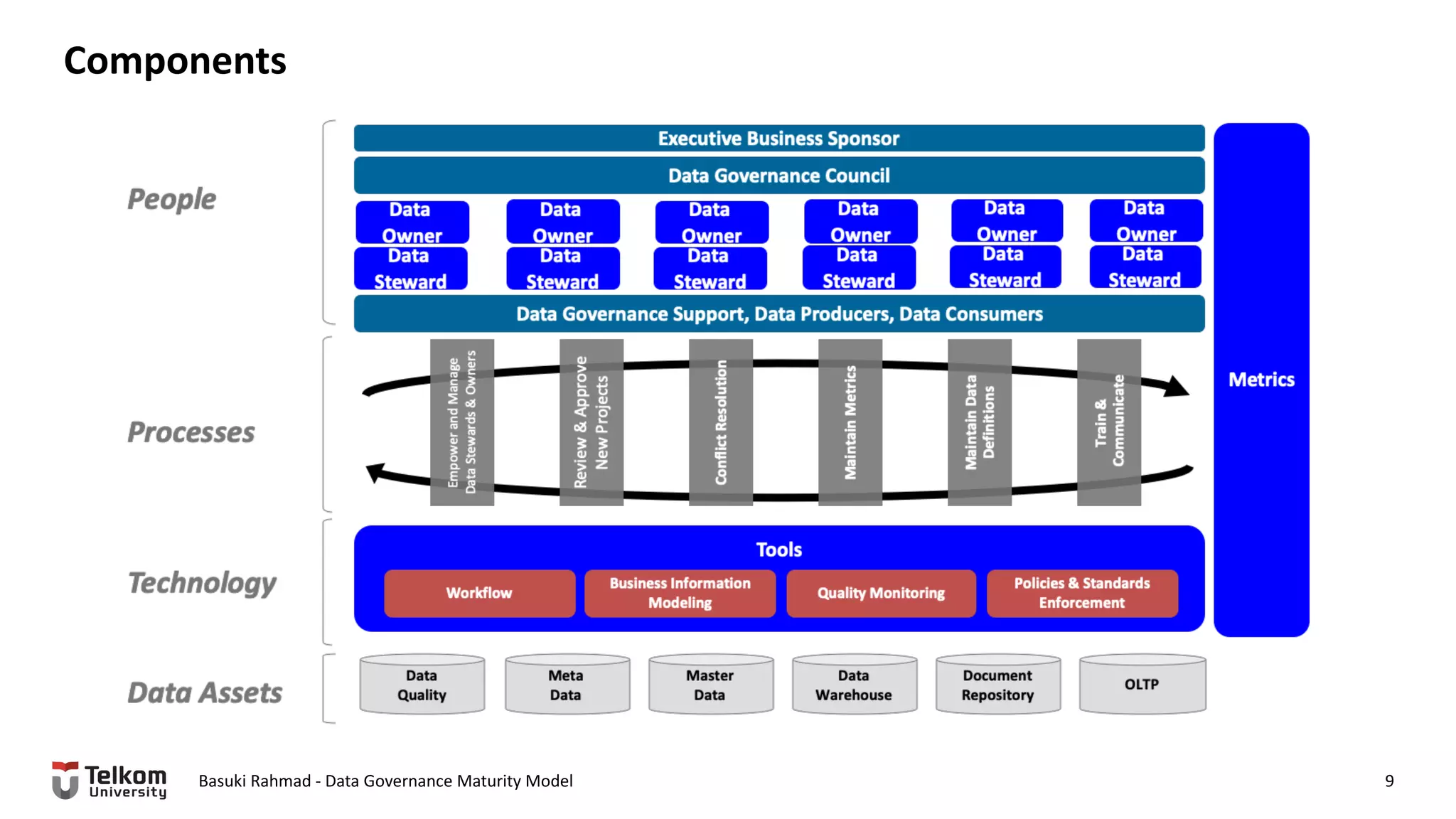
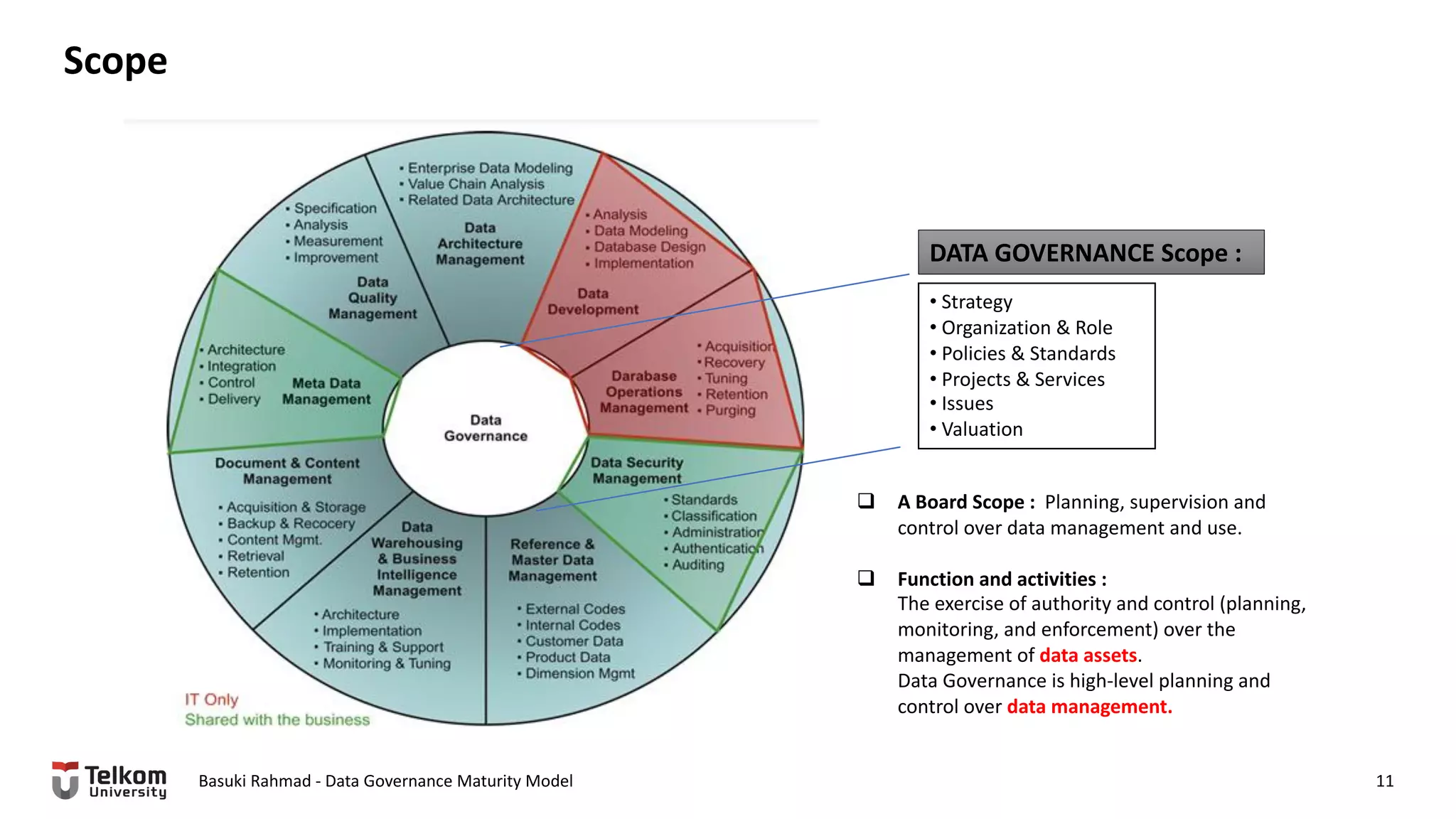
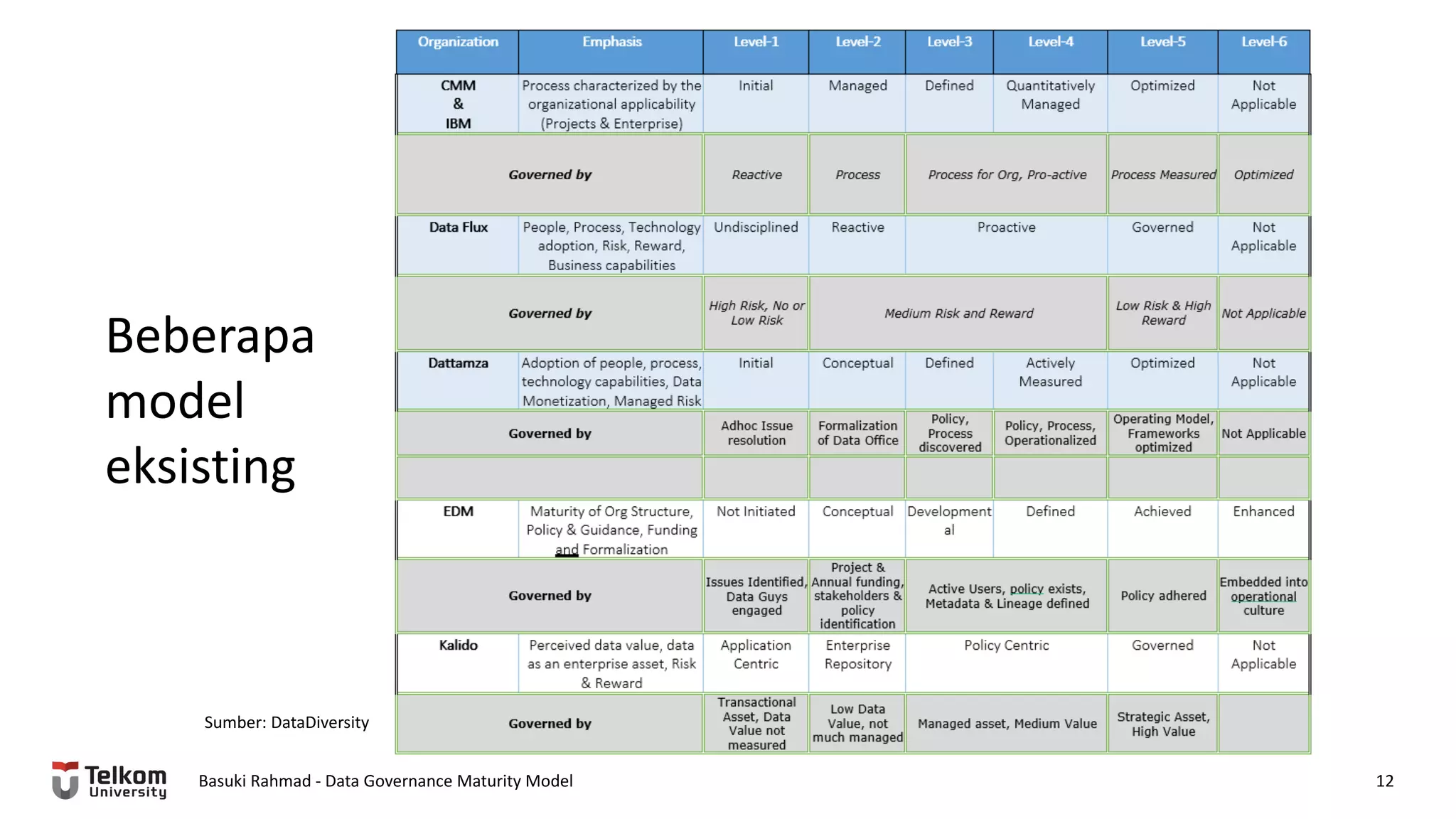
