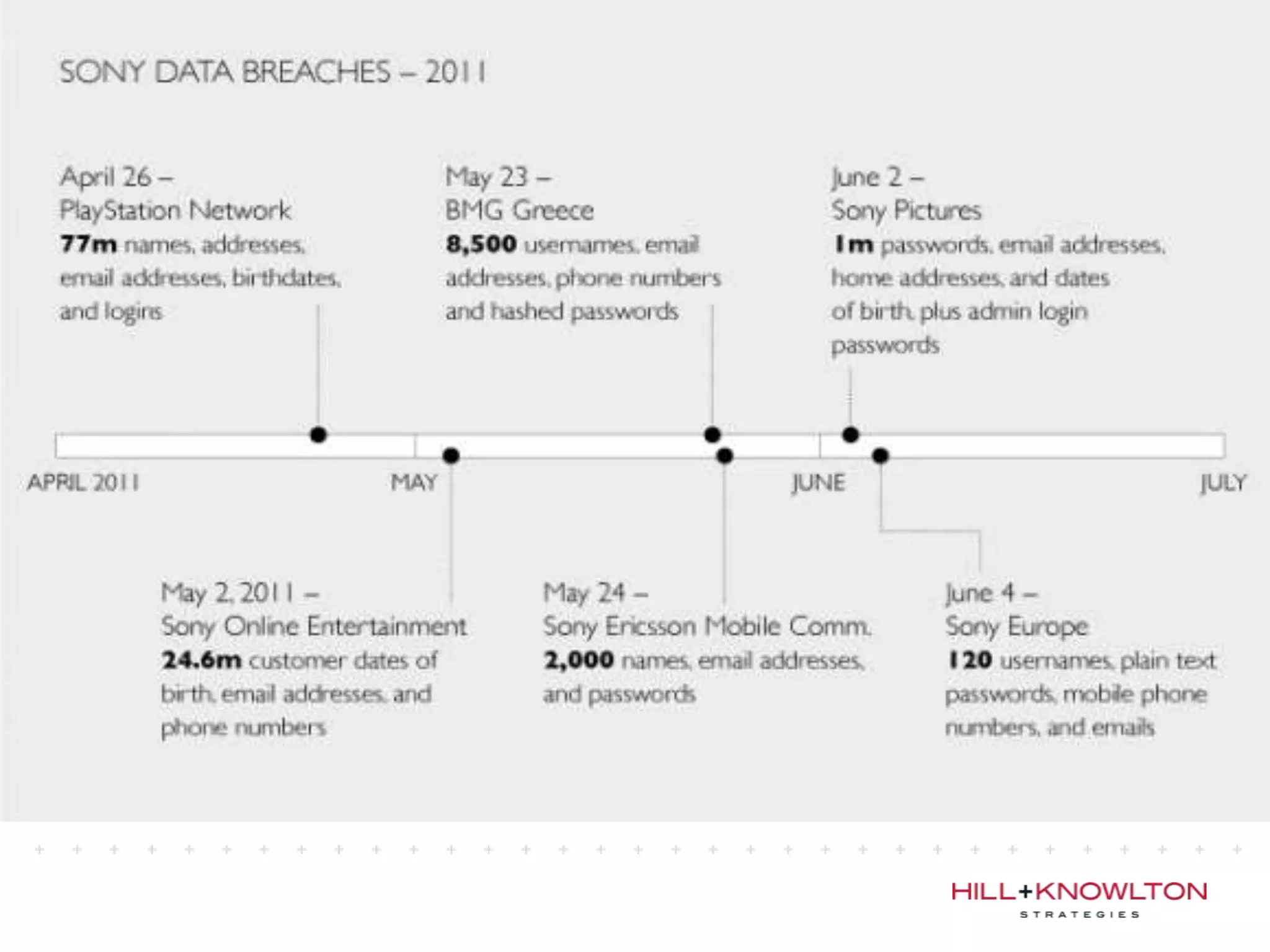
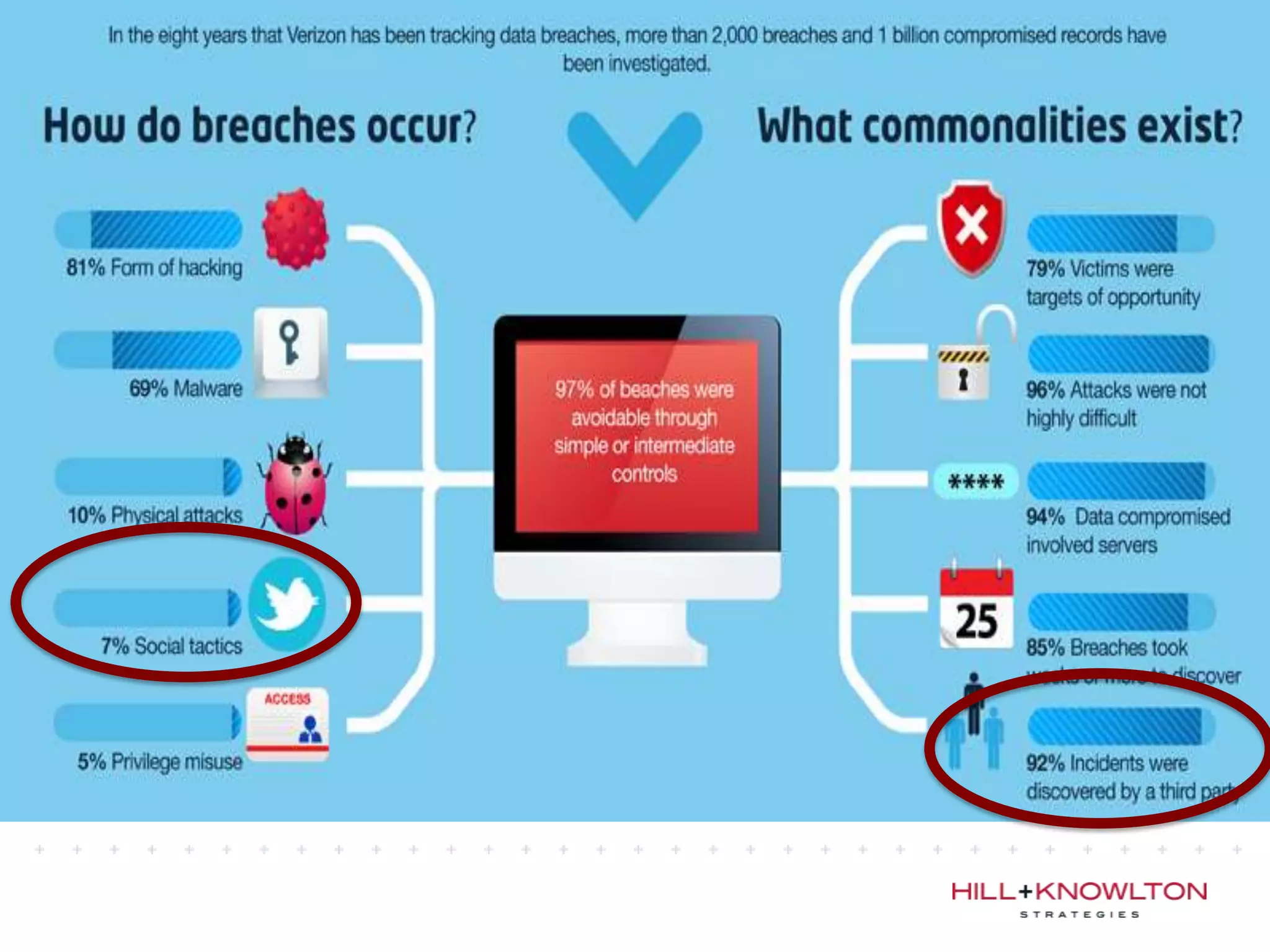
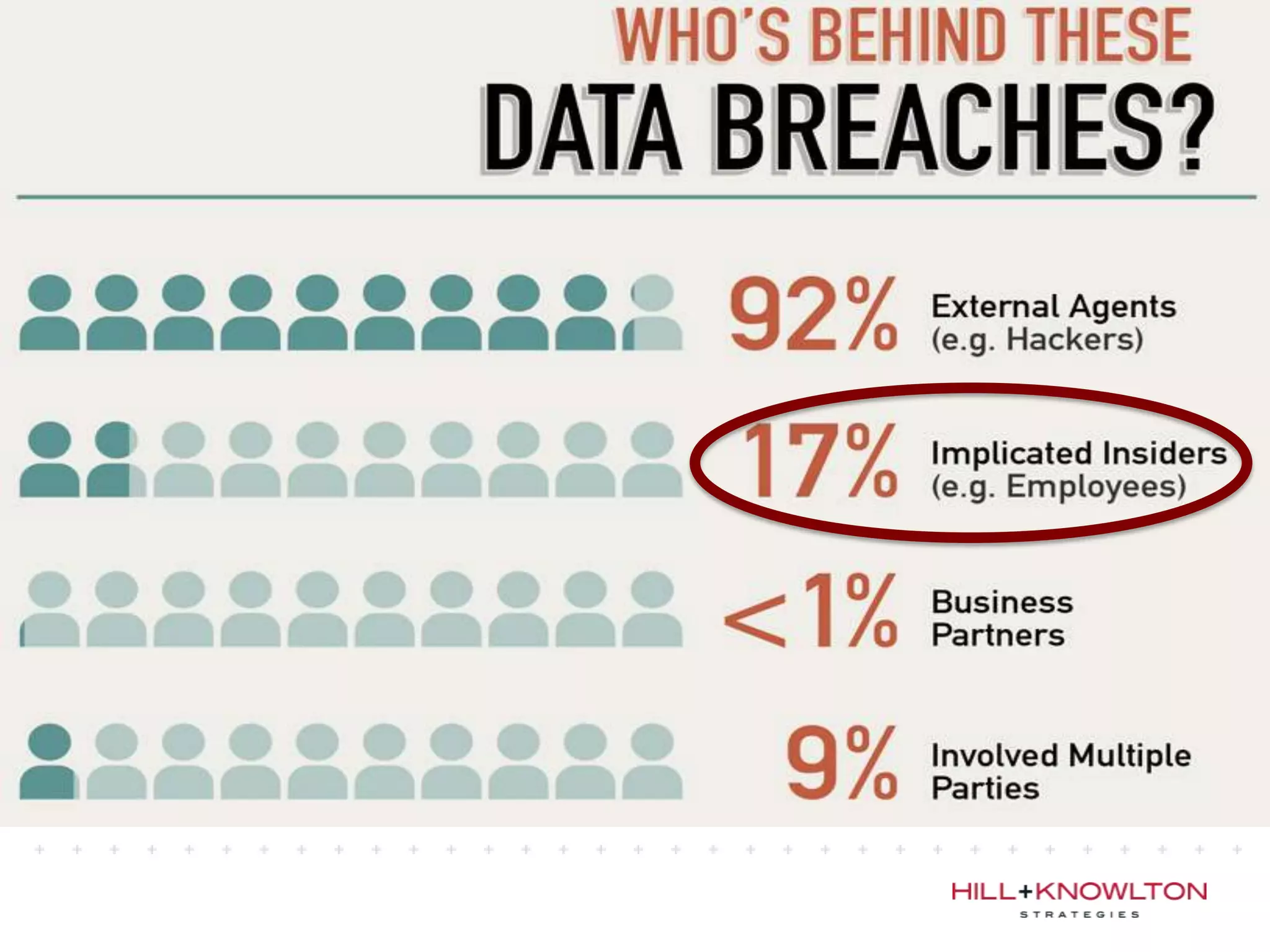
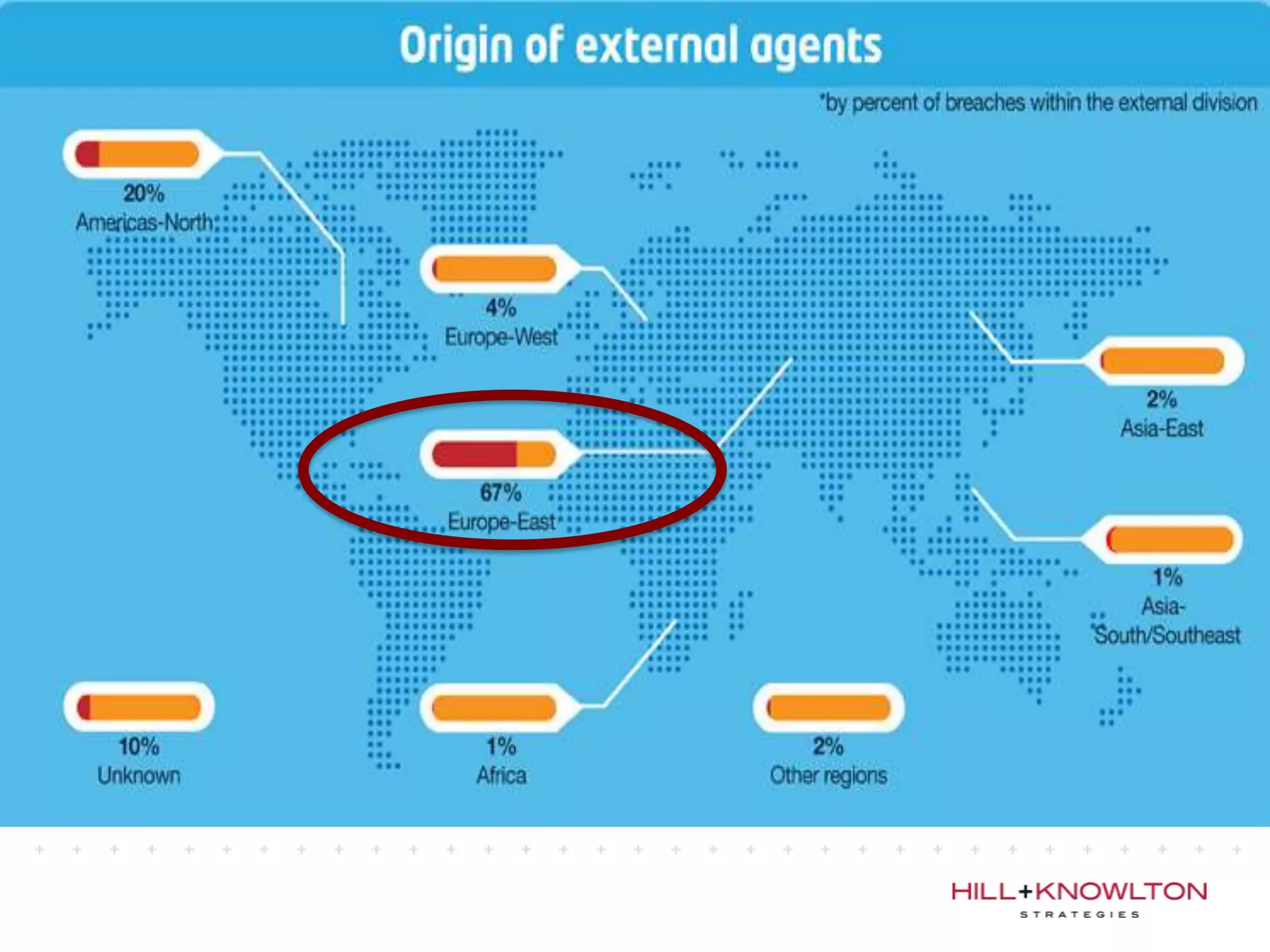
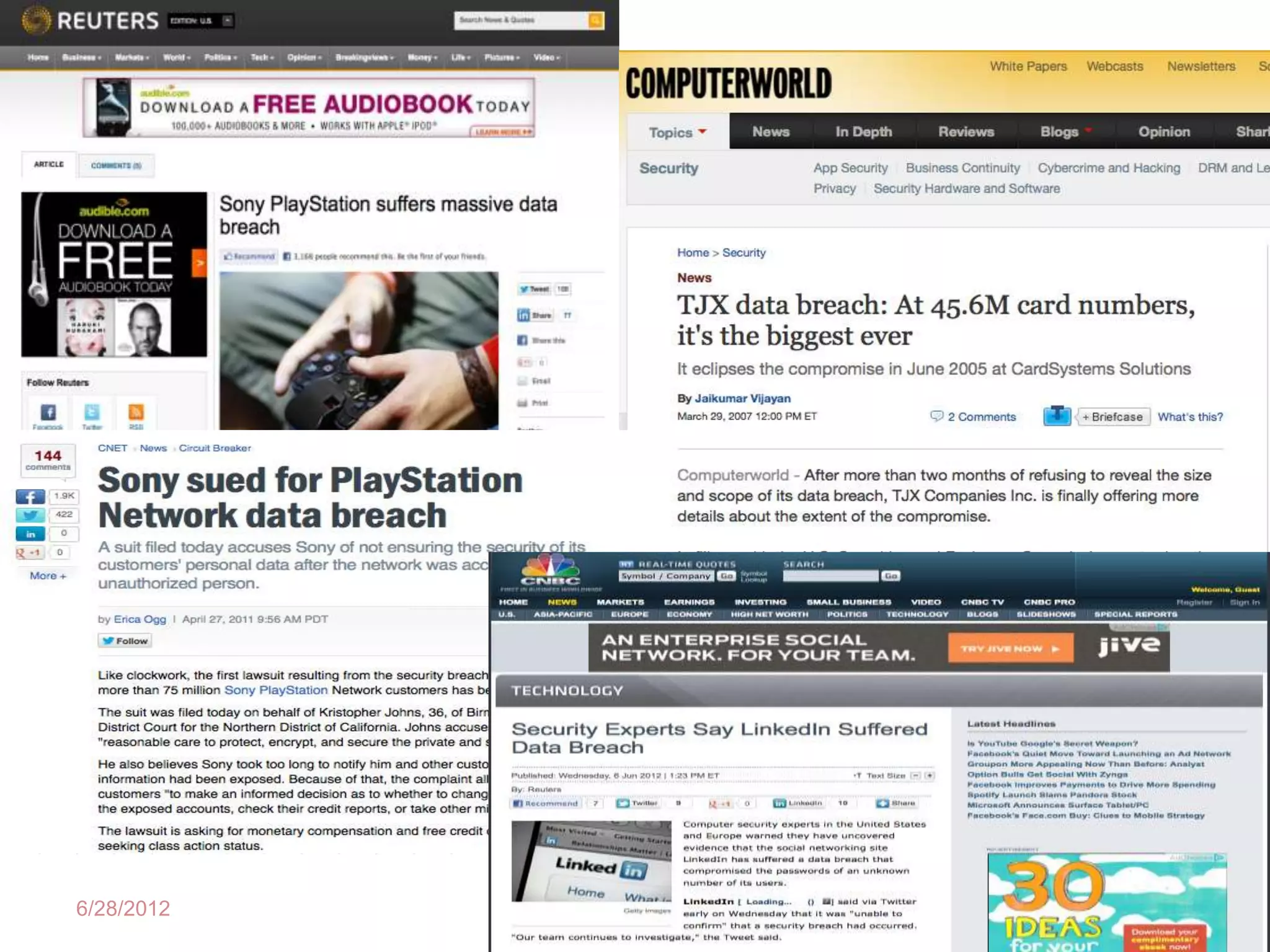
