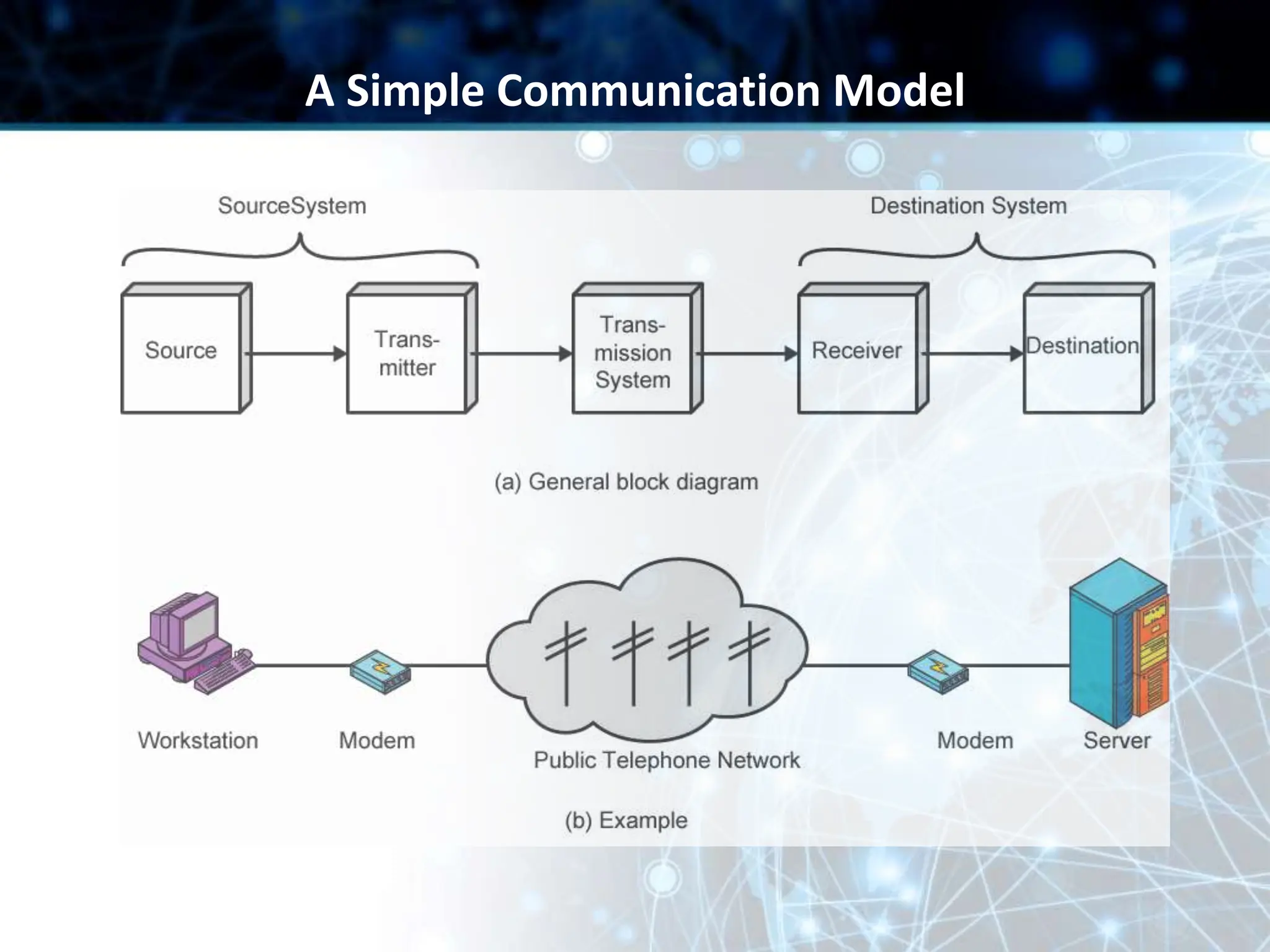
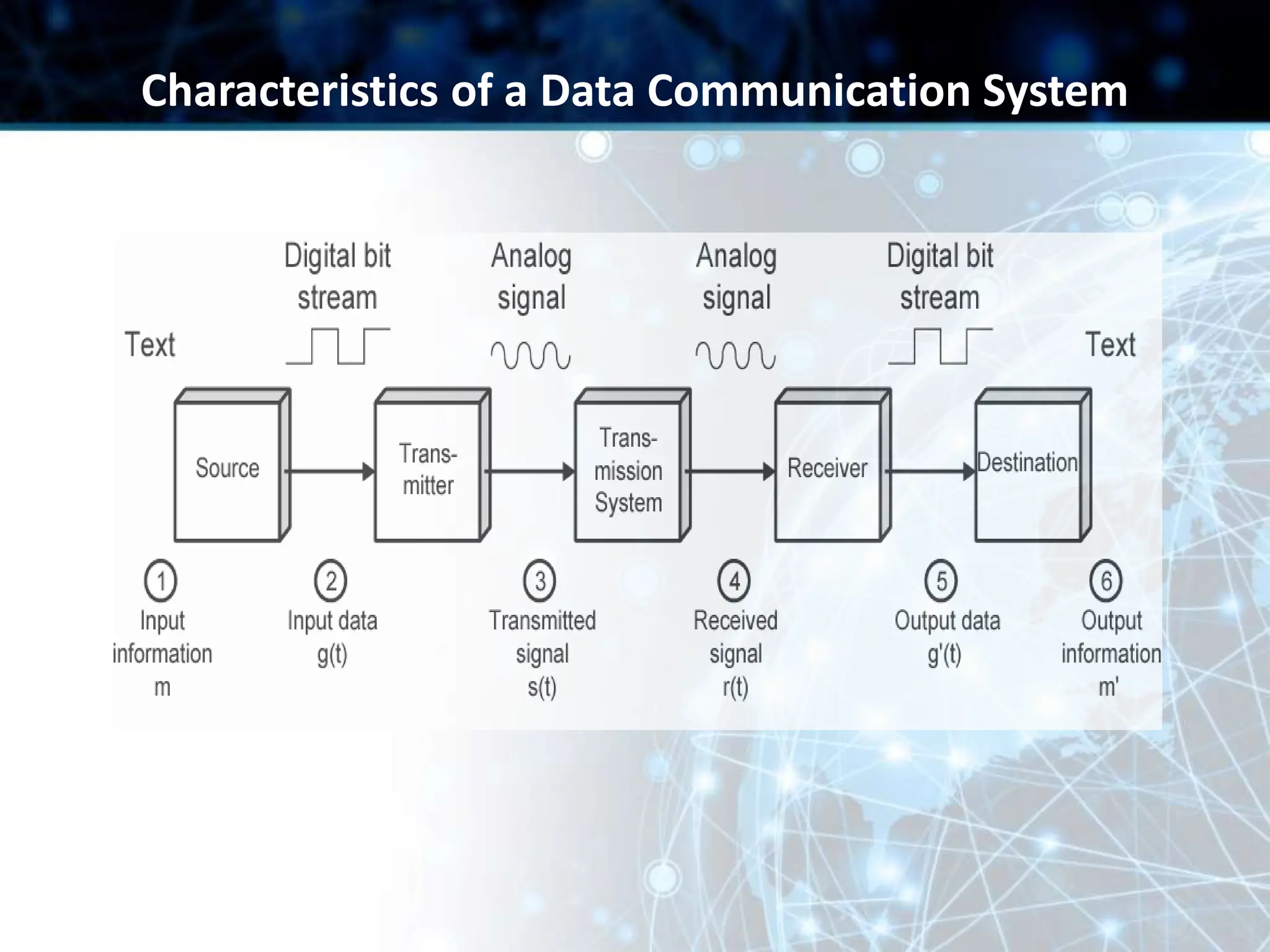
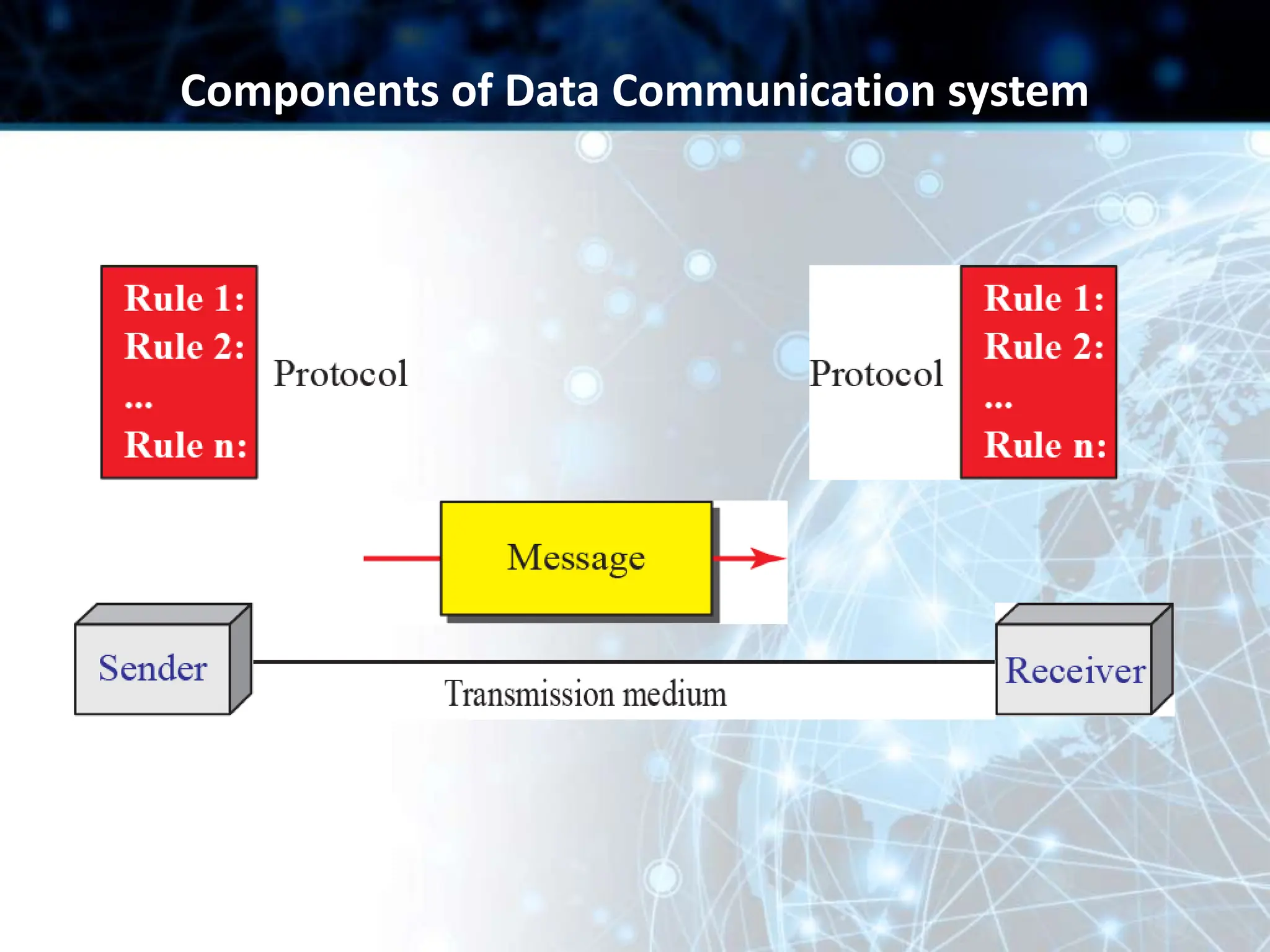
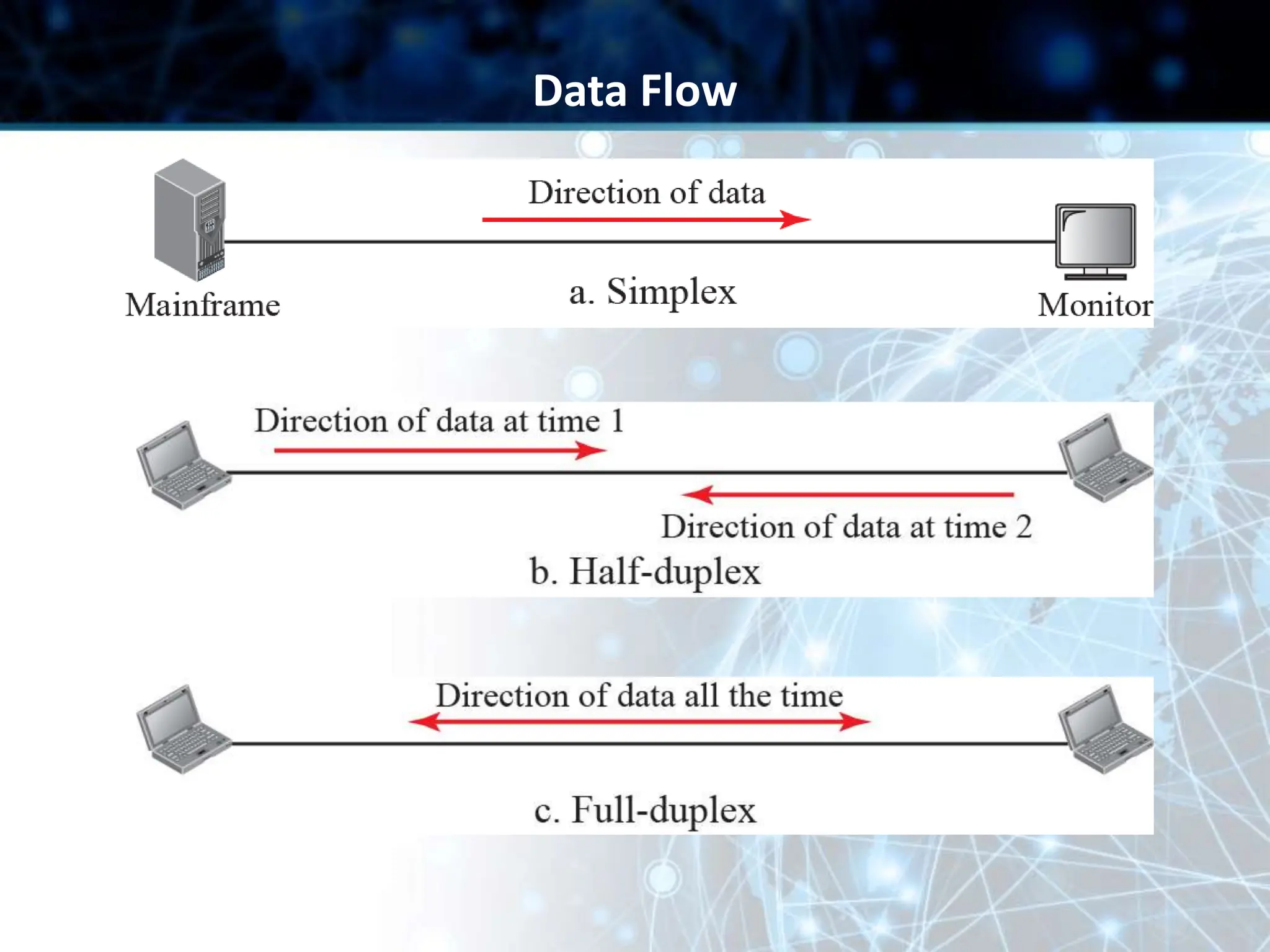