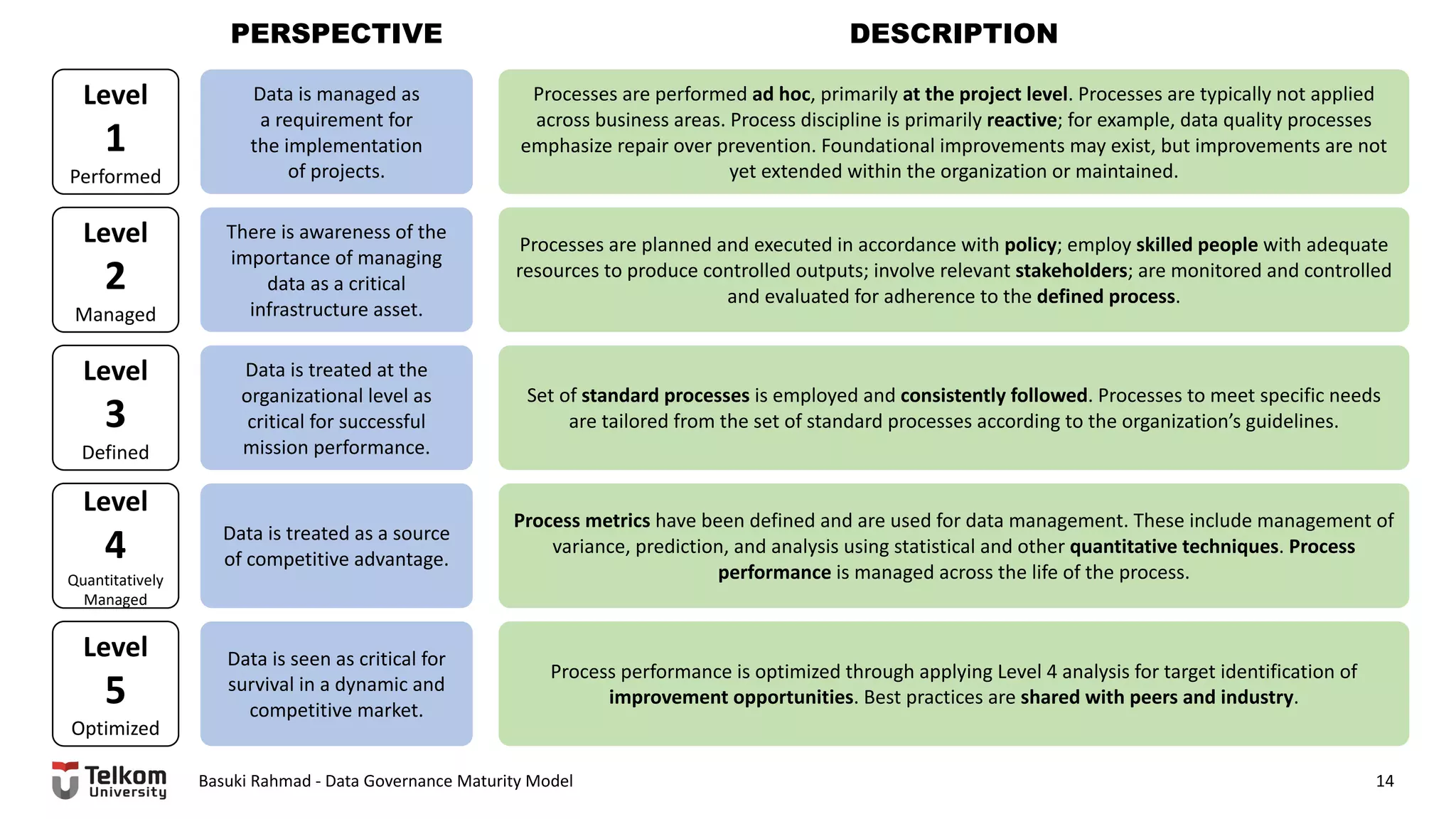
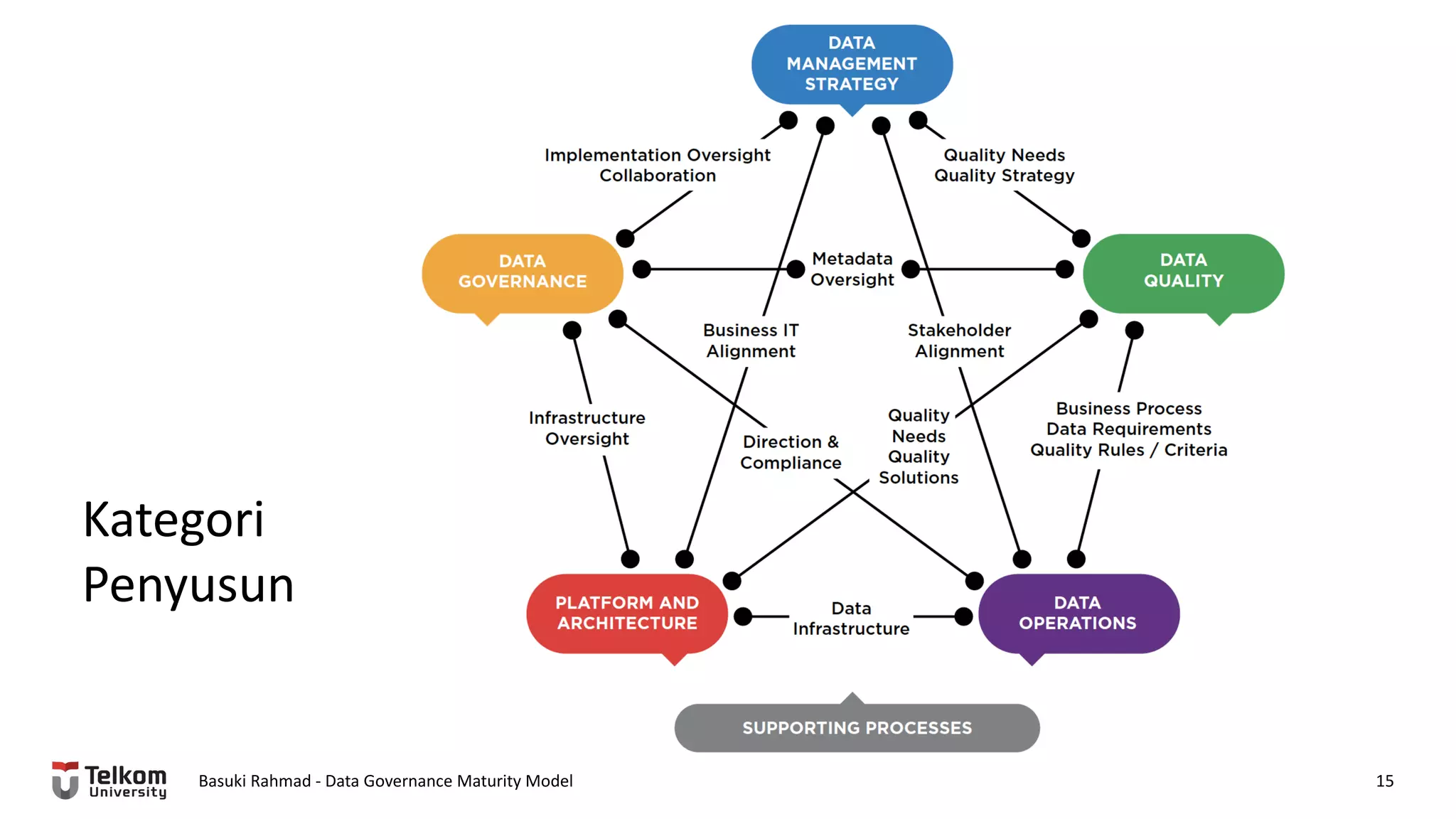
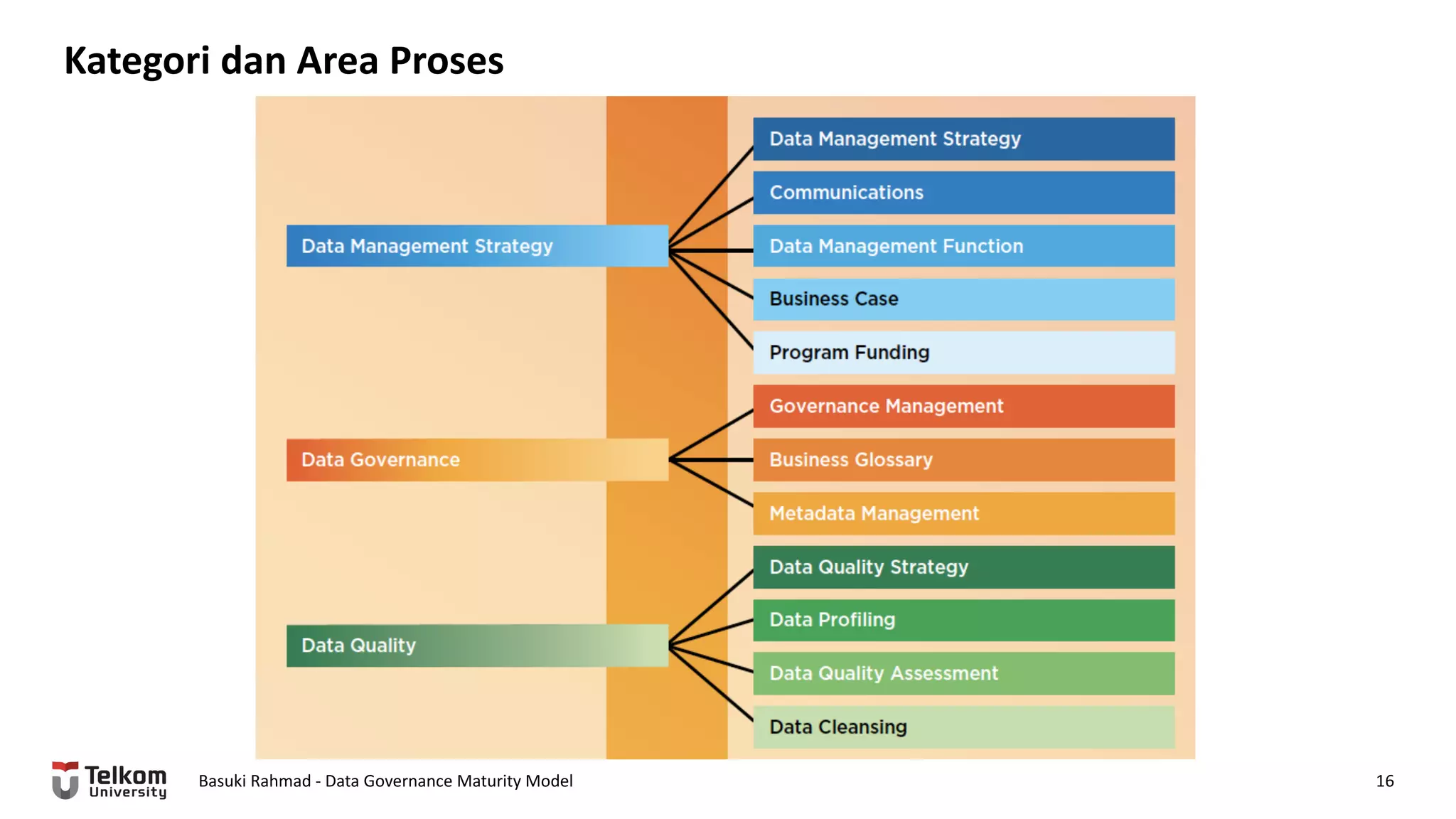
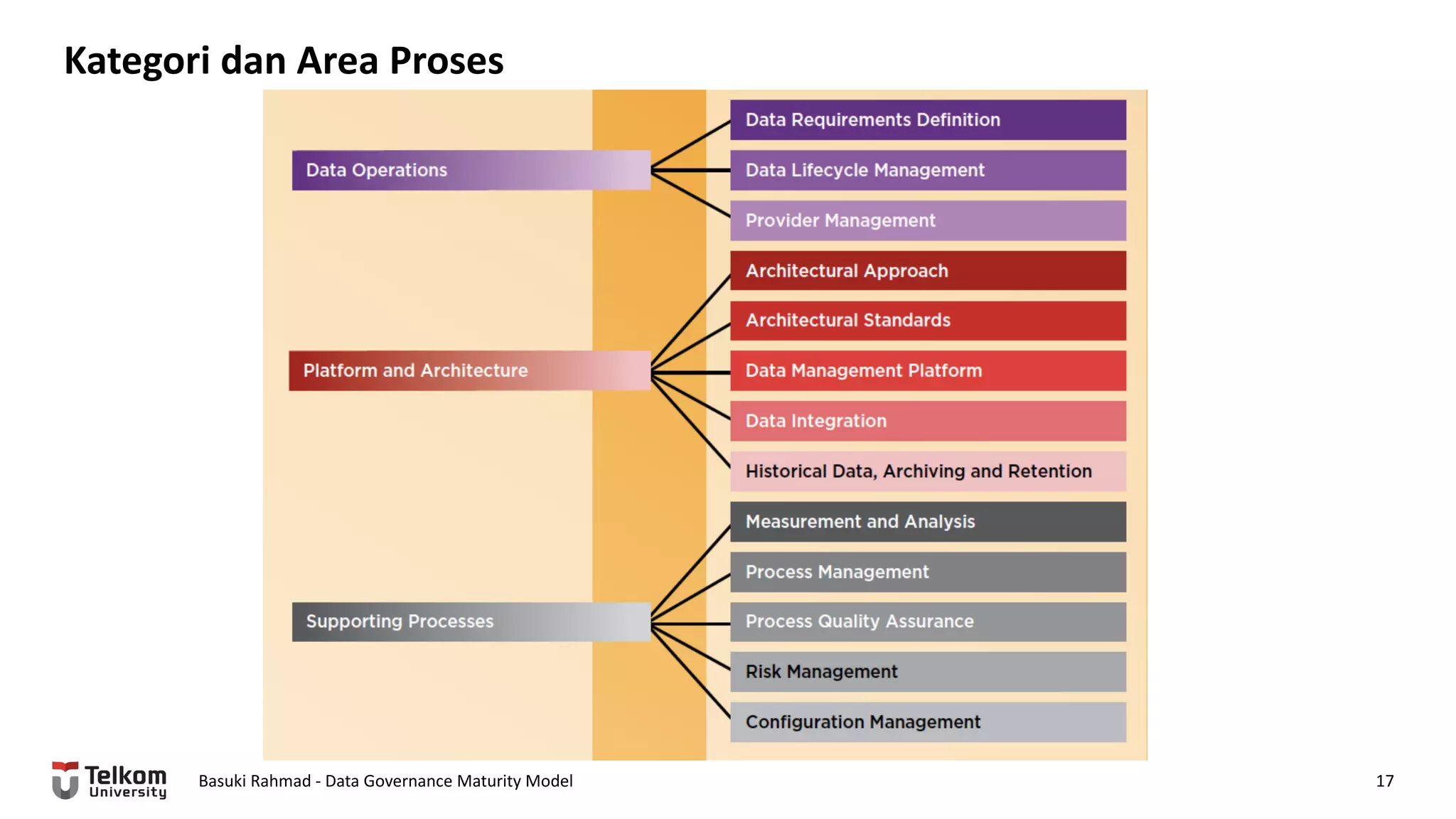
