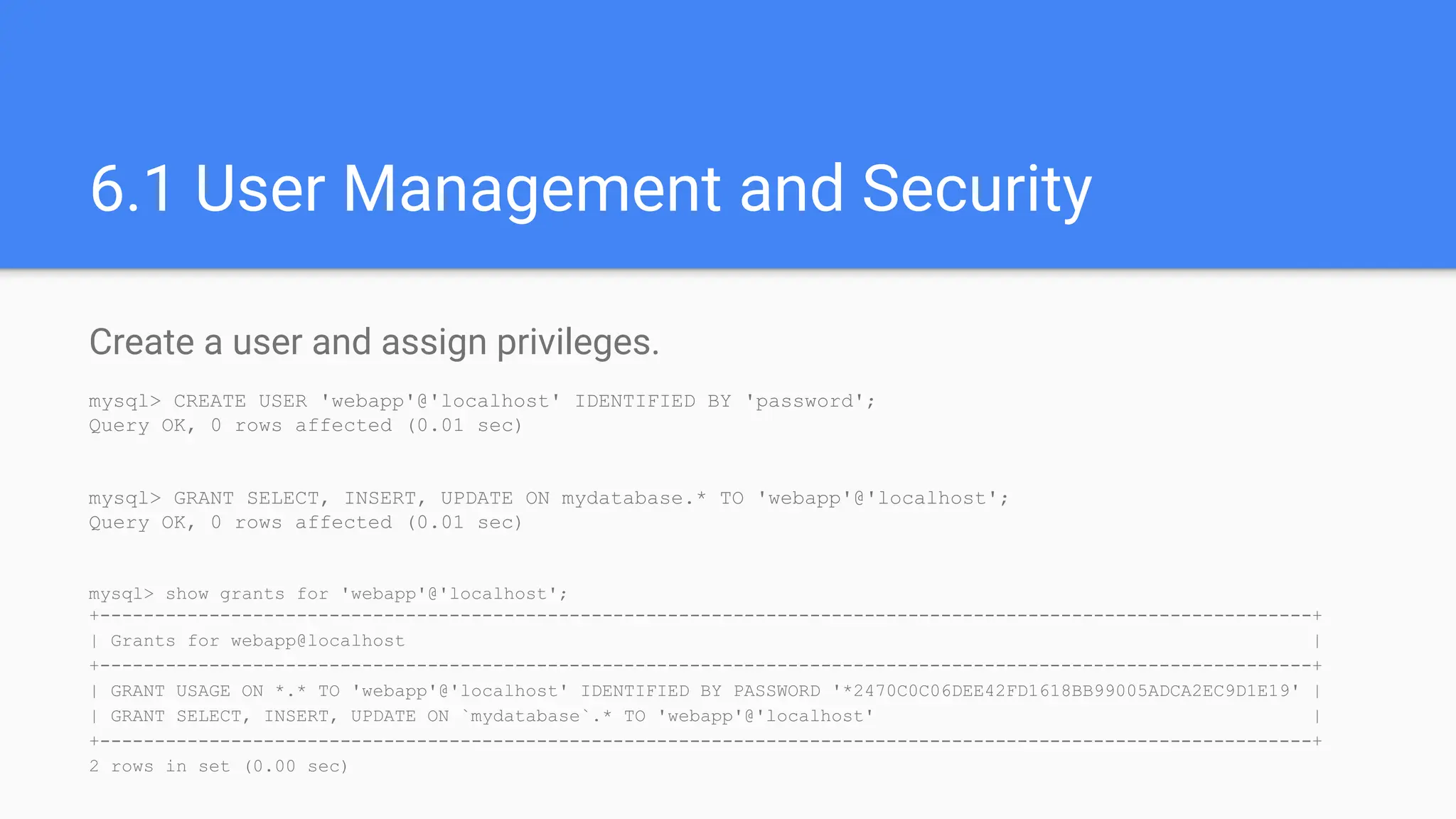
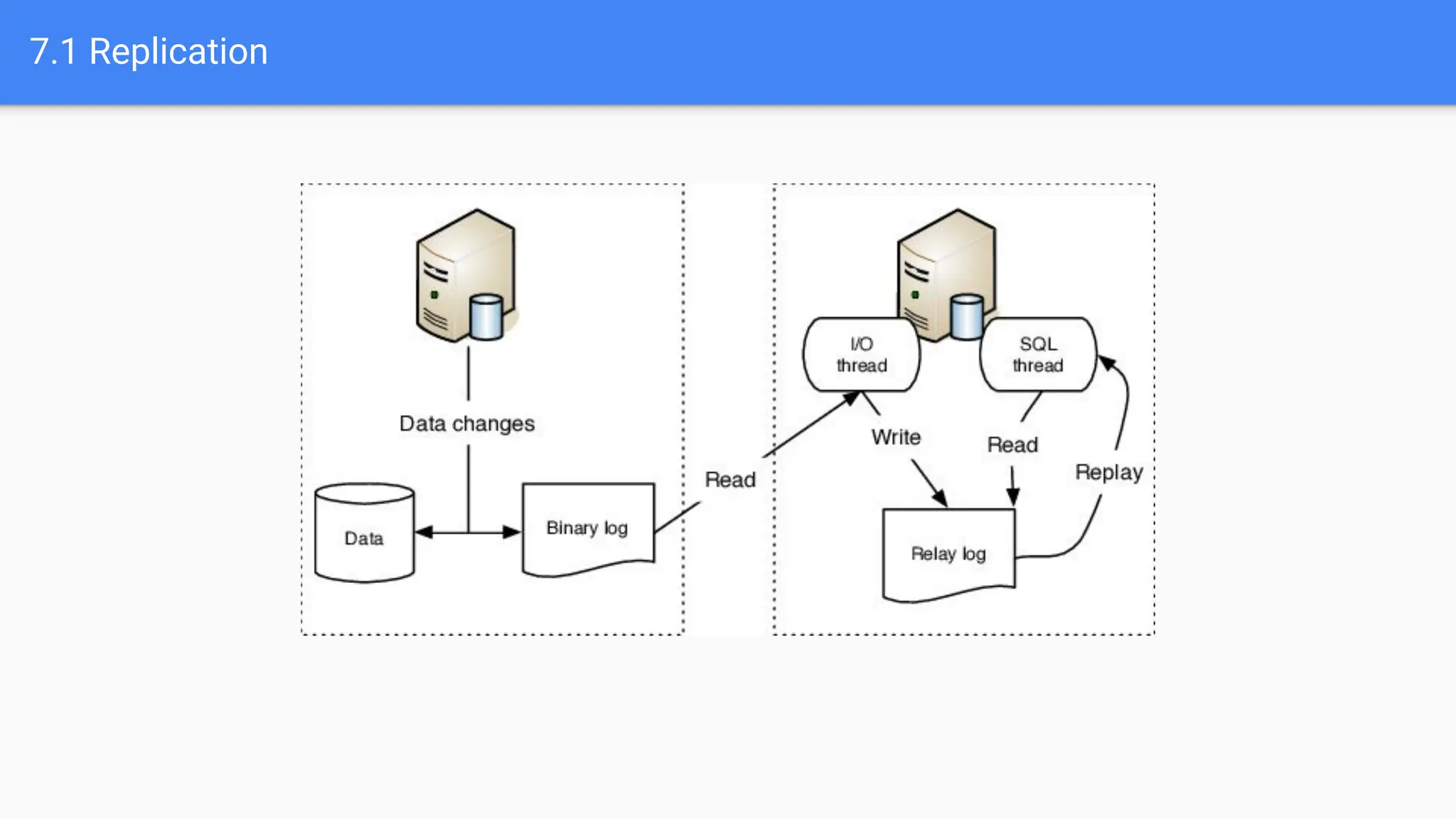
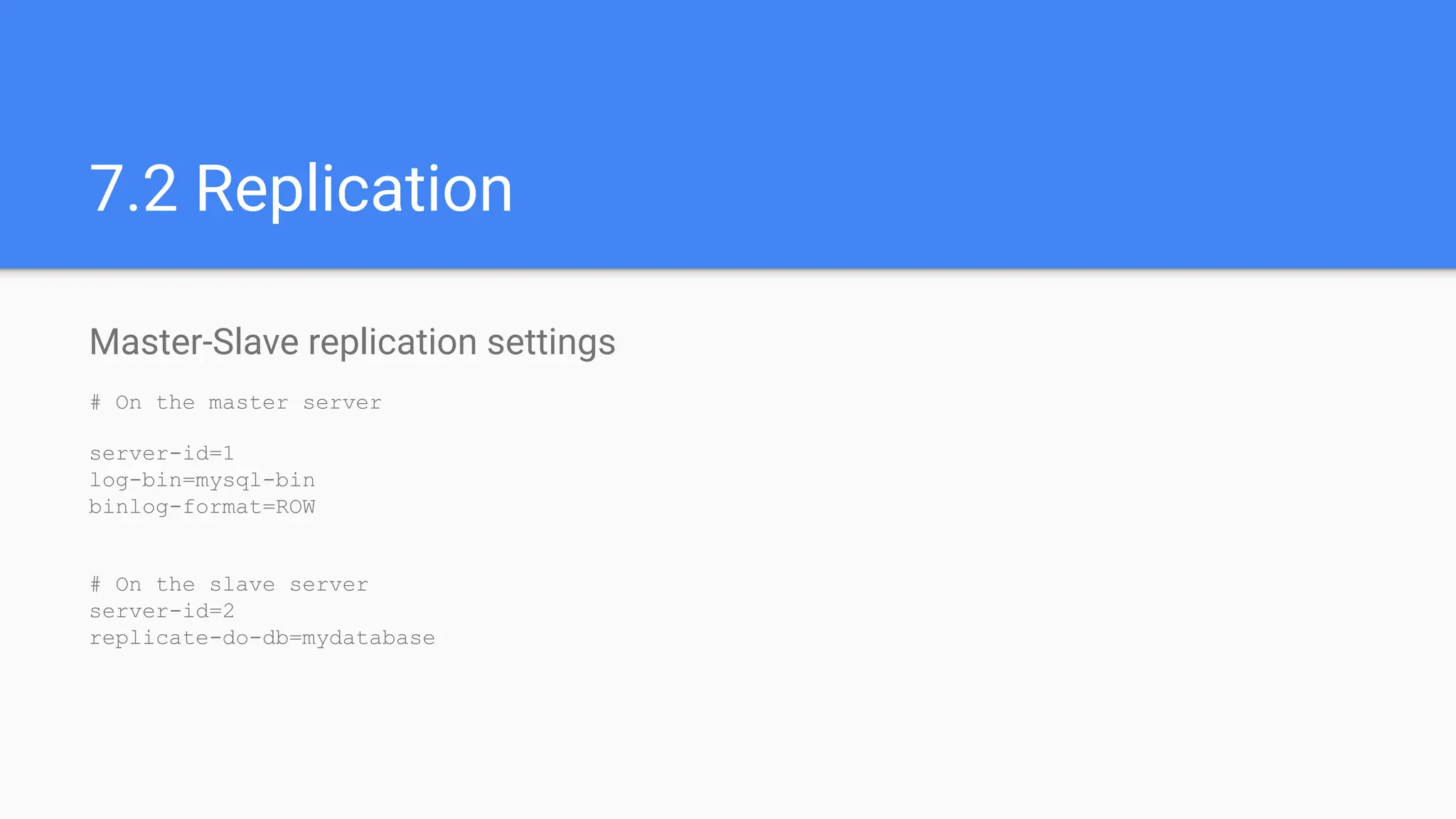
