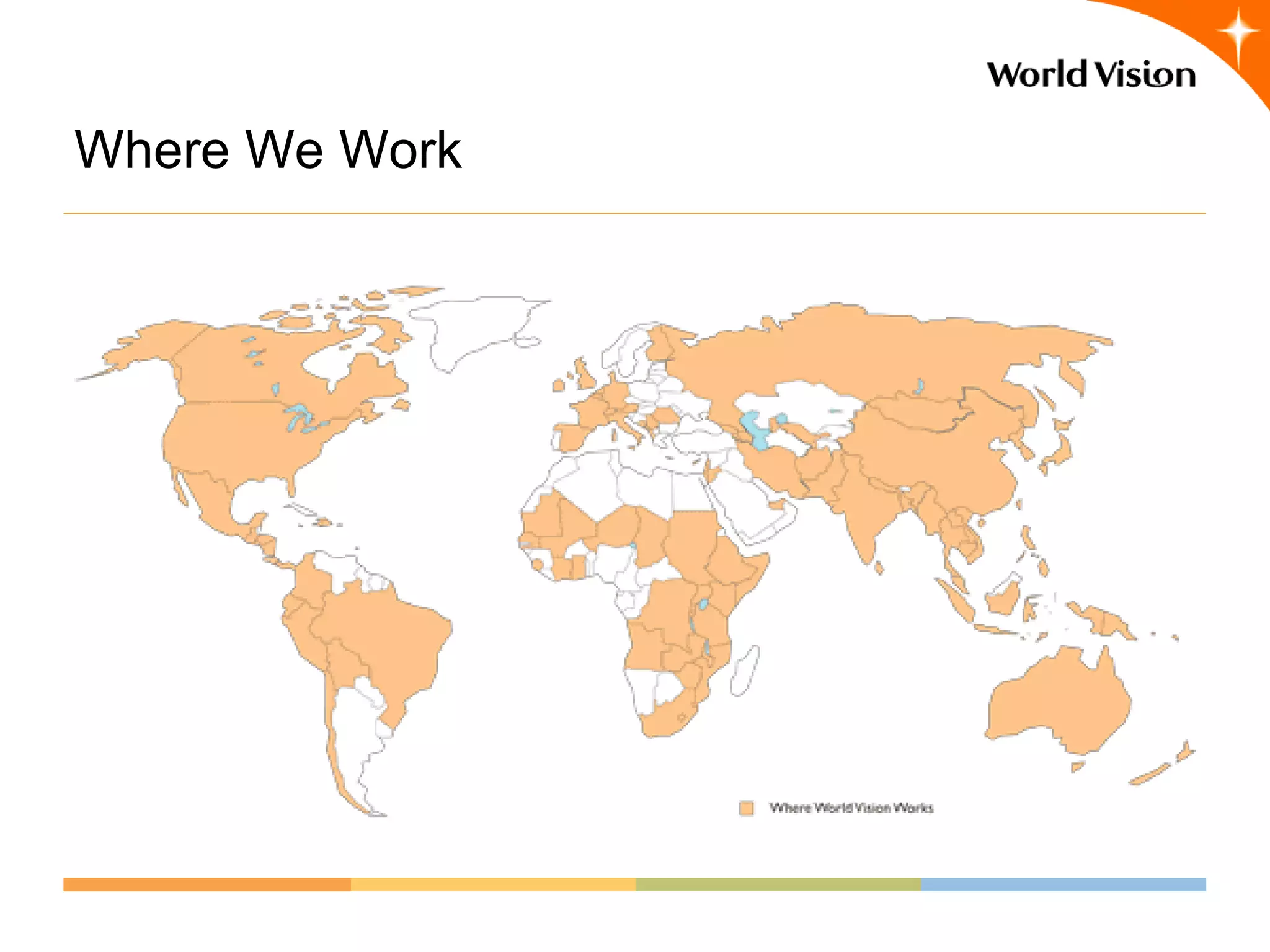
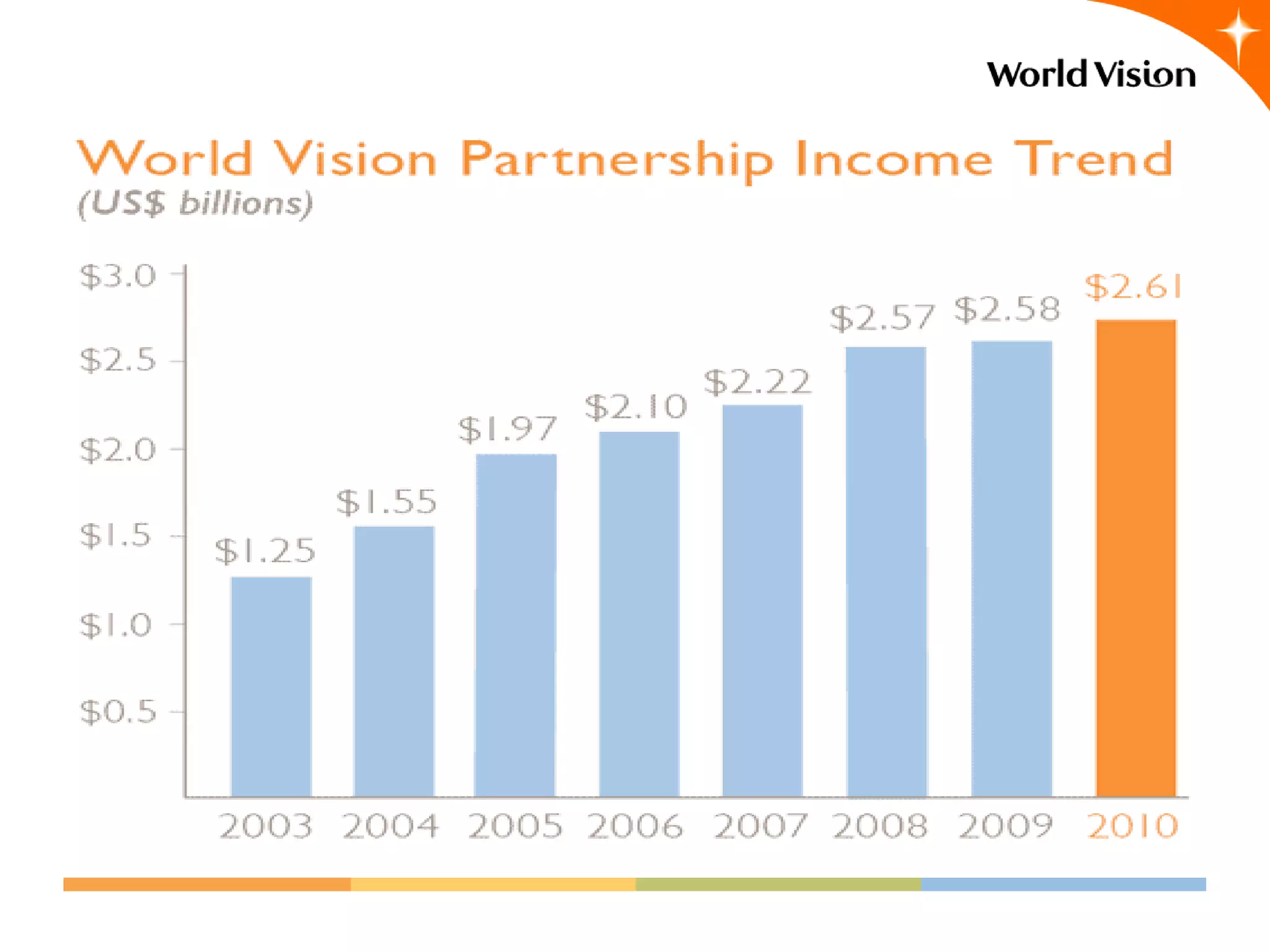
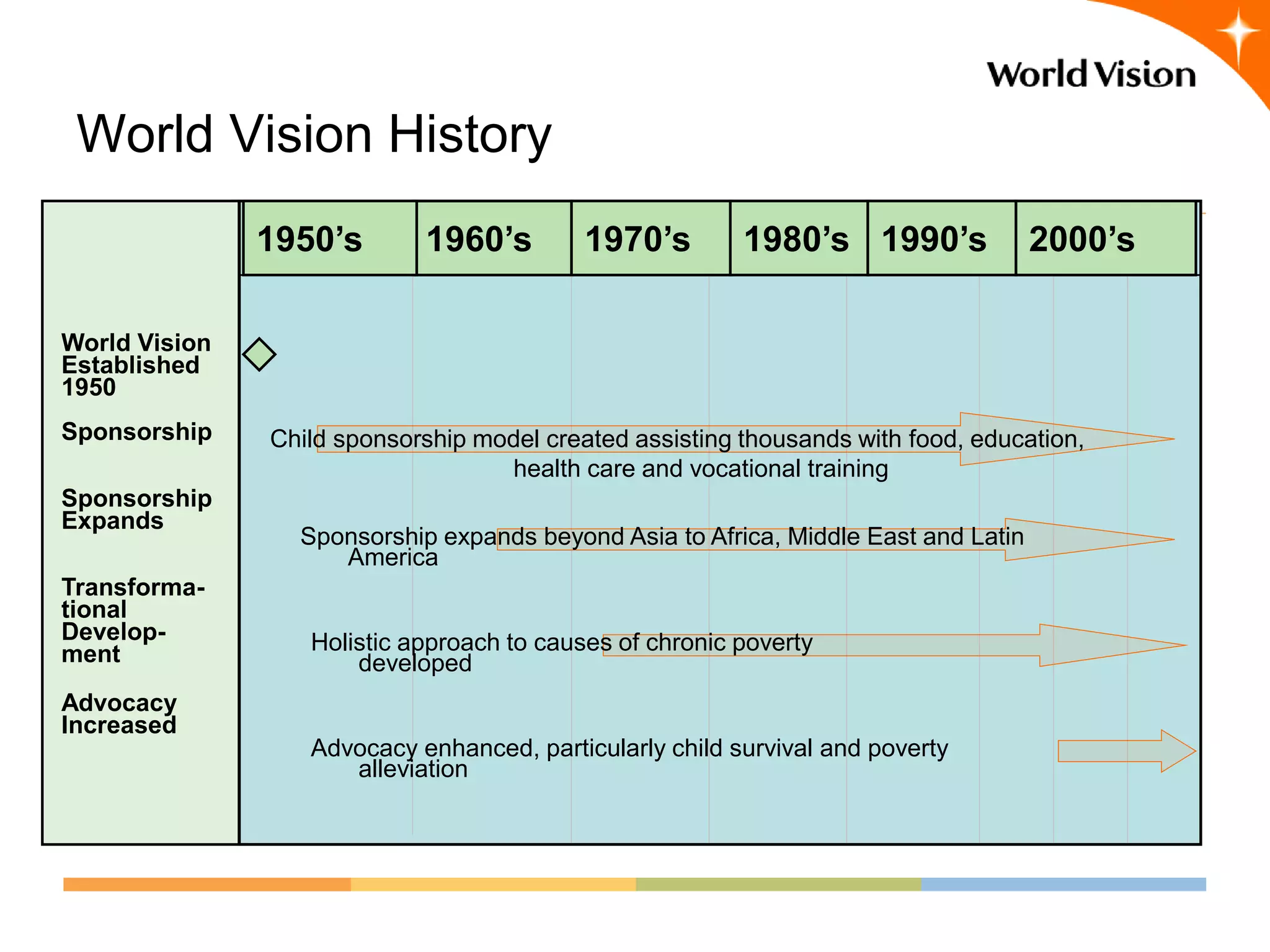
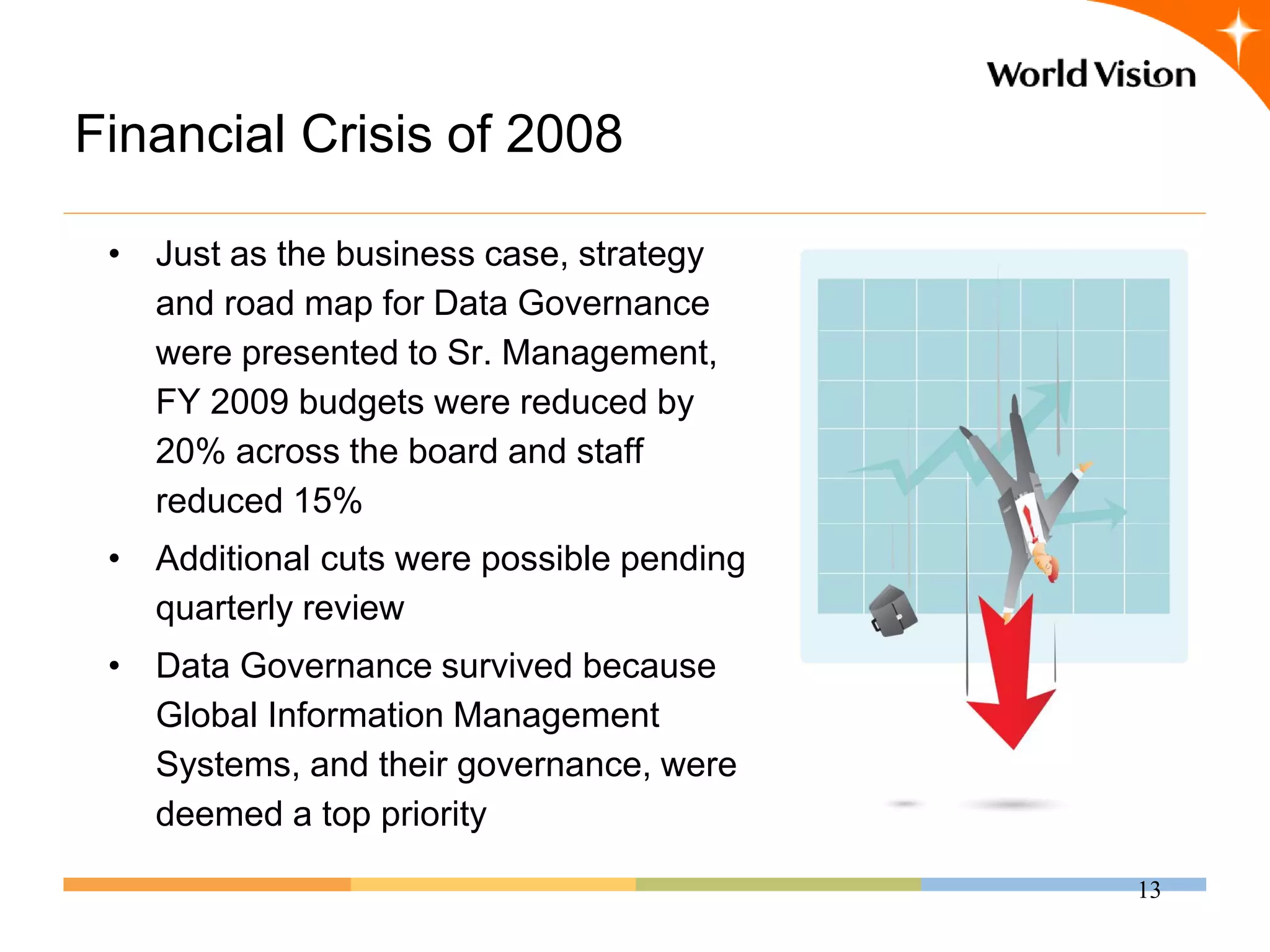