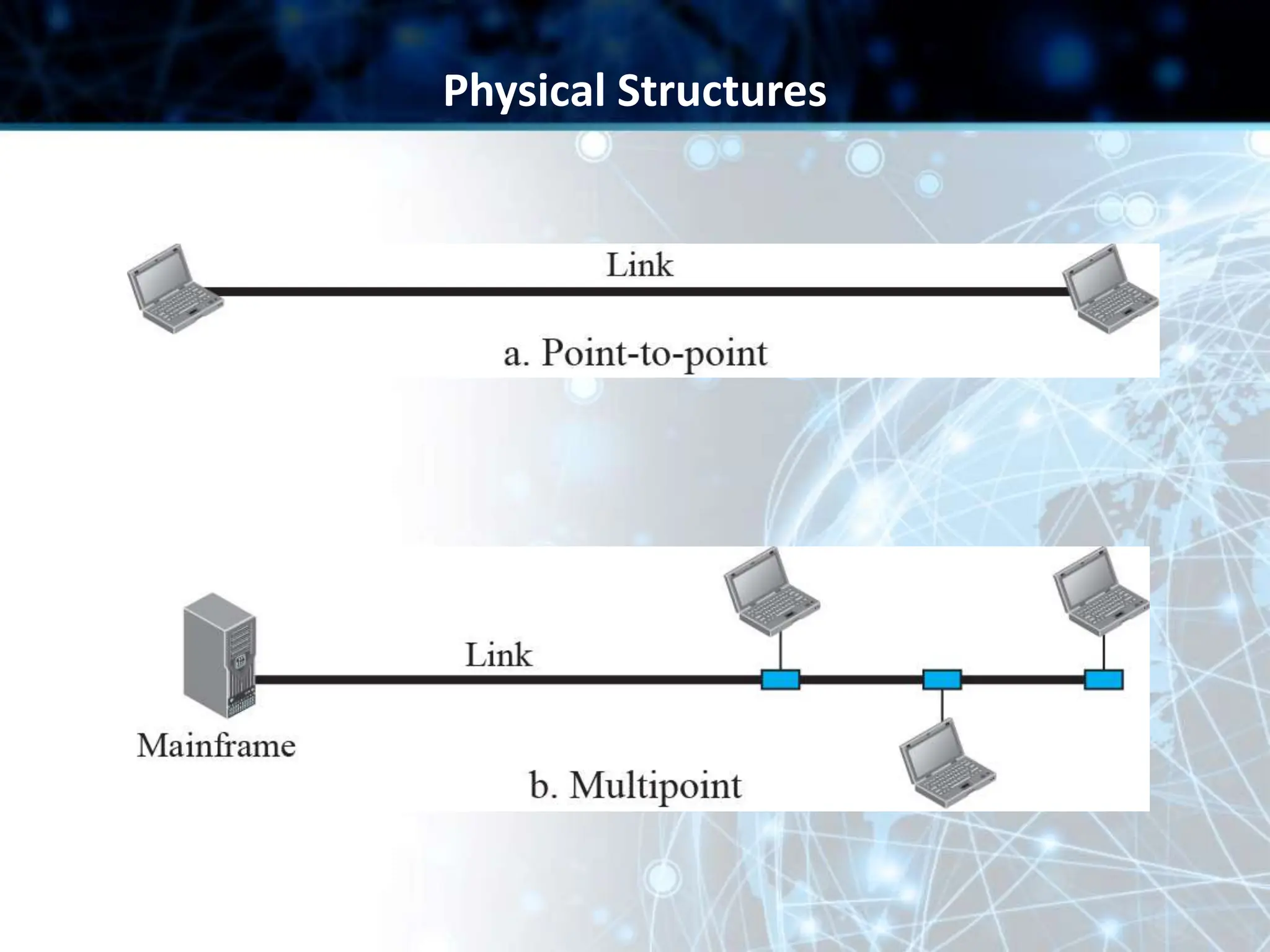
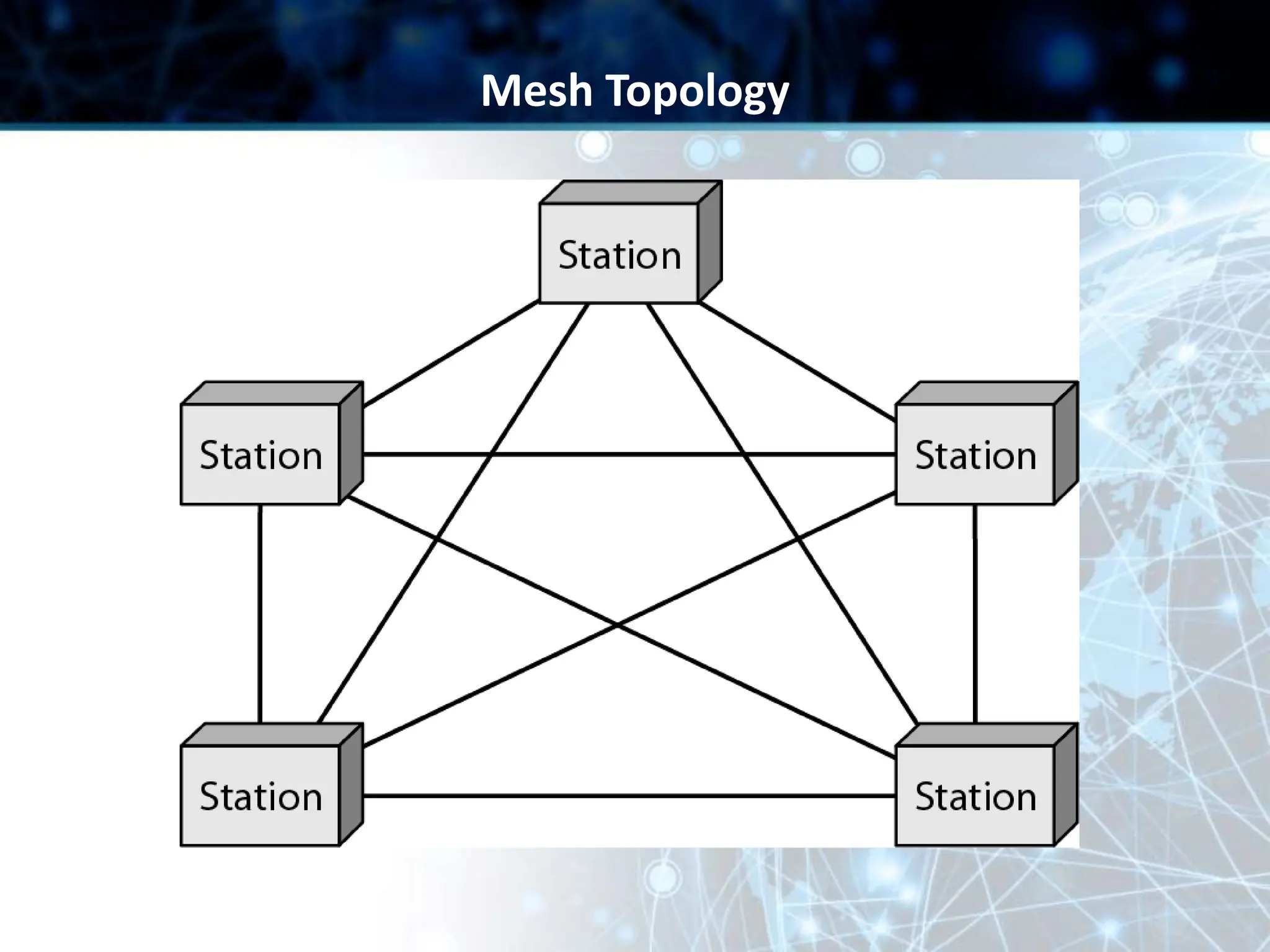
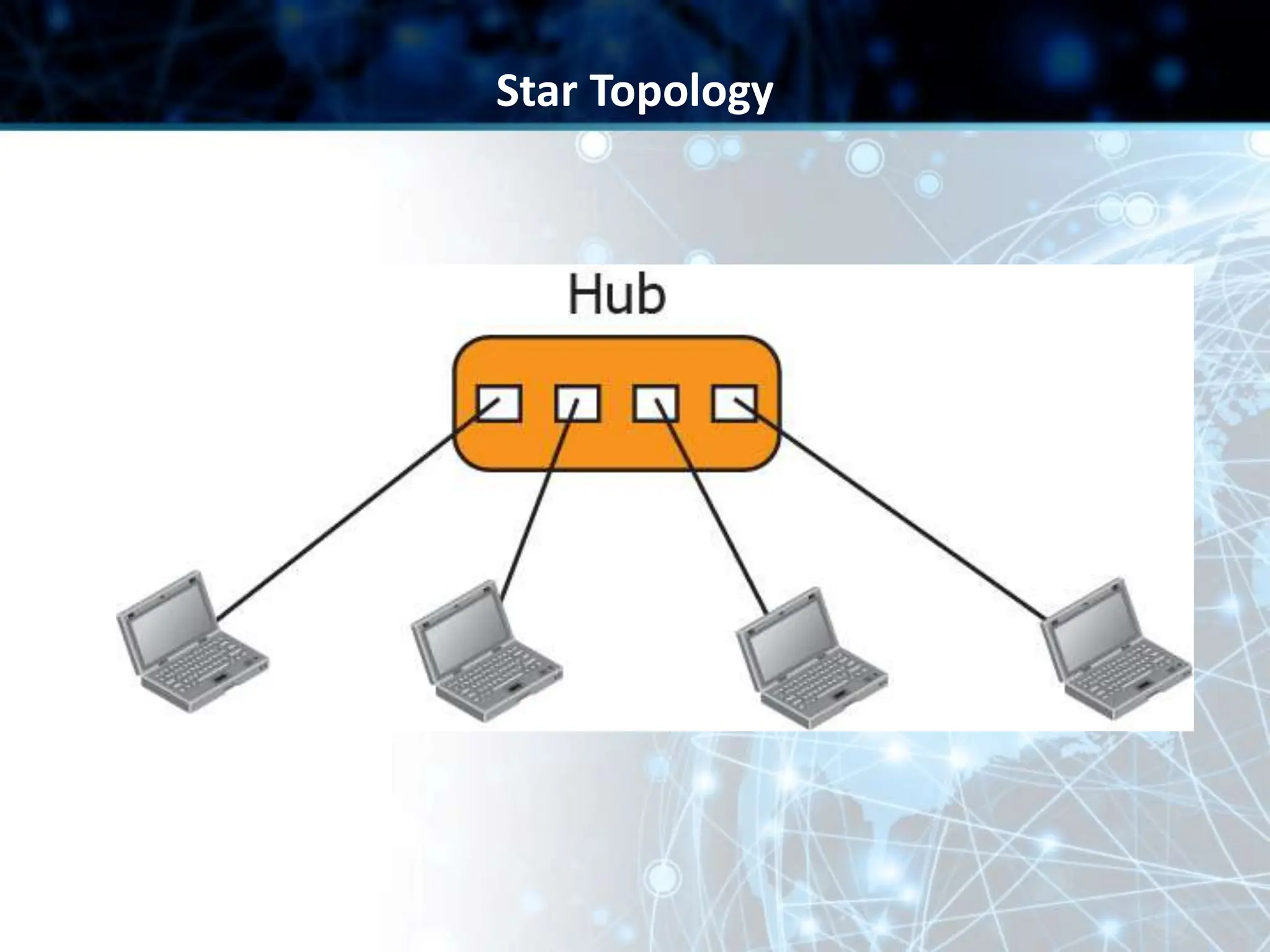
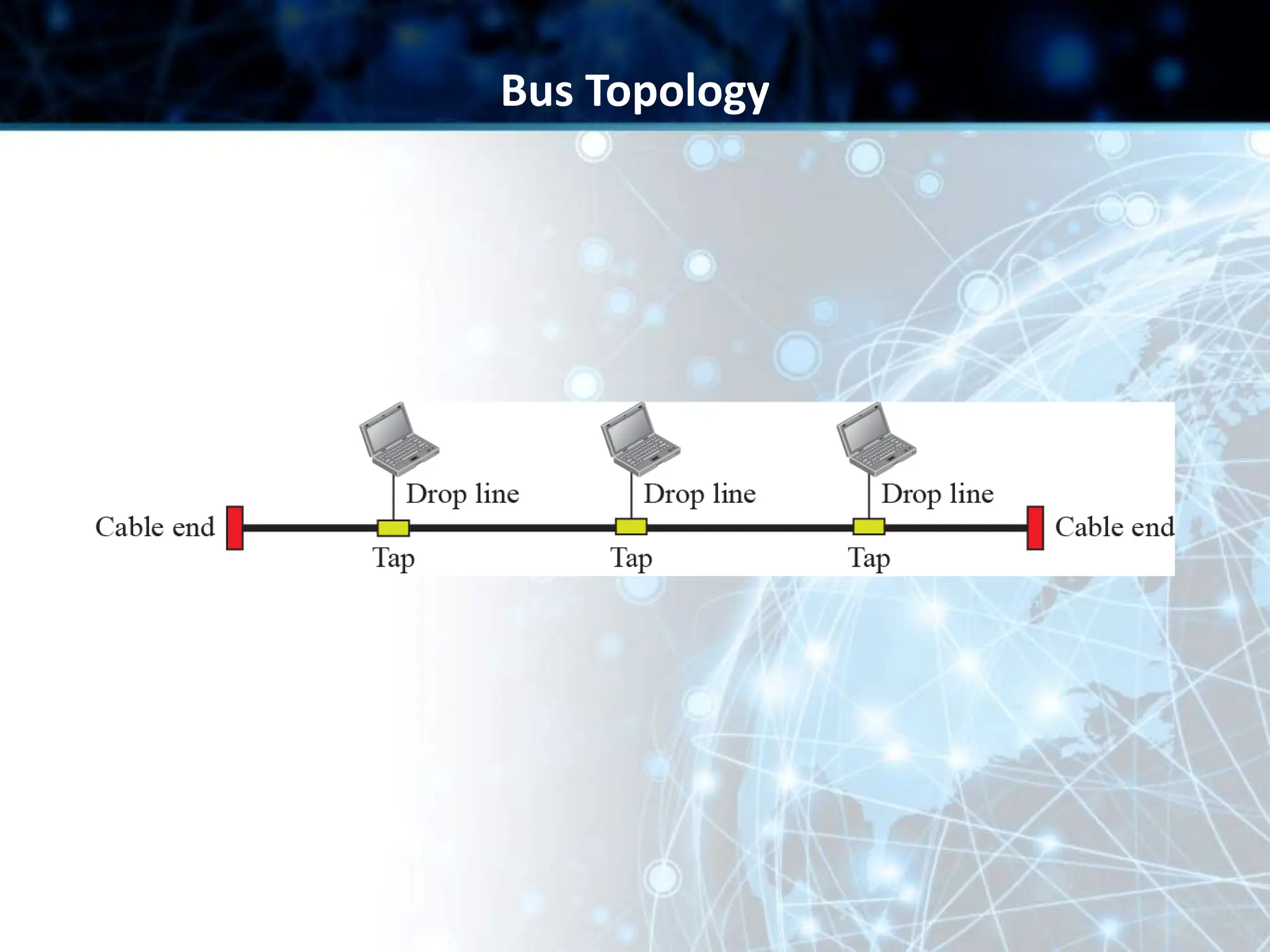