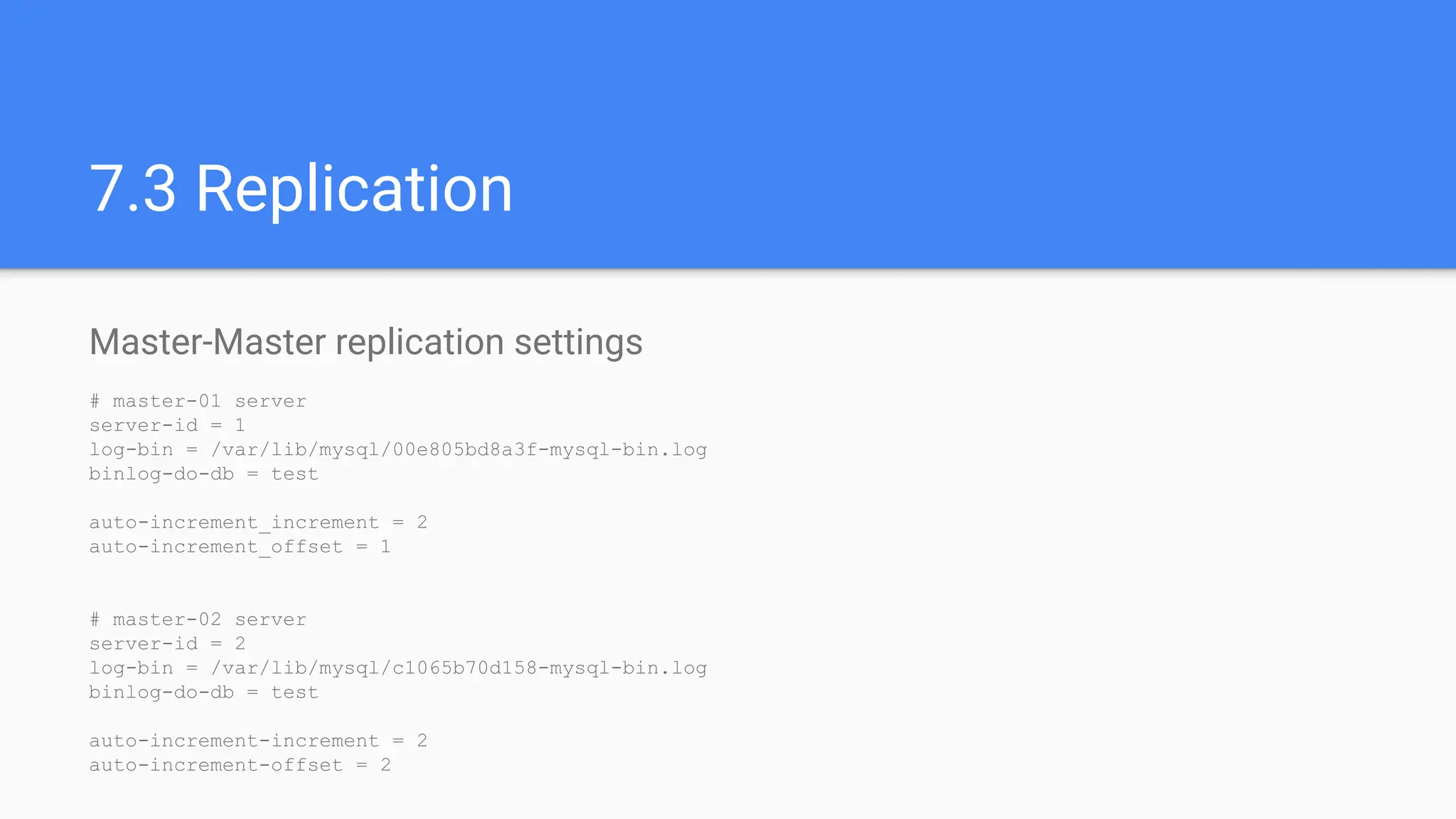
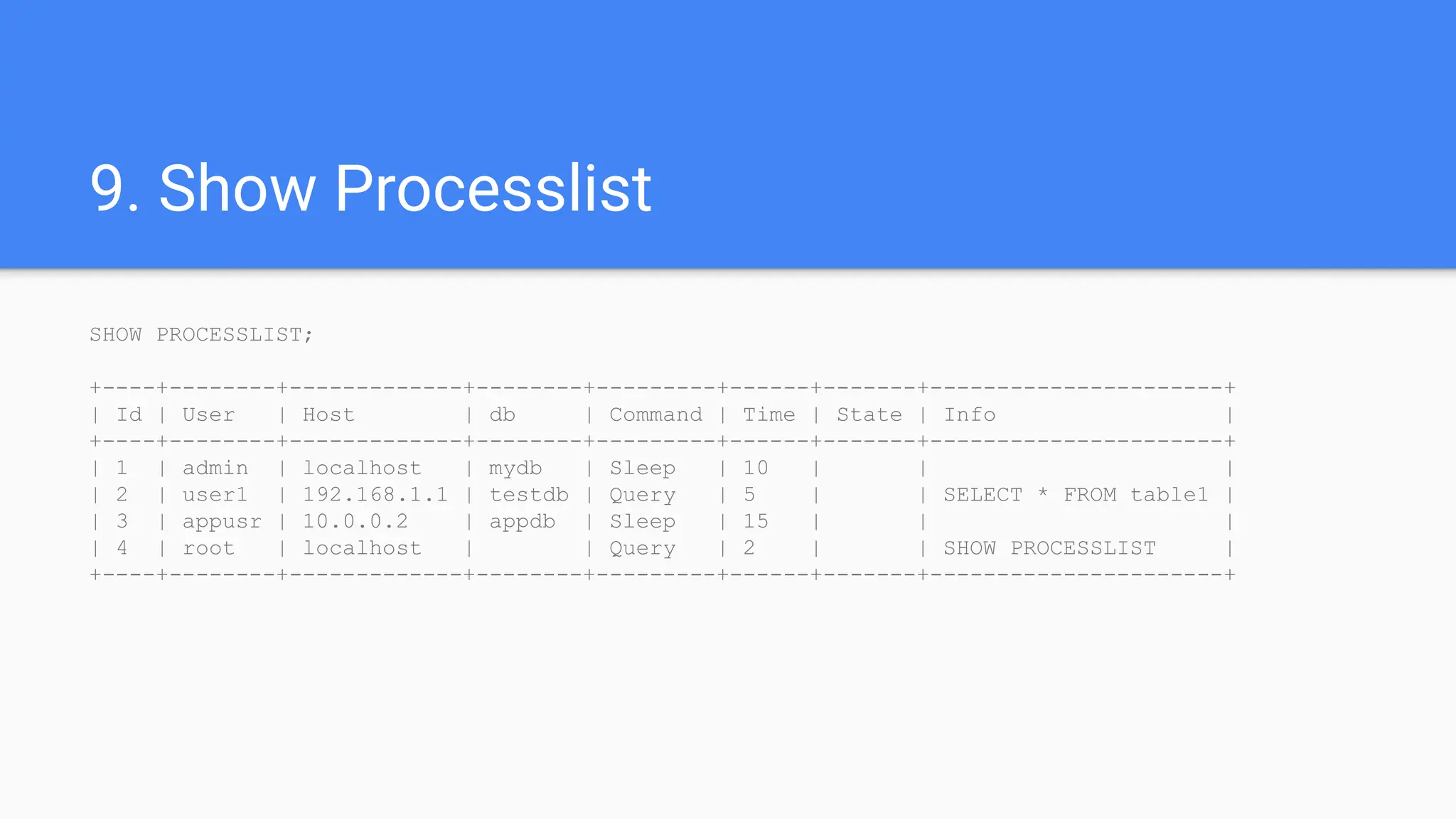