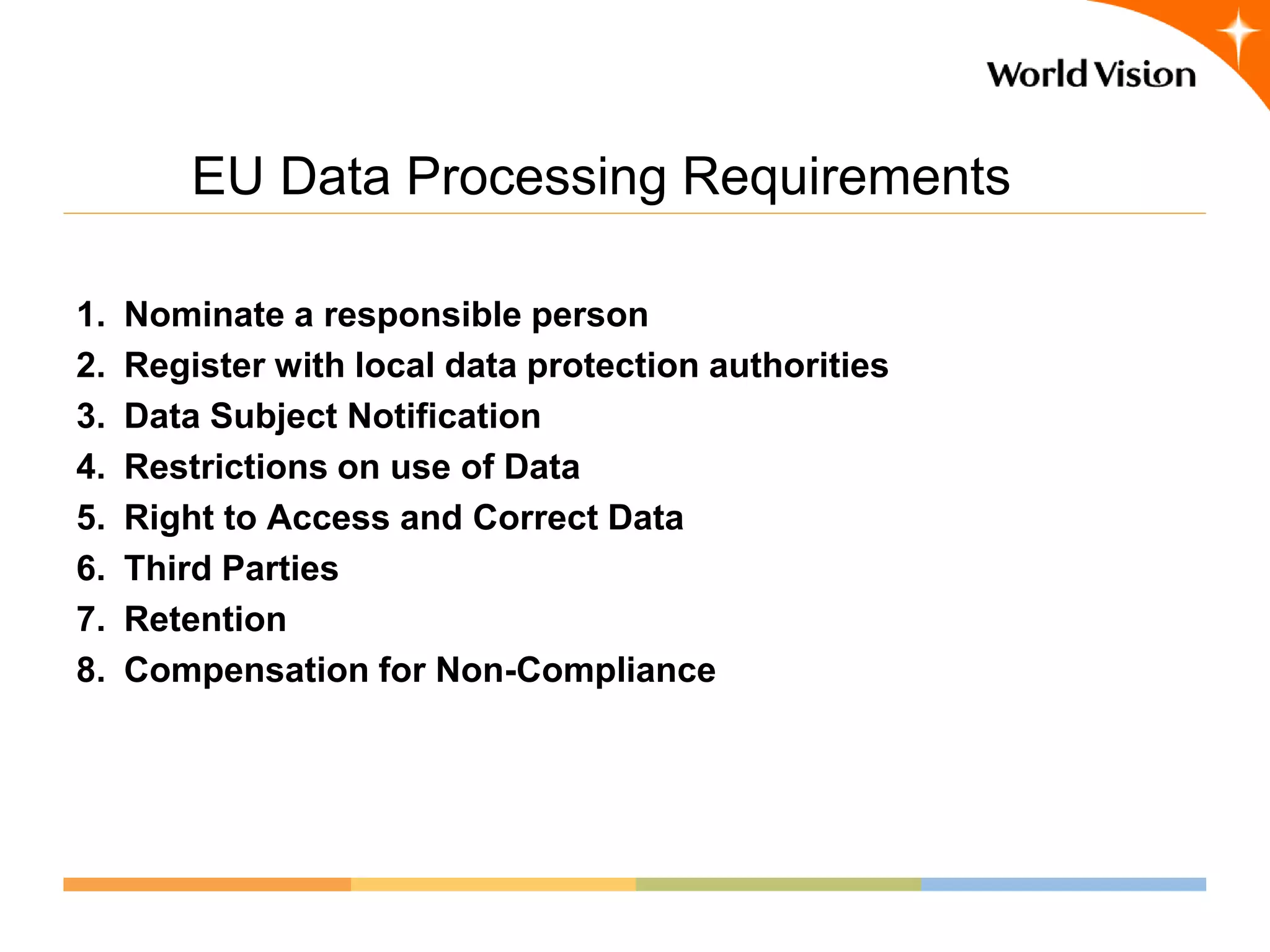
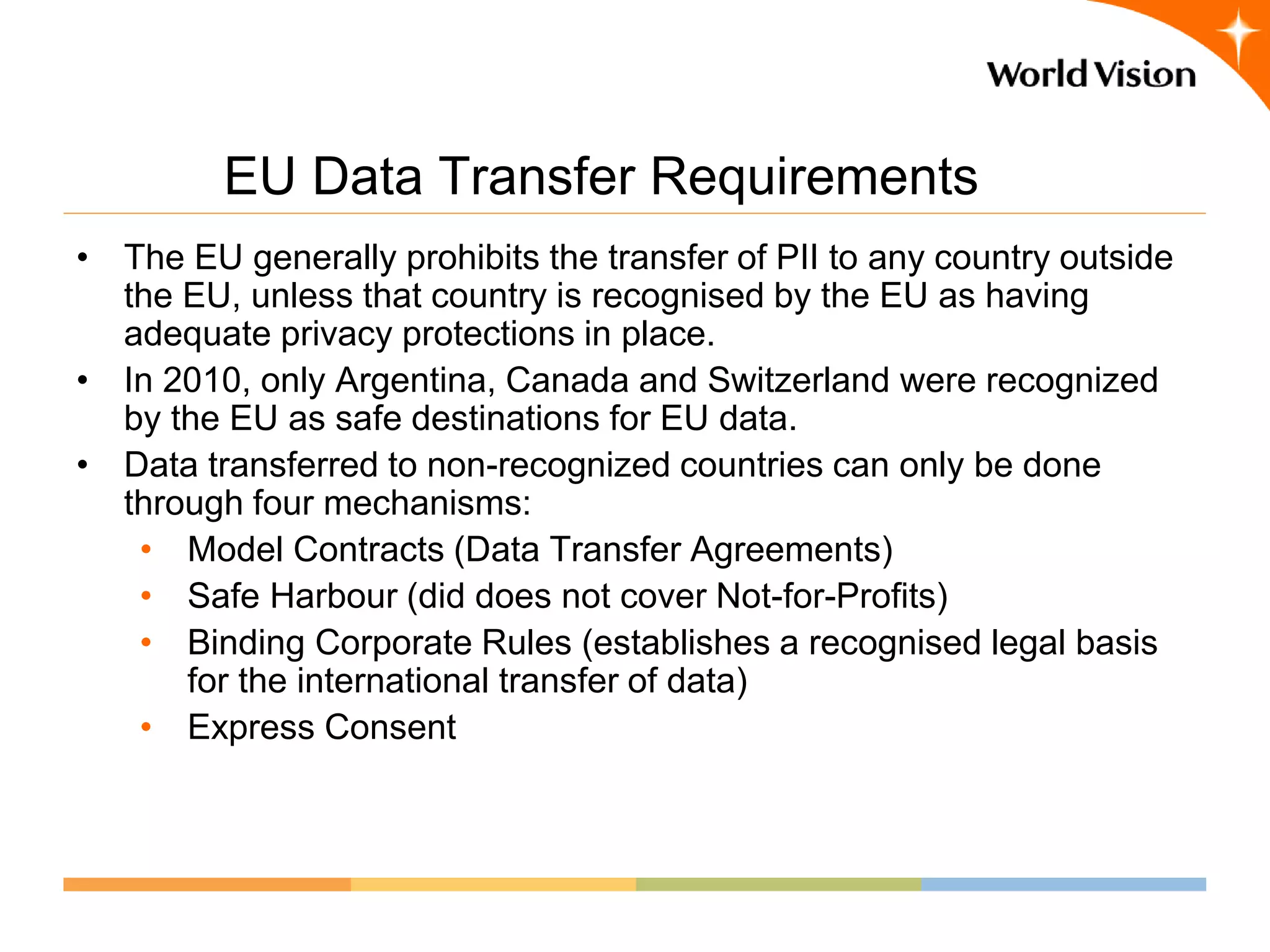
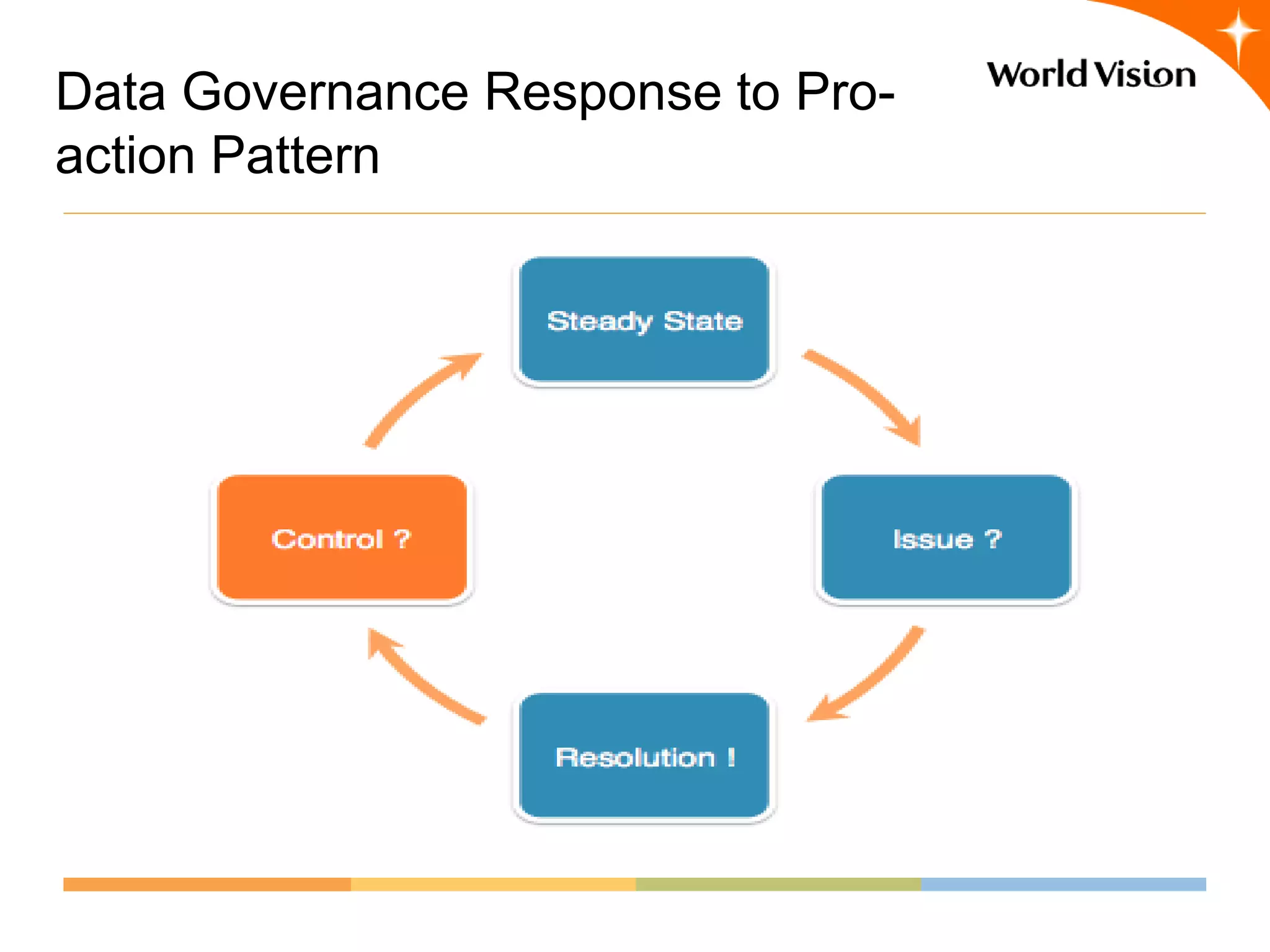