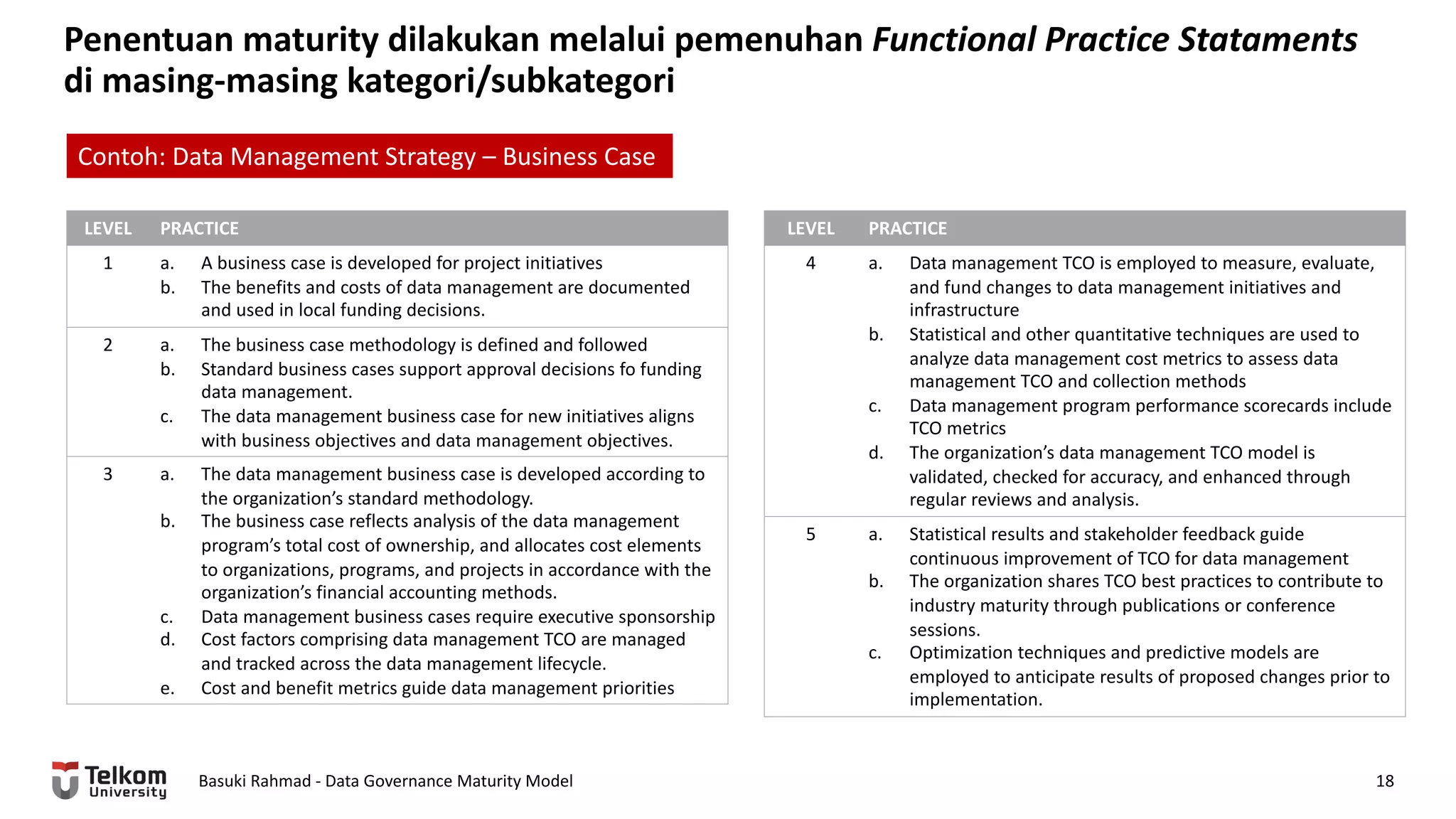
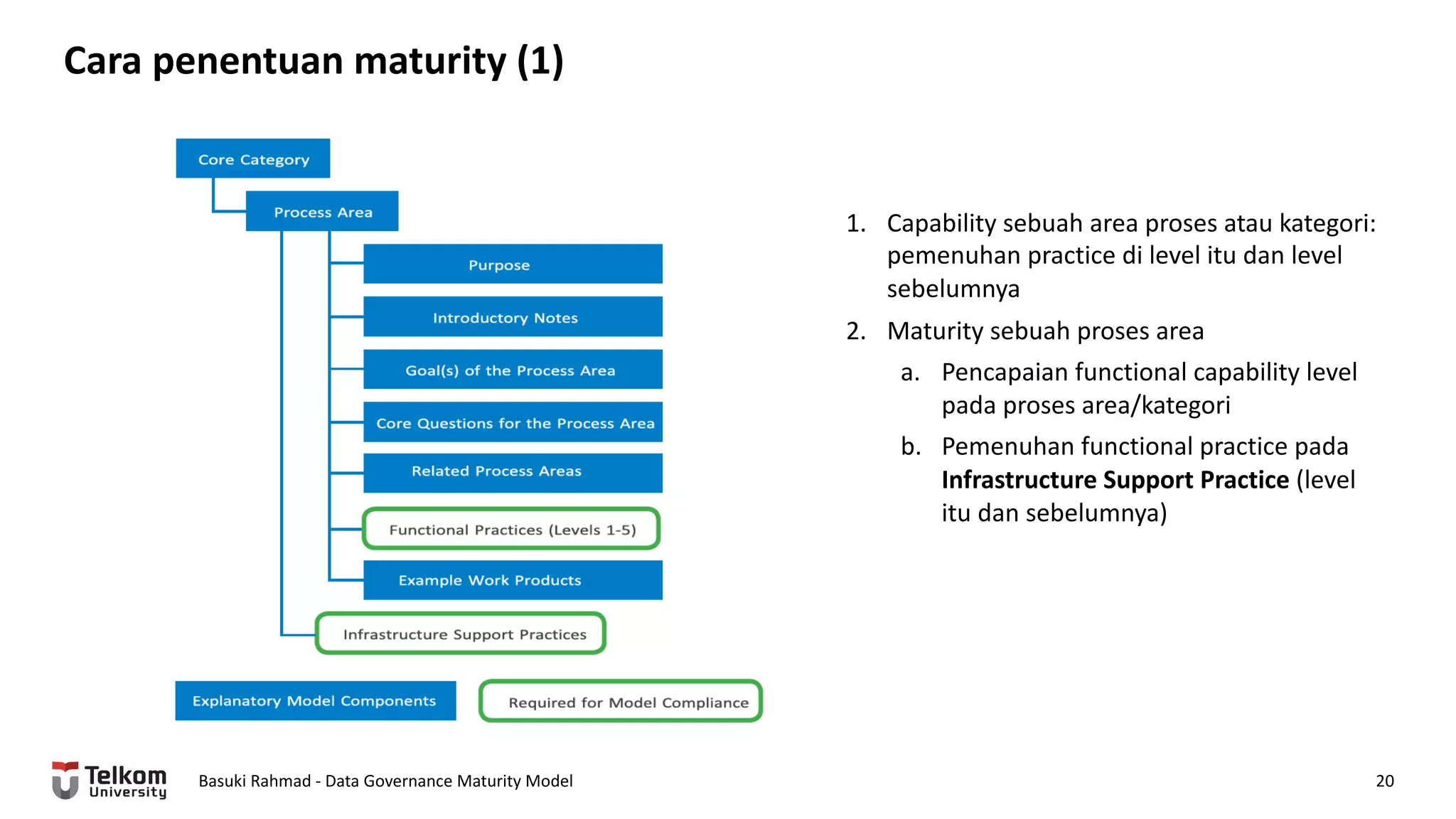
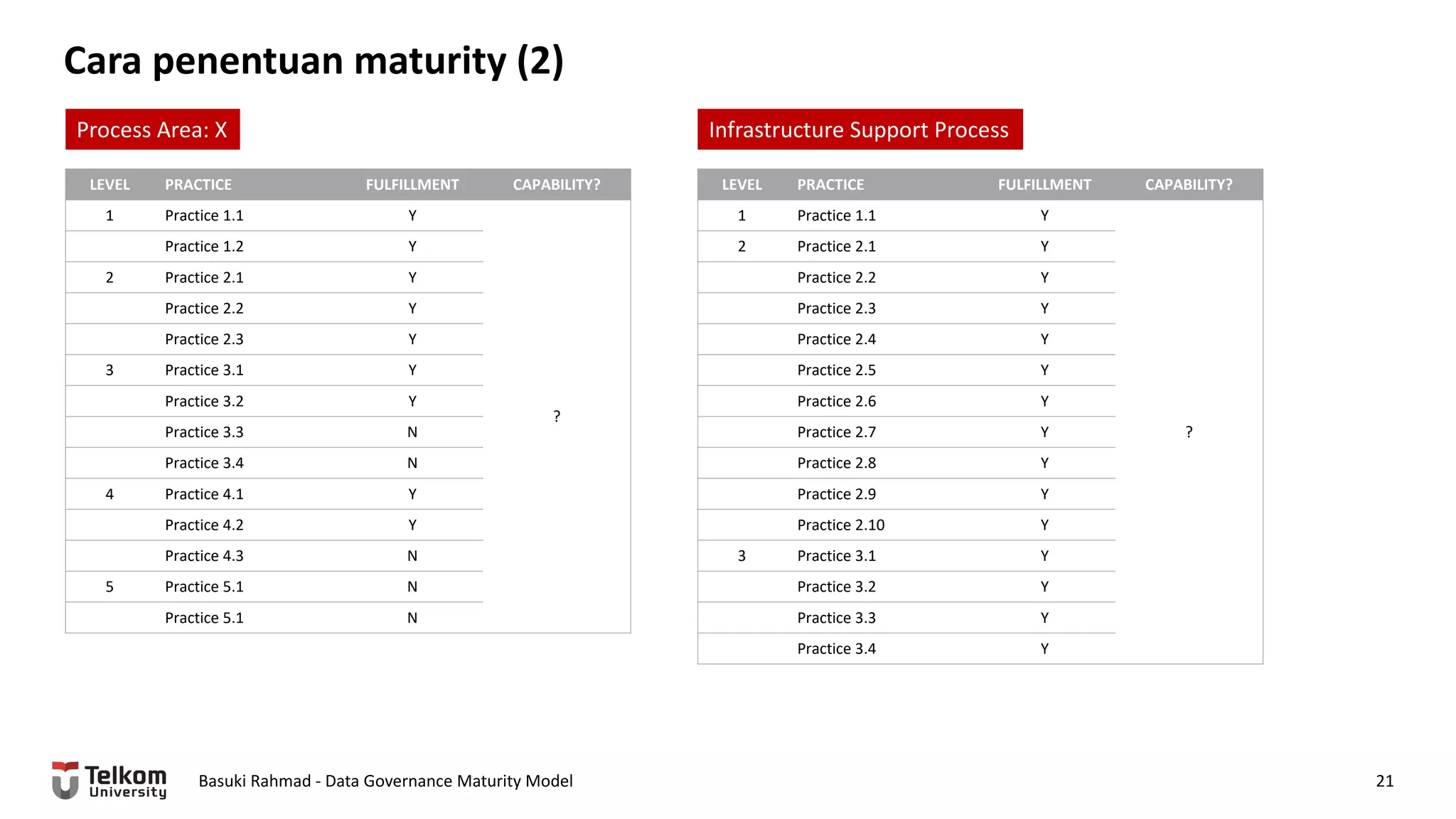