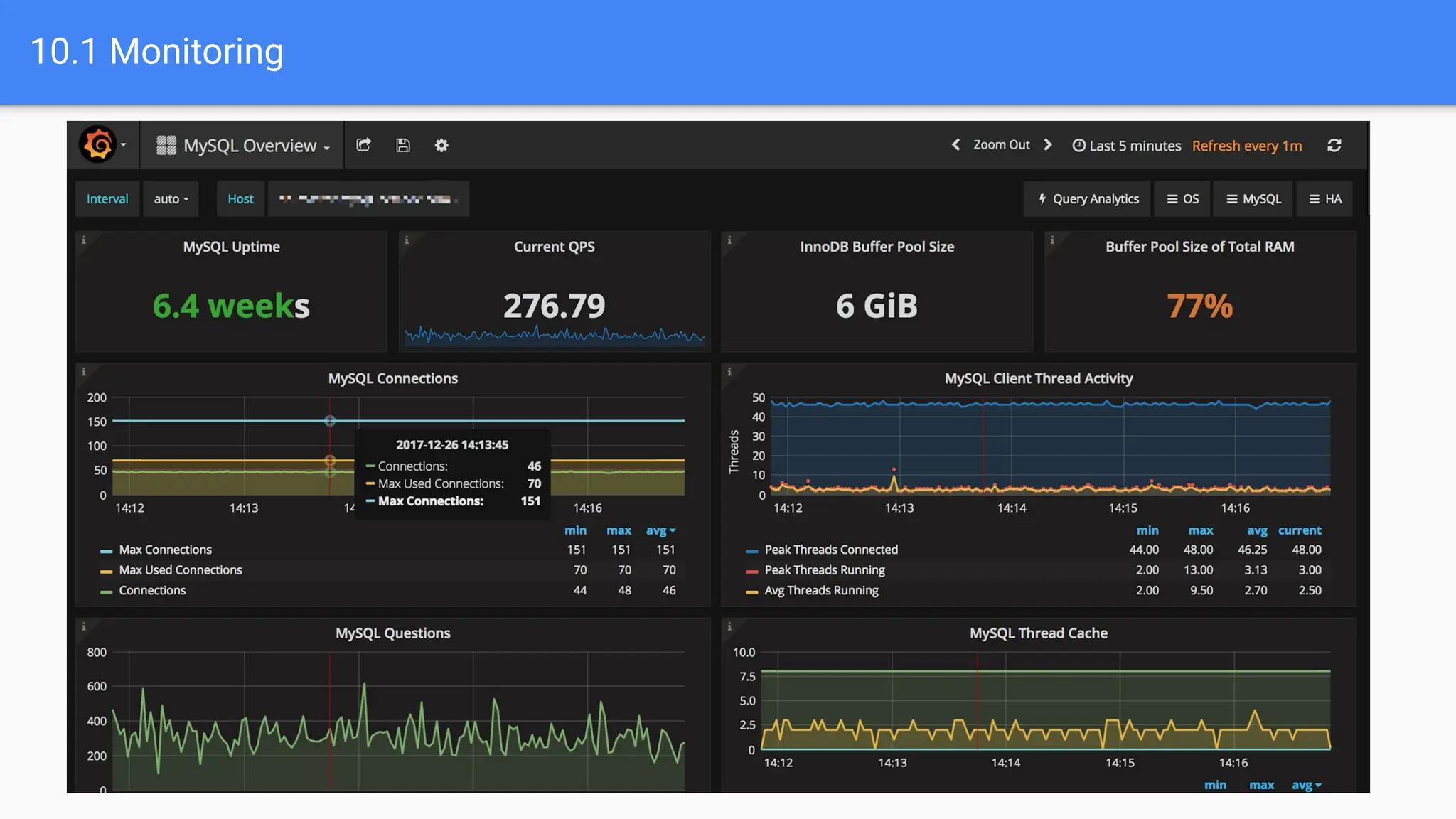
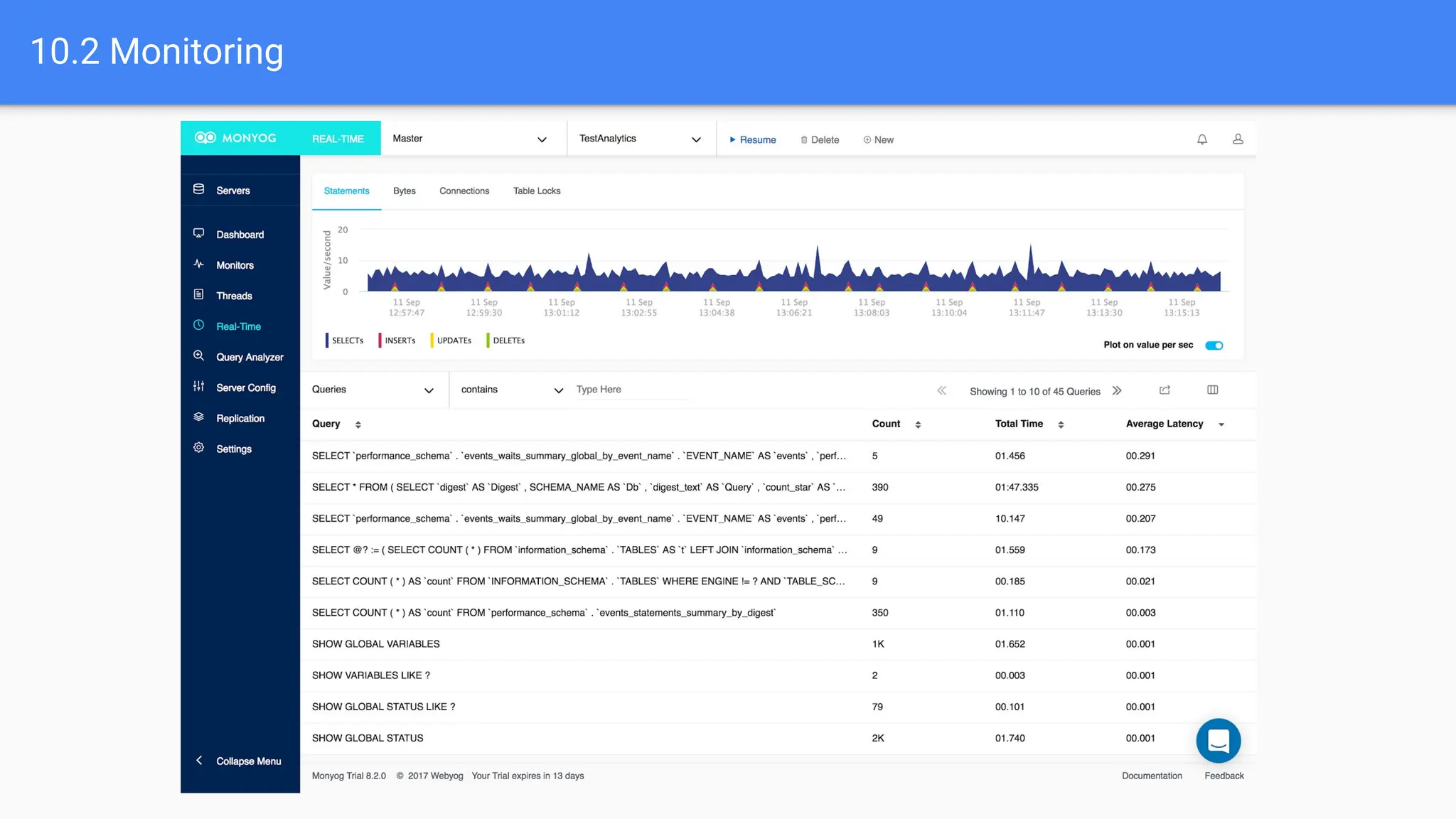
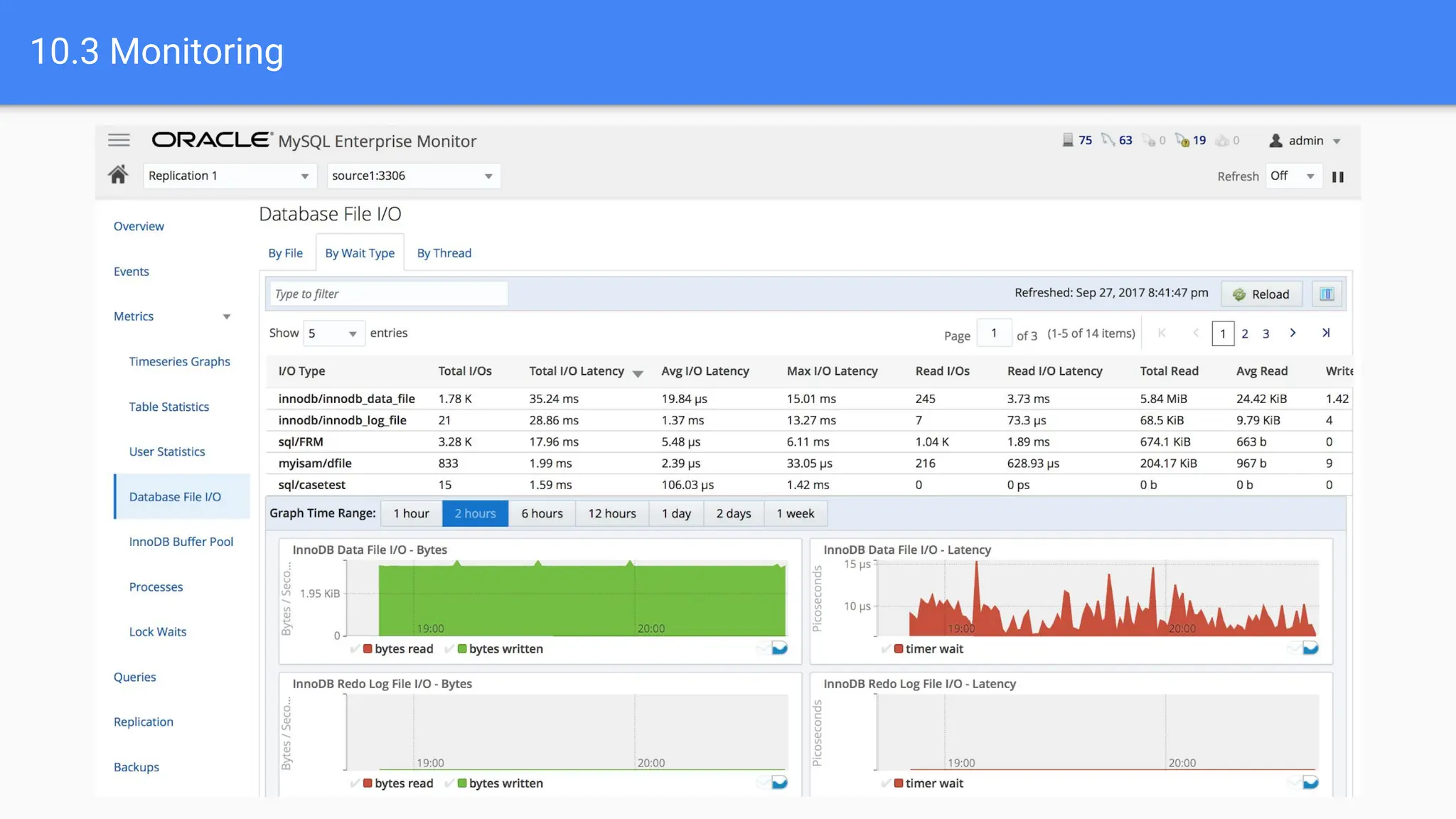
The document outlines advanced MySQL training topics including database optimization, stored procedures, triggers, user management, replication, and backup strategies. It provides detailed explanations and examples of performance tuning techniques, indexing methods, and security best practices. Additionally, it covers the use of monitoring queries and backup procedures for effective database management.