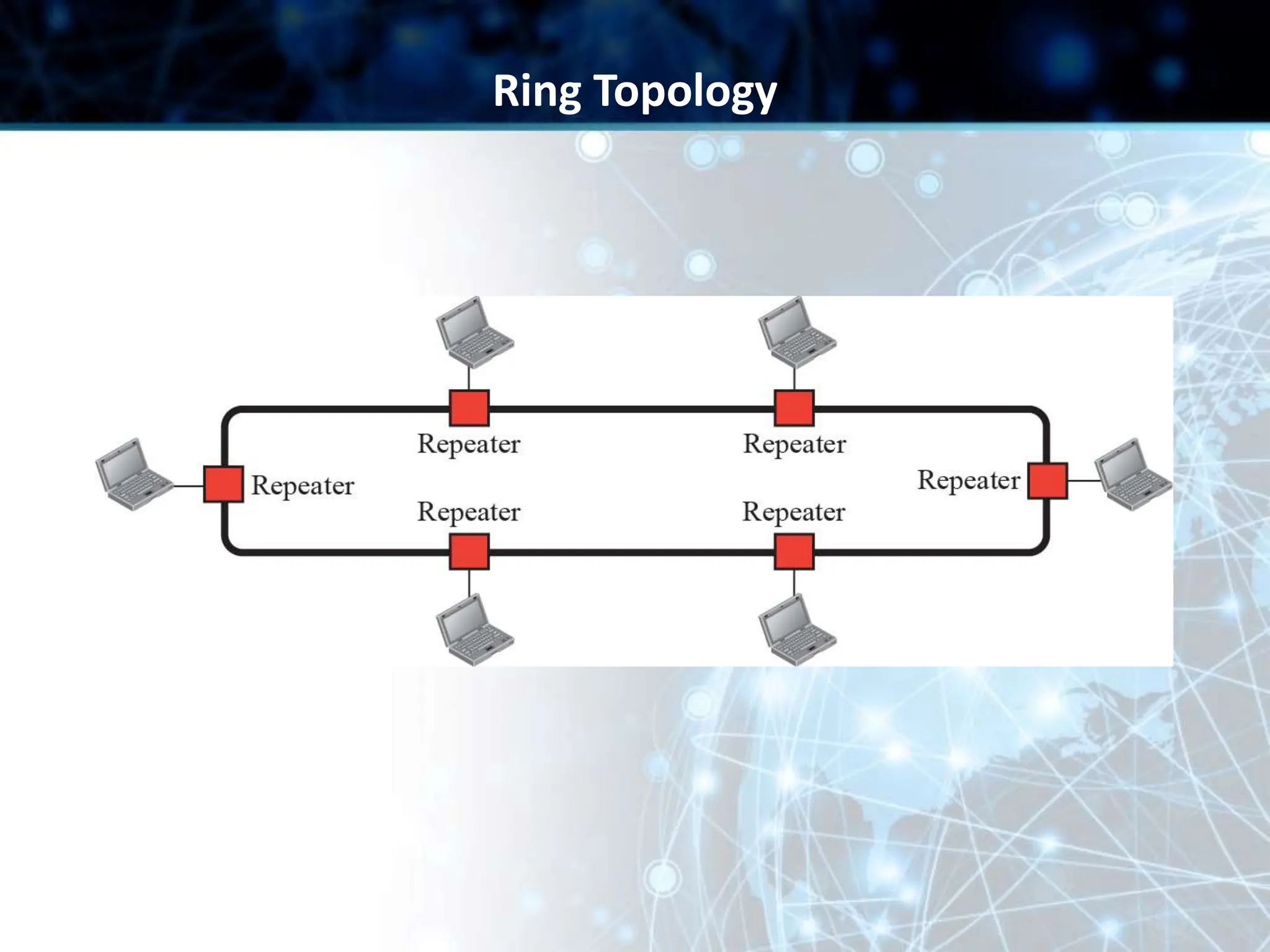
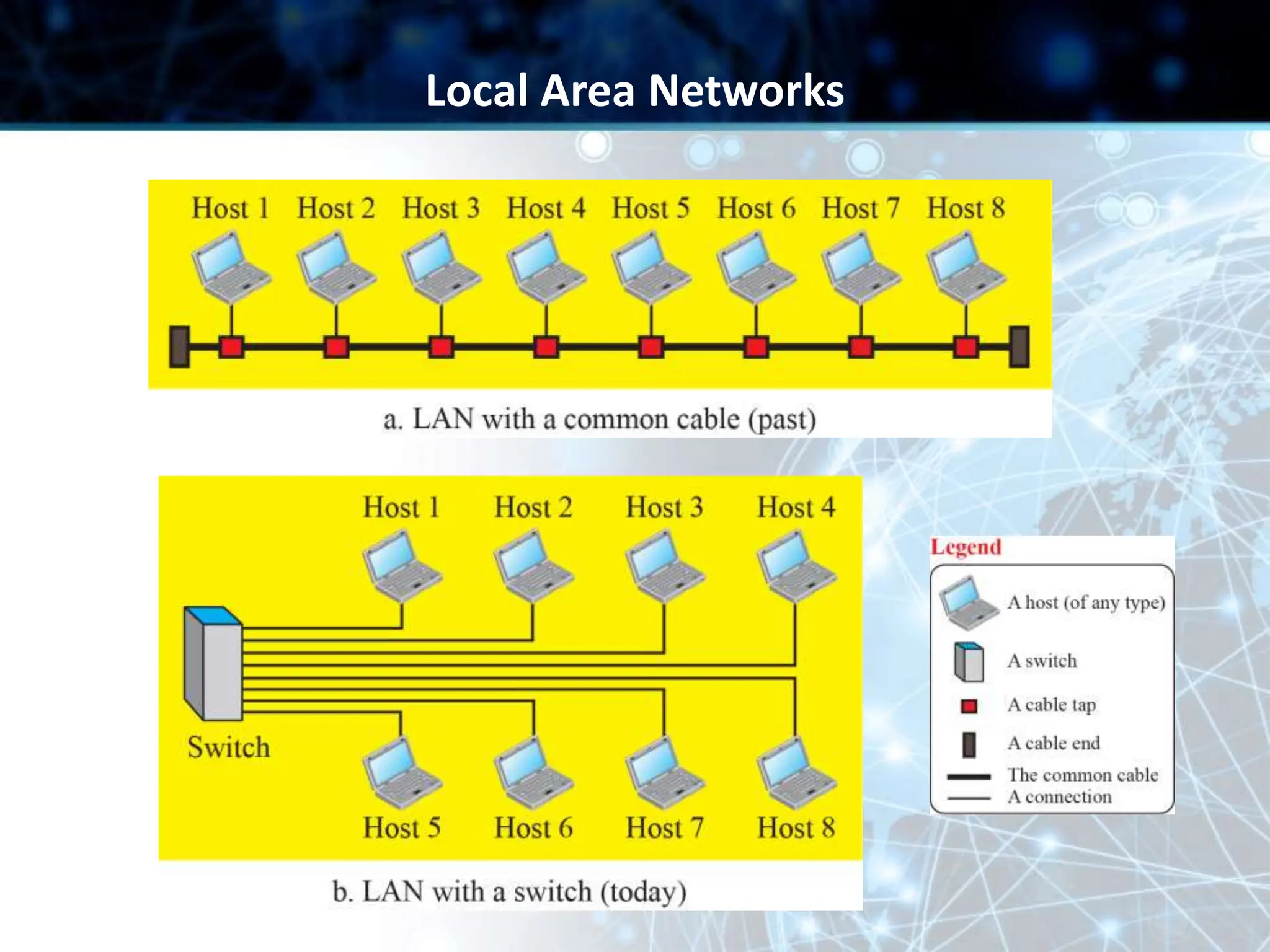
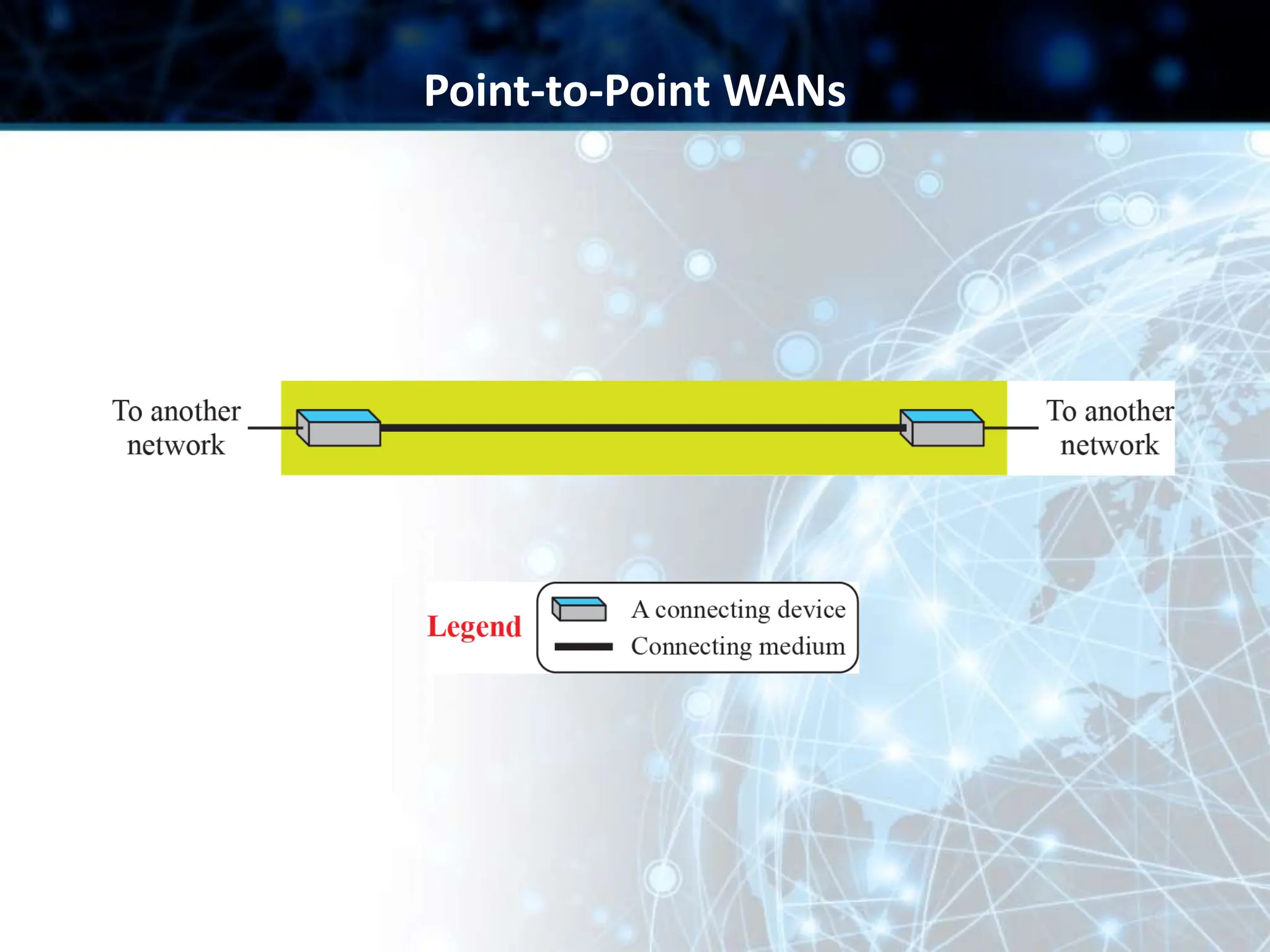
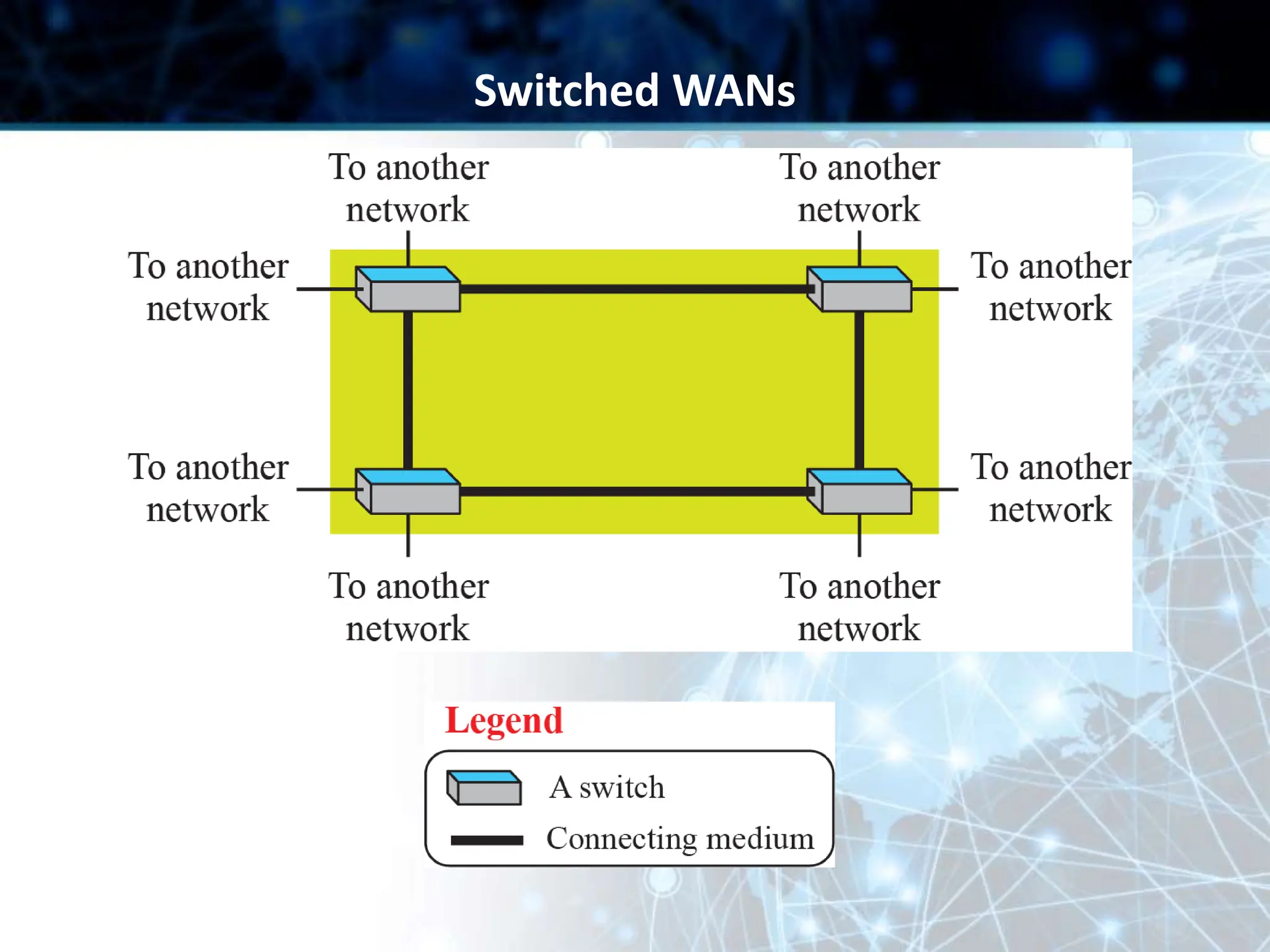