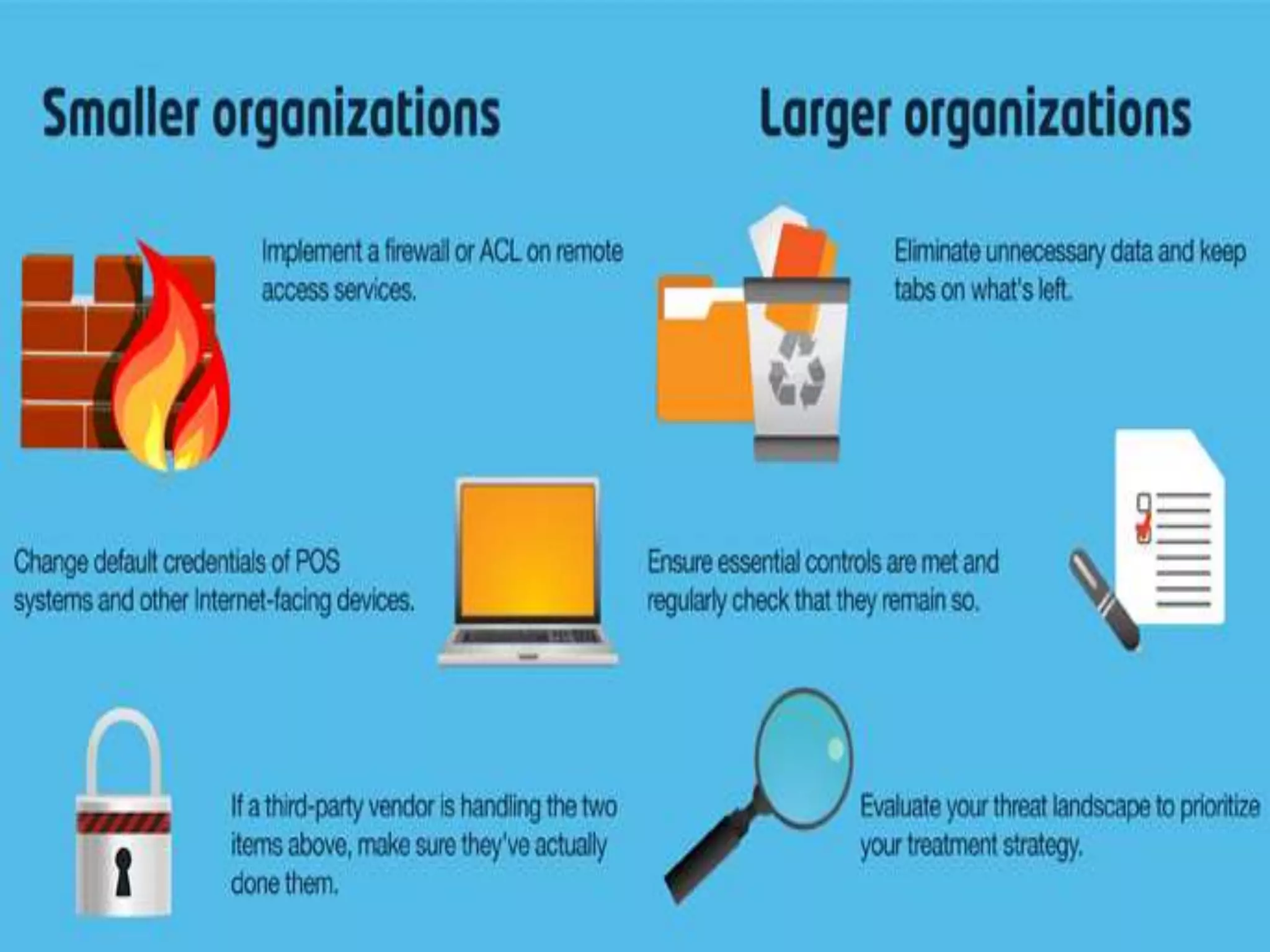
Social media and data breaches are intrinsically linked, as any significant event now will involve public participation online. When data breaches occur, organizations must communicate on social media in a timely, transparent manner to inform affected users and address questions with humility. An 11-point plan outlines best practices for multi-platform social media communication during a data breach, including driving internal notification, being transparent about impacts, coordinating protocols, engaging with online discussions, and committing to security improvements.














![25
“[Brands suffering data leaks] should email people, post on Twitter,
Facebook and address their customers where they are - you shouldn‟t
have to let people do a Google search or find out through word of
mouth.”
• Alys Woodward, research director at market intelligence firm IDC
Europe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wcdmcrisispresentationfinal-120628113651-phpapp02/75/Data-Breaches-and-the-Social-Web-25-2048.jpg)



