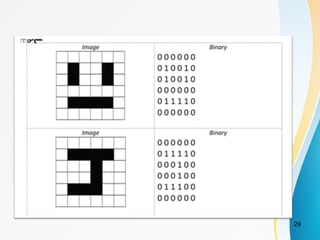
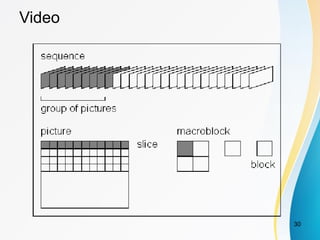
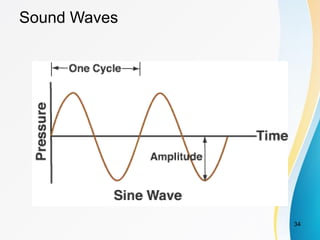
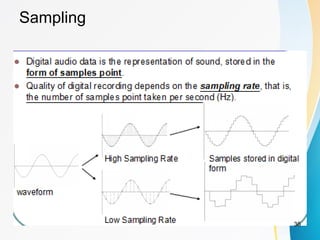
This document discusses key concepts related to data communication and networks. It covers topics such as signal propagation, analog and digital signals, bandwidth, encoding, standards organizations, and multimedia. Specifically, it provides 3 key points:
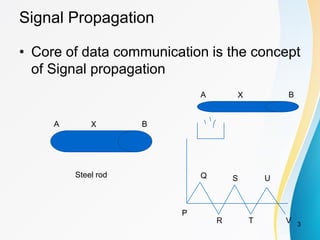
1. Signal propagation refers to how a signal such as heat, voltage, or current is transferred through a conducting medium like a steel rod or wire from one end to the other over time. This establishes the basic principle by which data is communicated through networks.
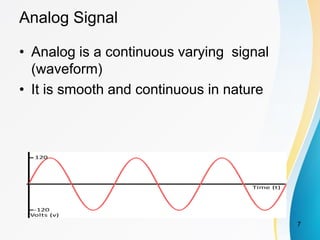
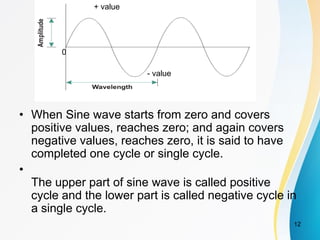
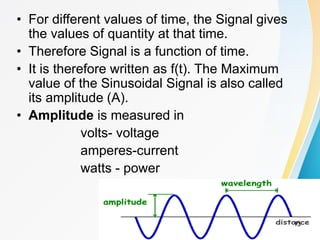
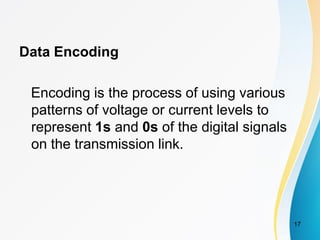
2. Analog signals are continuous varying waveforms, while digital signals represent information as discrete pulses that can only take on binary values of 1 or 0. Encoding is the process of converting data into digital signals for transmission.
3. Mult