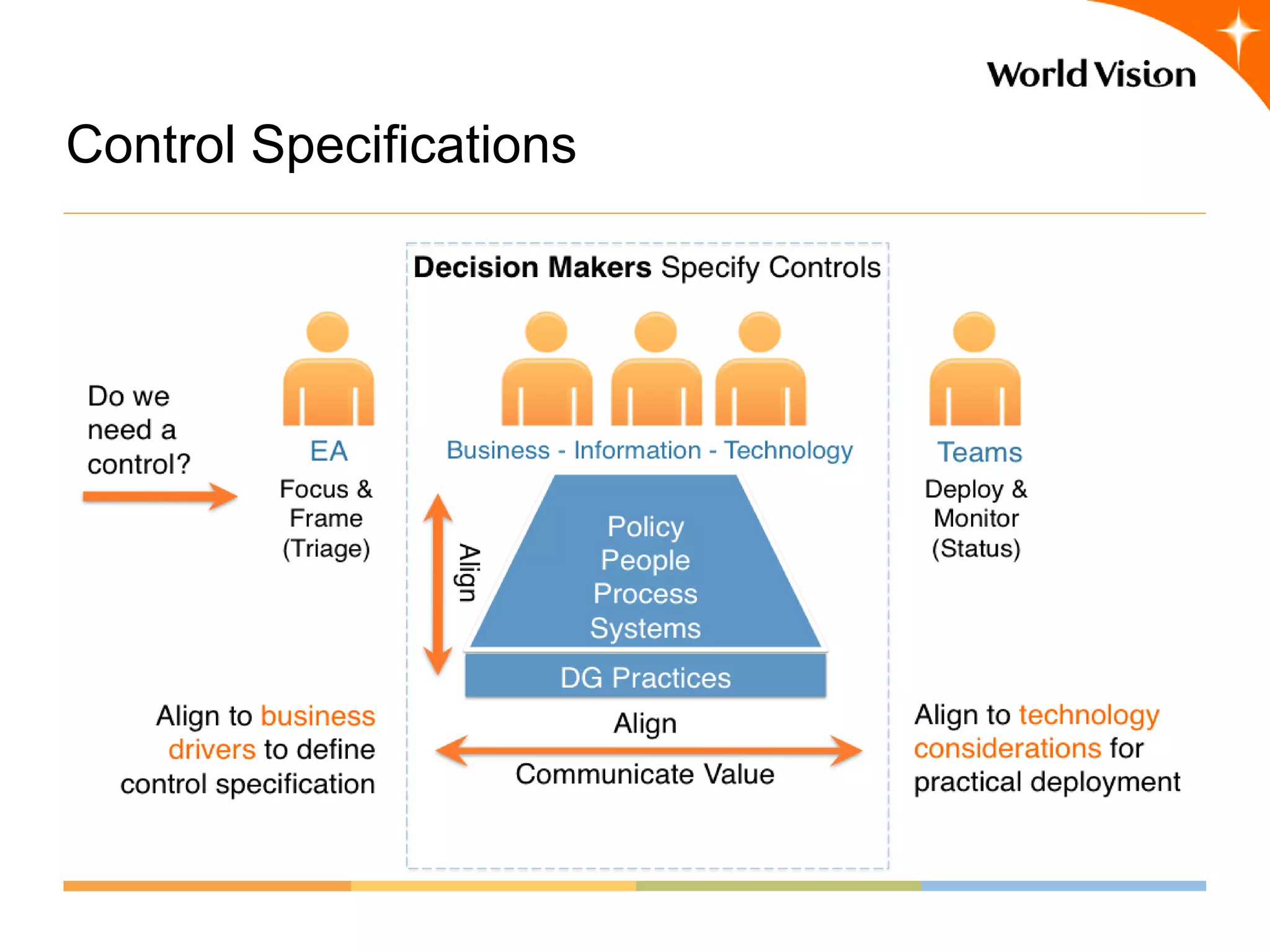
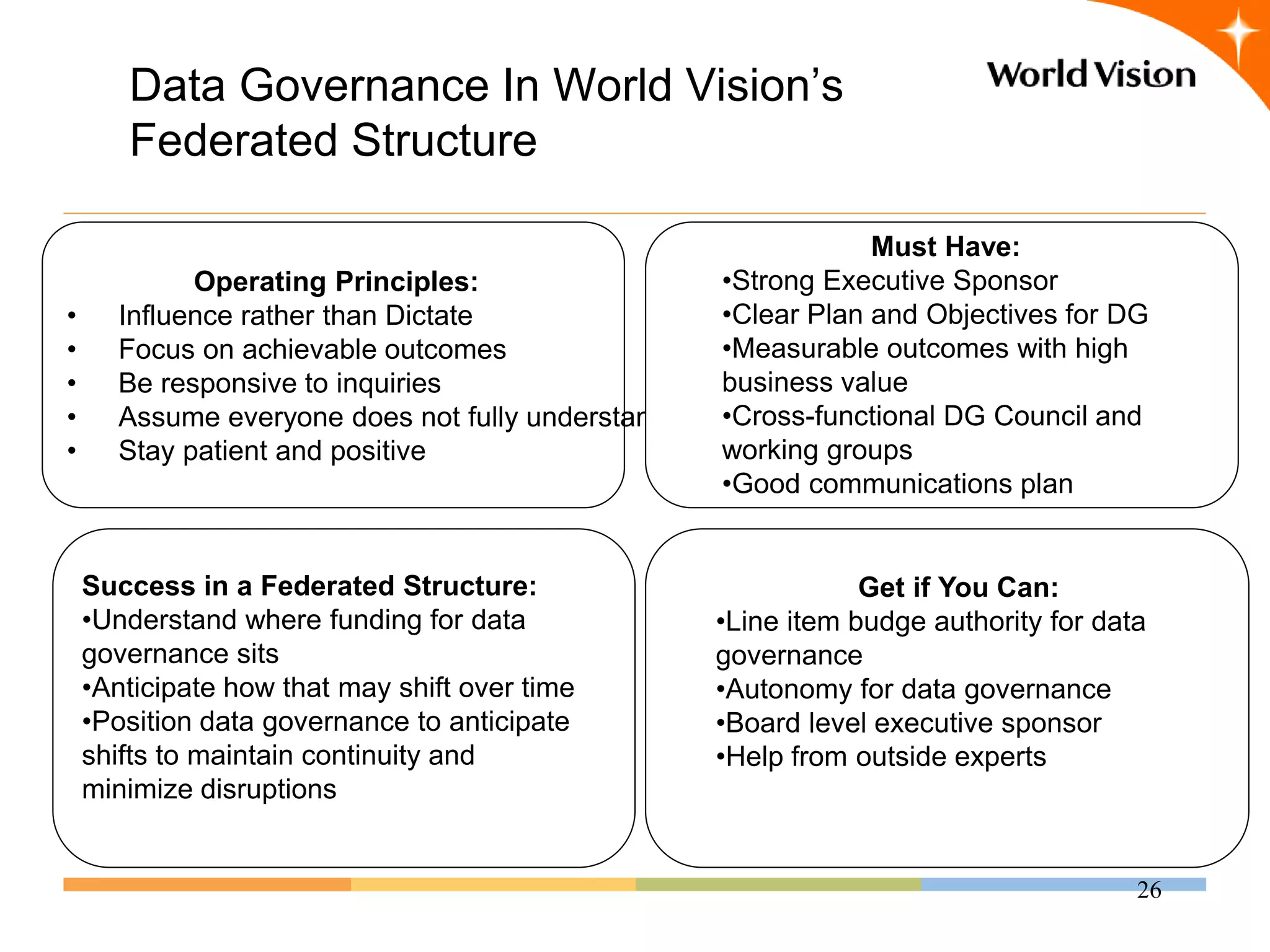
This document provides an overview of World Vision's development of a data governance program within its federated organizational structure. World Vision is a global Christian humanitarian organization made up of multiple independent national entities. It established a Data Governance Office in 2008 to help govern data across these entities. The office developed a strategy and roadmap but then faced budget cuts during the 2008 financial crisis. It focused on governing child sponsorship data by bringing records together and complying with EU privacy laws. This incremental approach helped the program survive and establish governance working groups and a council. Lessons included starting small and building value, having a clear plan, and gradually expanding the program's scope through proven results.