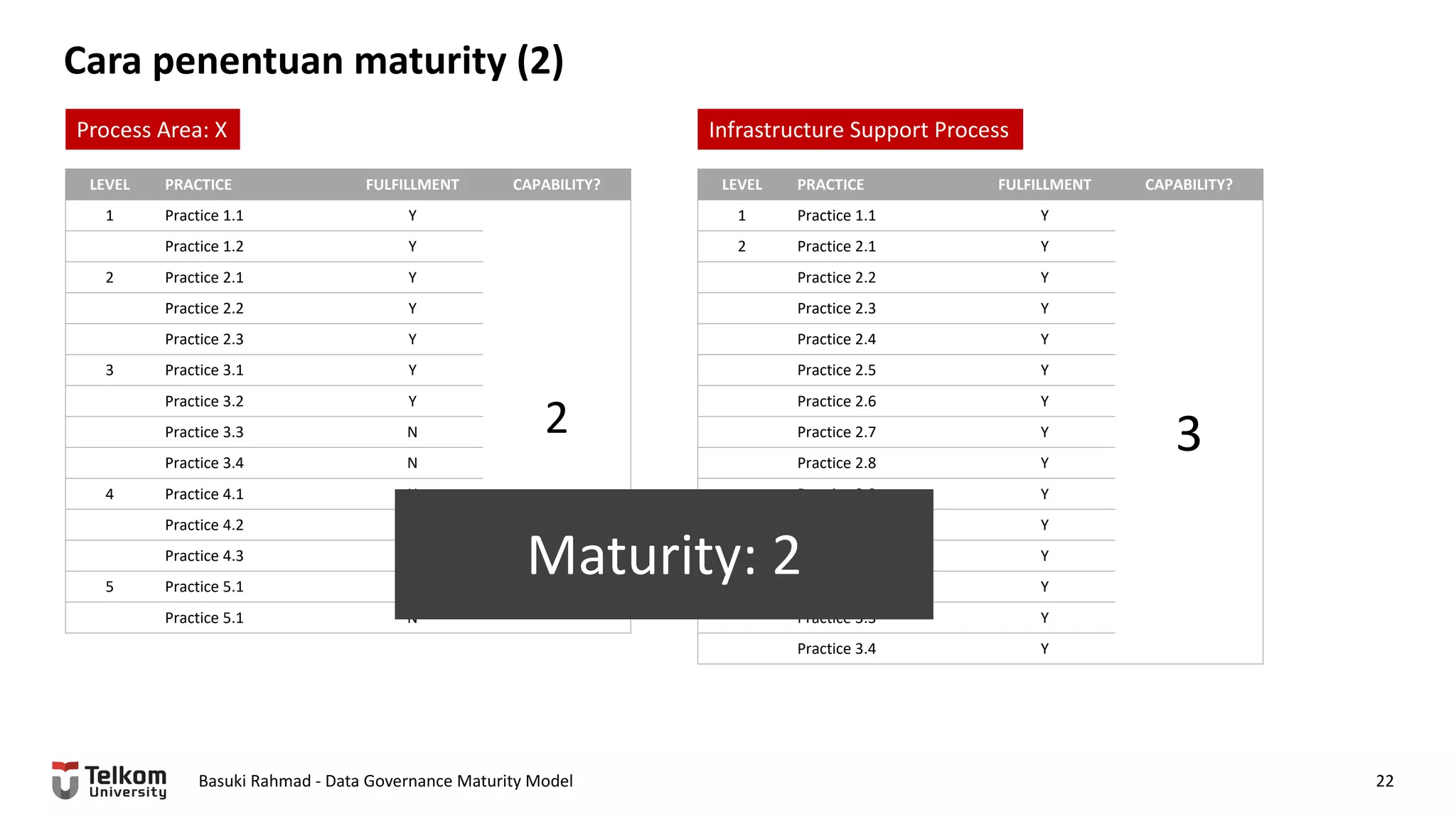
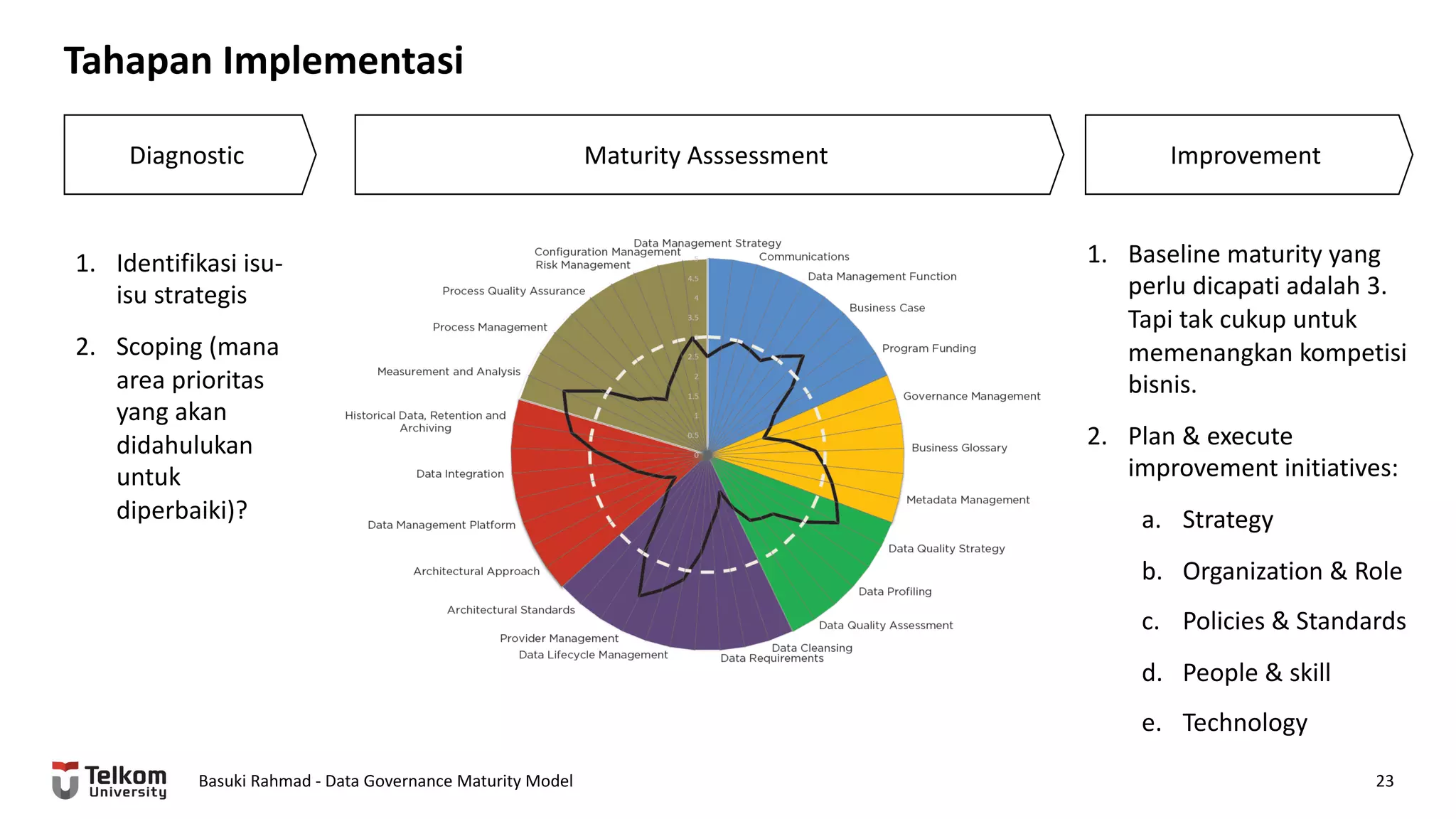
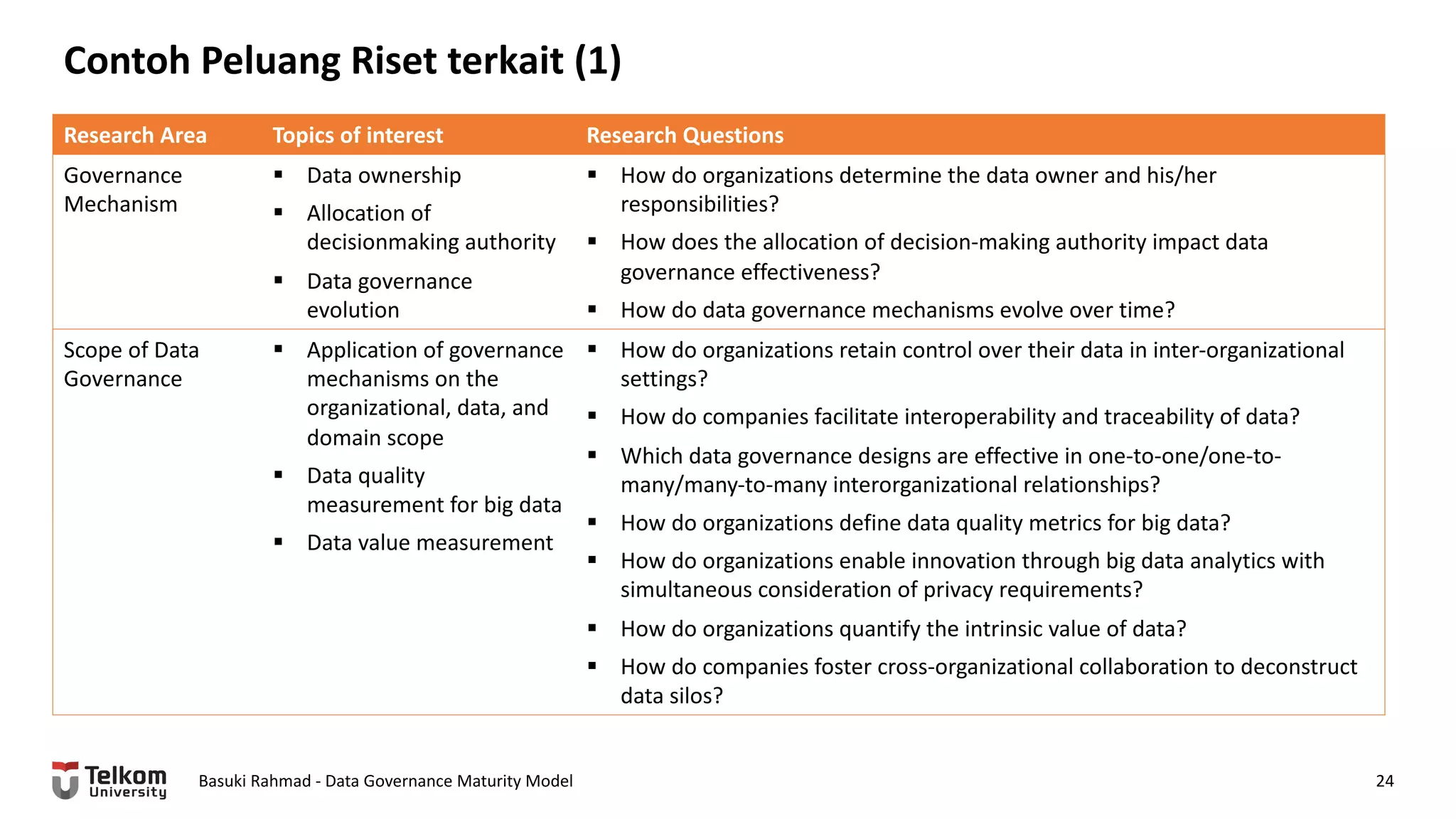
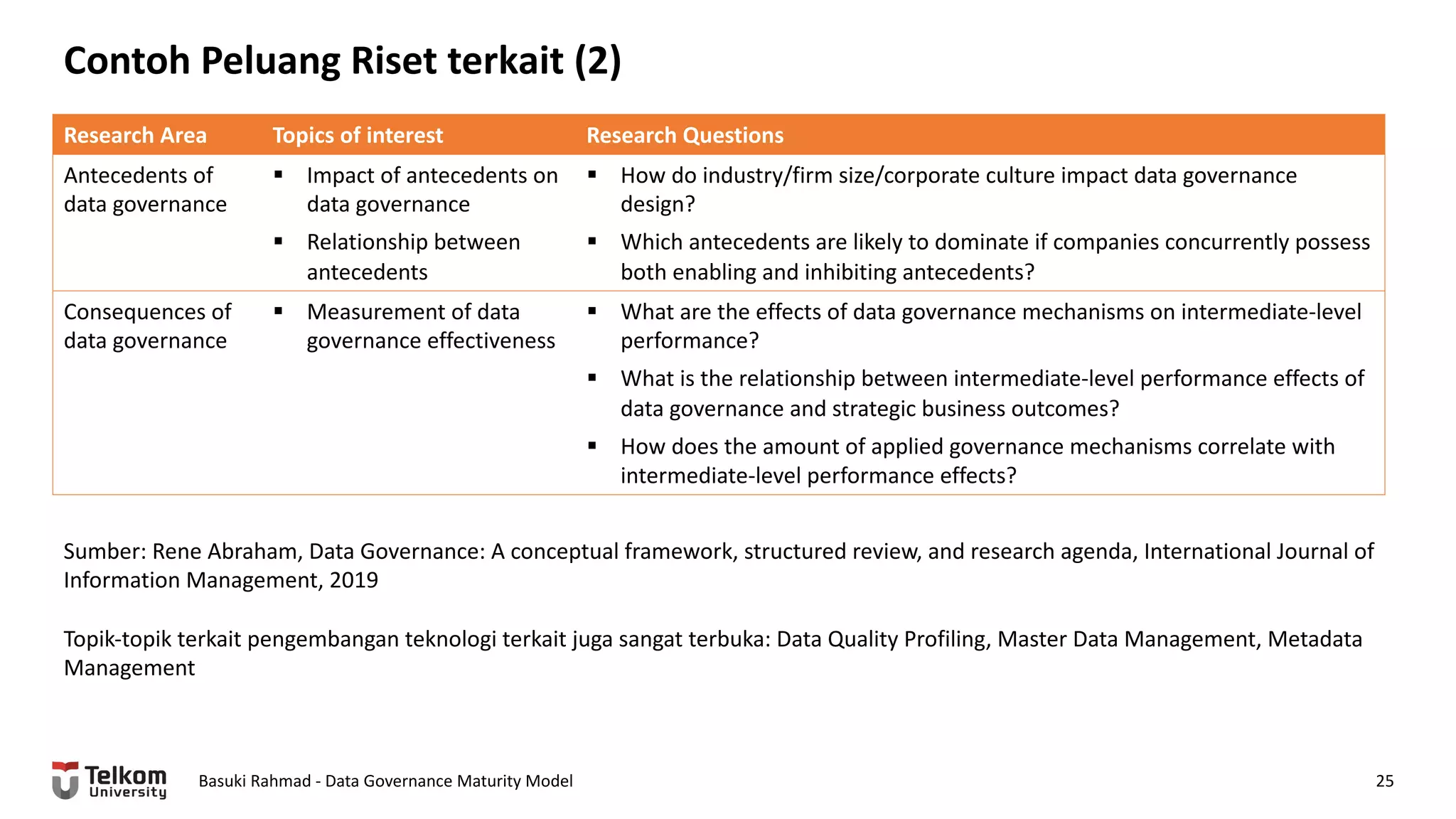
This document provides a brief biography of Dr. Basuki Rahmad and outlines his presentation on data governance maturity models. It includes his educational and professional background, areas of research focus, academic and professional activities, and professional associations. The presentation outline covers an overview of data governance, existing data governance maturity models, and the CMM data governance maturity model developed by Rahmad. It also identifies potential areas for further research related to data governance mechanisms, scope, and implementation.