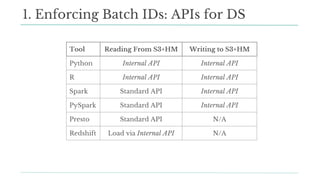
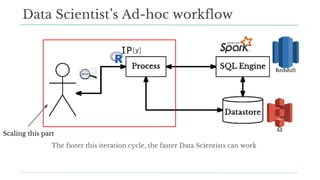
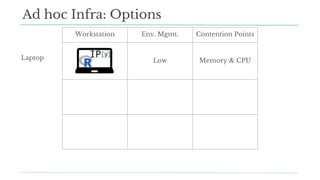
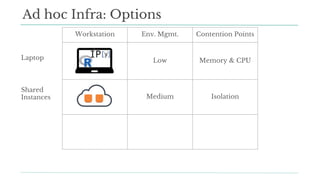
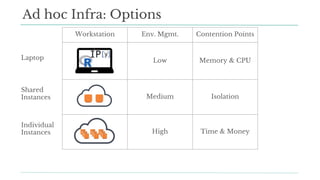
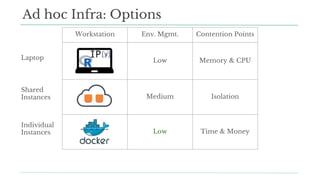
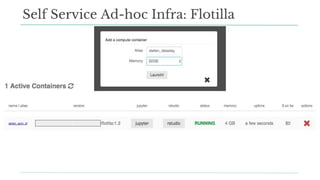
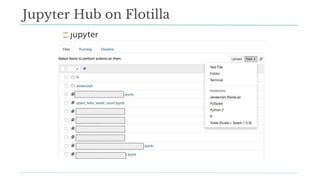
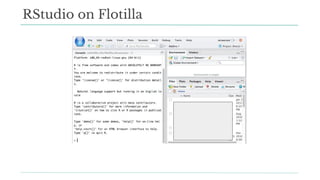
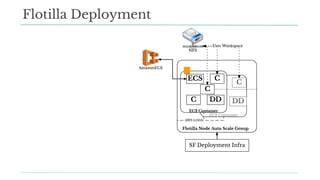
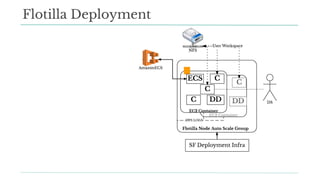
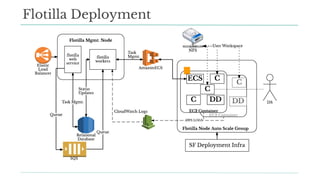
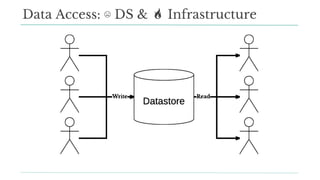
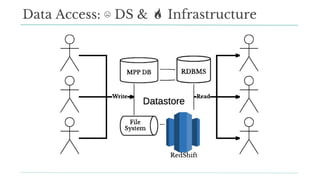
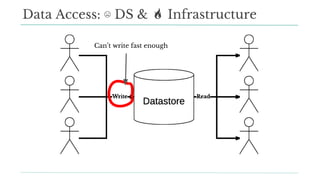
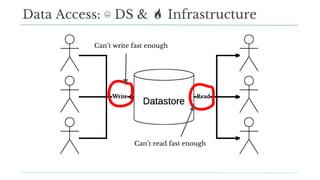
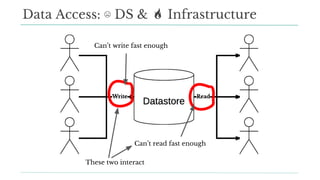
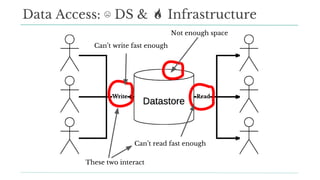
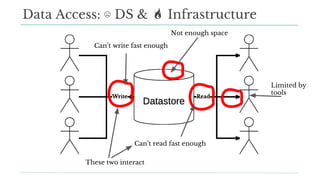
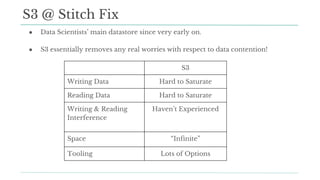
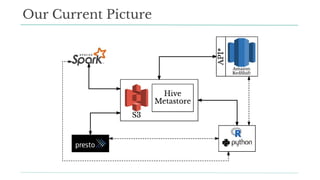
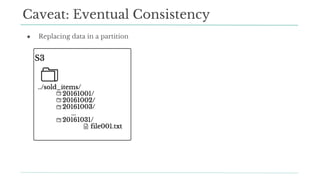
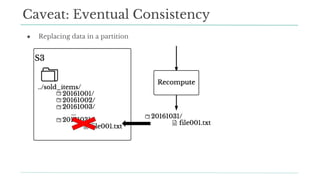
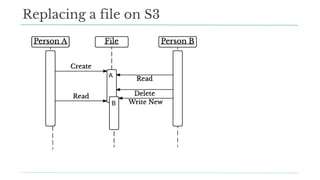
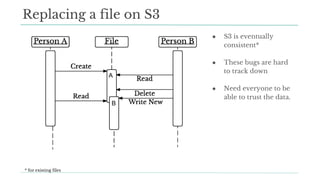
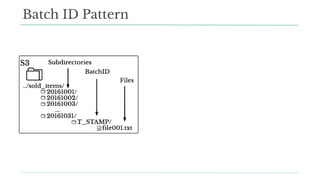
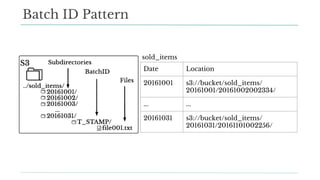
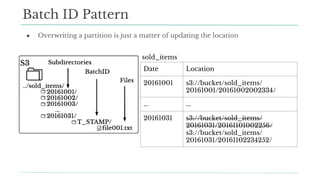
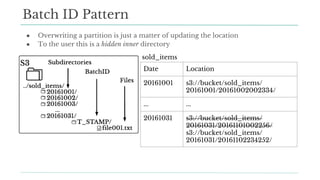