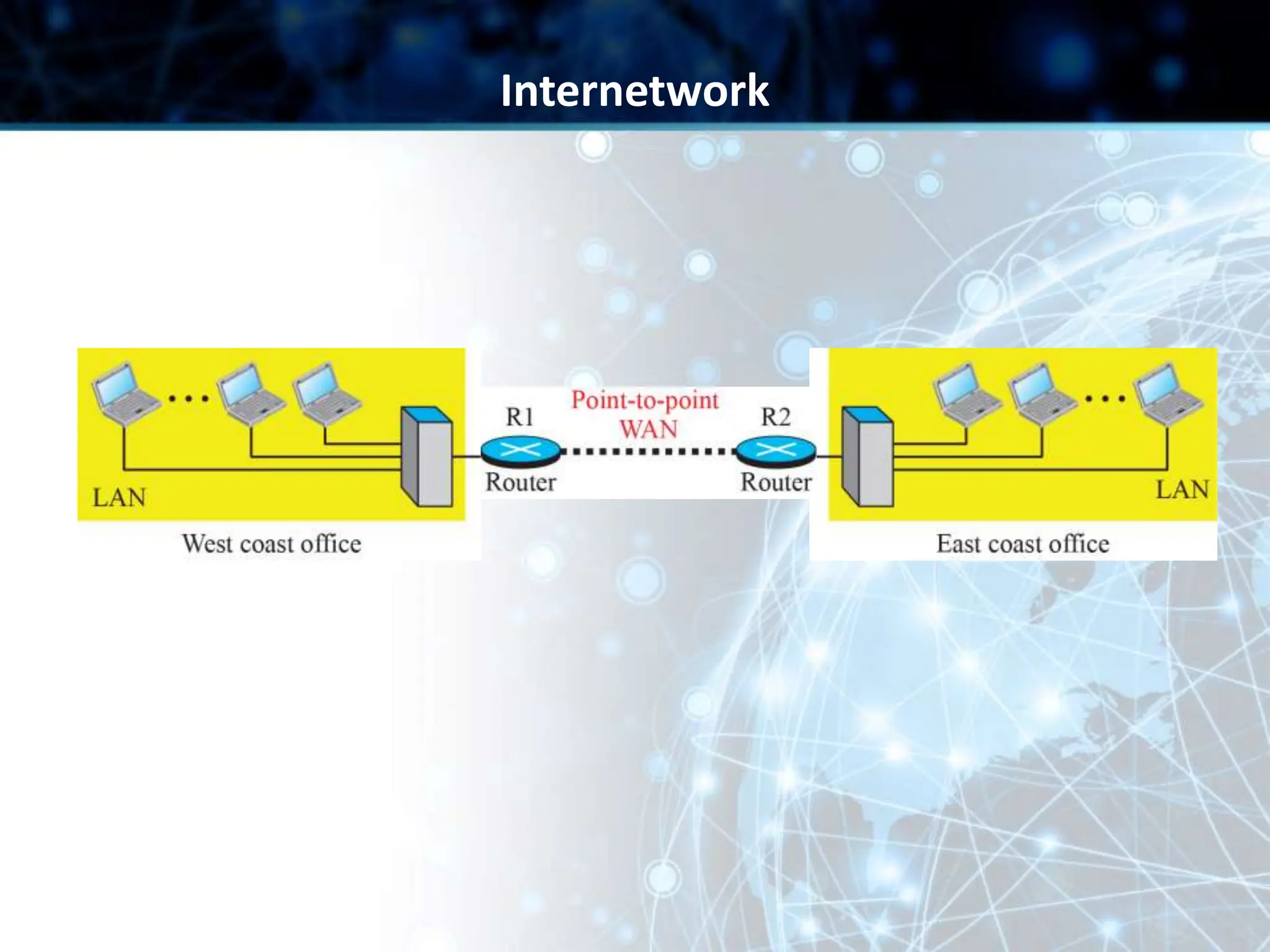
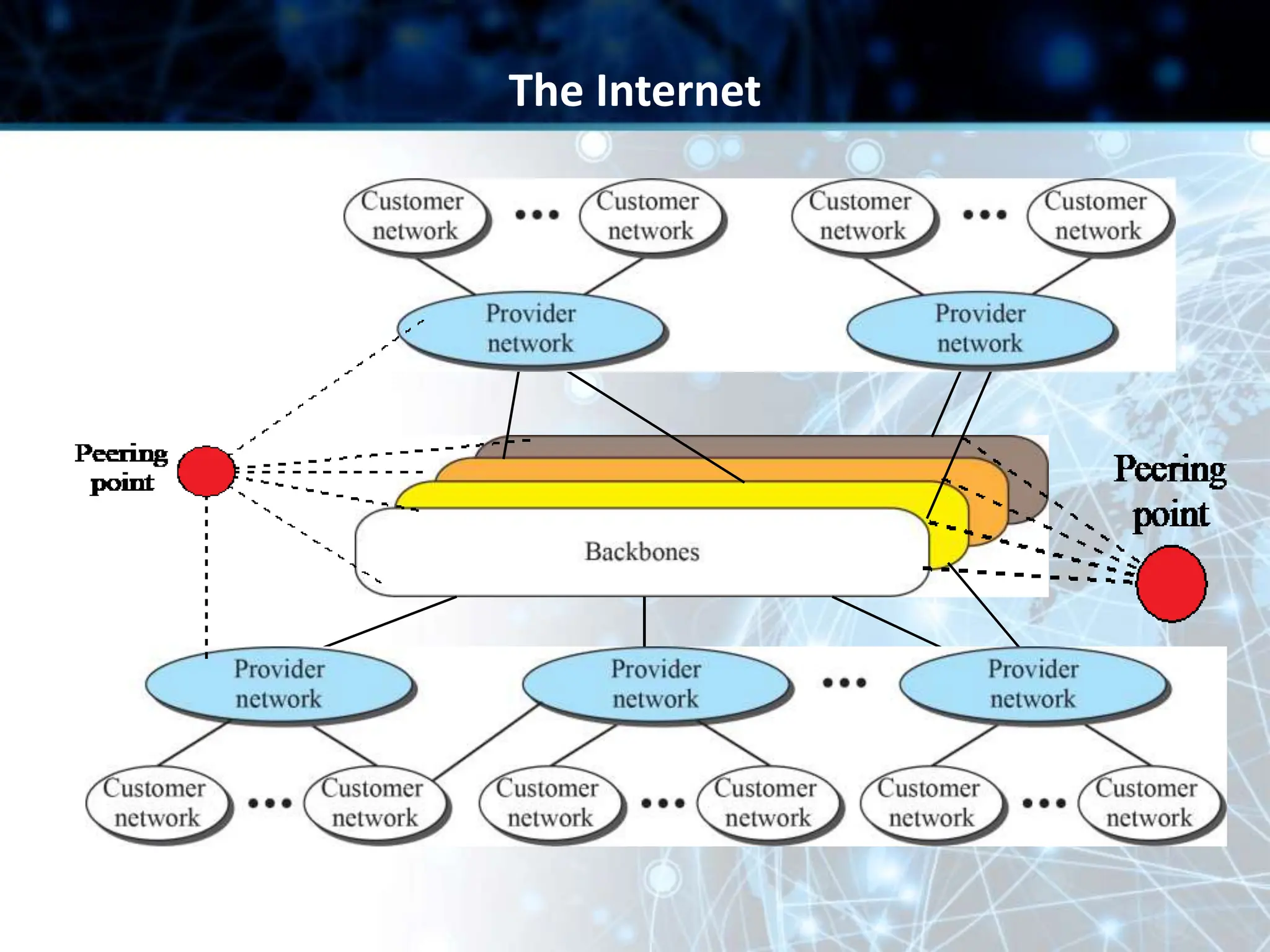
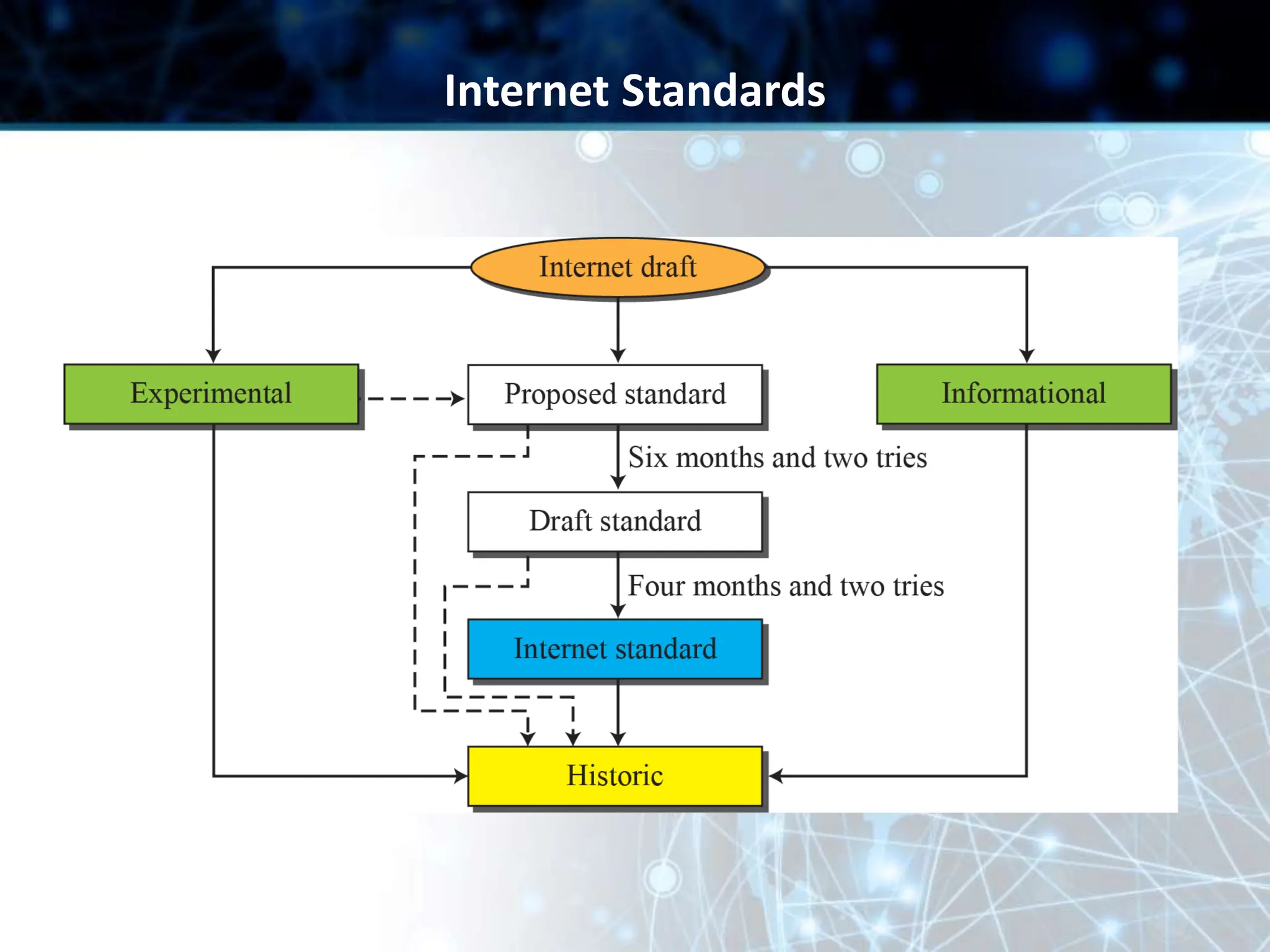