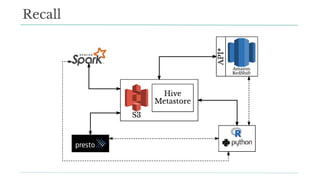
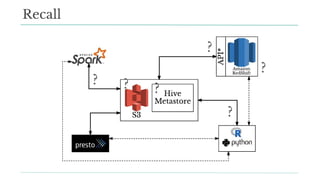
Stitch Fix scales its data science operations with a focus on reducing contention among data scientists and optimizing data access through S3 and a Hive Metastore. By establishing efficient APIs and utilizing Docker for environment consistency, they enhance data handling and speed up the data science workflow. Their architecture allows for high flexibility in data storage, ensuring minimal contention and facilitating easier collaboration among data scientists.







































![Python:
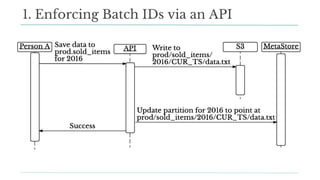
store_dataframe(df, dest_db, dest_table, partitions=[‘2016’])
df = load_dataframe(src_db, src_table, partitions=[‘2016’])
R:
sf_writer(data = result,
namespace = dest_db,
resource = dest_table,
partitions = c(as.integer(opt$ETL_DATE)))
df <- sf_reader(namespace = src_db,
resource = src_table,
partitions = c(as.integer(opt$ETL_DATE)))
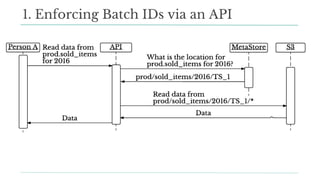
1. Enforcing Batch IDs: APIs for DS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stefanddtexas2017final-170118191838/85/Data-Day-Texas-2017-Scaling-Data-Science-at-Stitch-Fix-62-320.jpg)