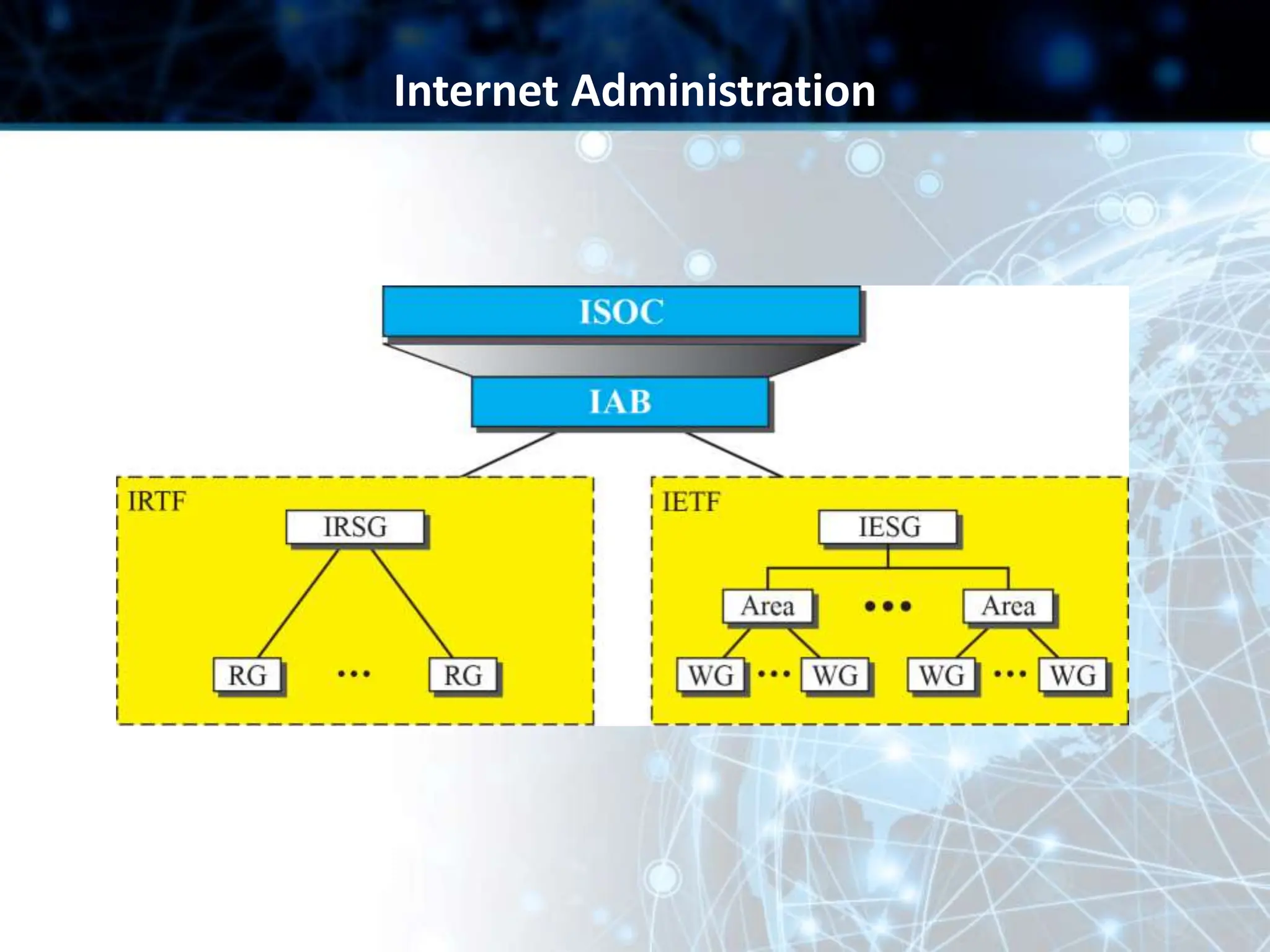
This document provides an overview of data communication and computer networks. It discusses key topics such as the components of a data communication system including transmission media, hardware, software, connection structures, and network topologies. The document also examines different types of networks including local area networks (LANs) that connect devices within an office and wide area networks (WANs) that span a wider geographical area. Additionally, it provides a brief history of the Internet and how it has evolved from early networks like ARPANET to the large-scale system it is today.