![Get top 10 Slow queries
mysqldumpslow -a -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/00e805bd8a3f-slow.log
Reading mysql slow query log from /var/lib/mysql/00e805bd8a3f-slow.log
Count: 1 Time=6.08s (6s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=1.0 (1), root[root]@localhost
select count(*) from salaries_wo_partition where from_date between '1998-01-01' and '1998-12-31'
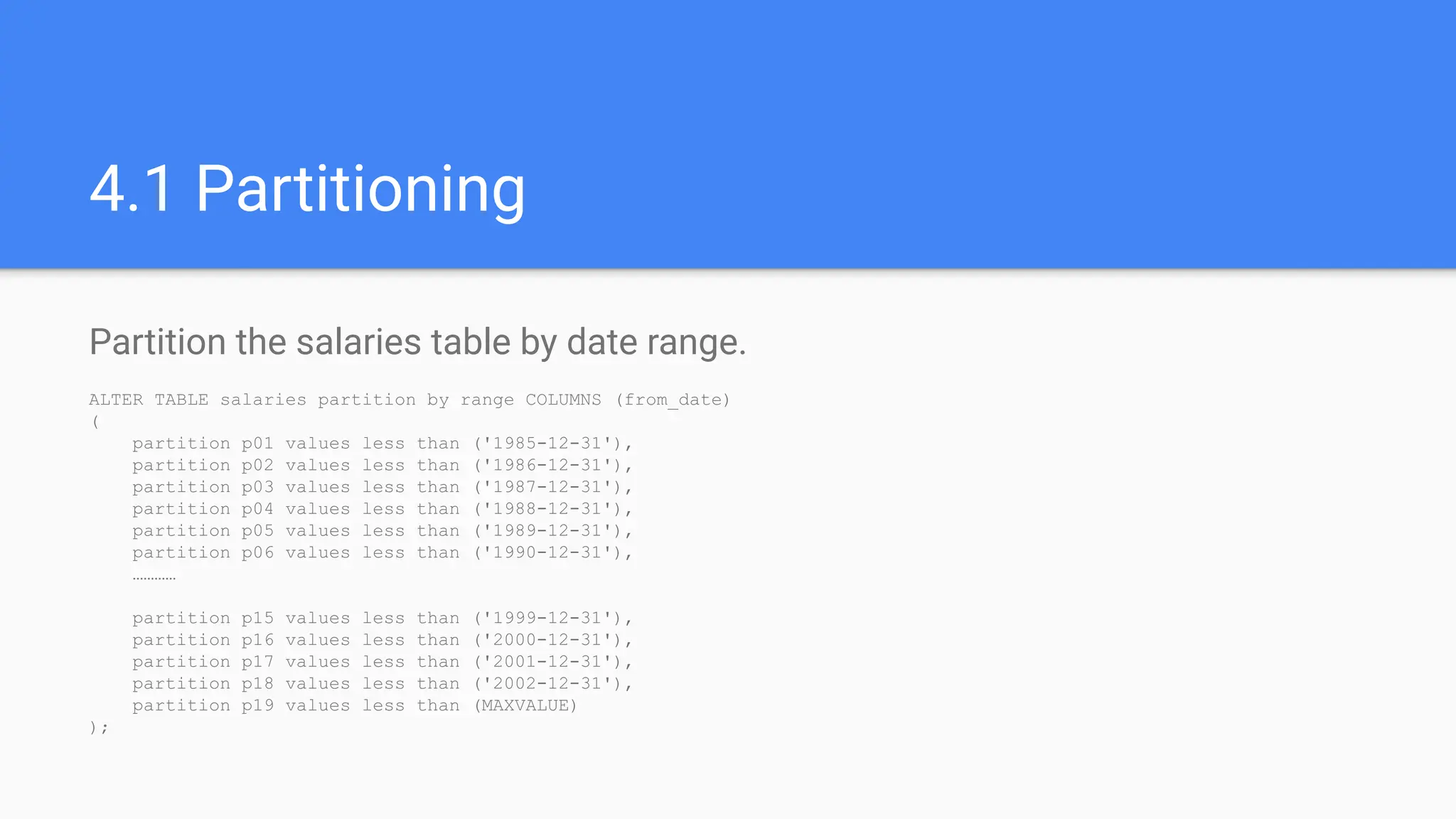
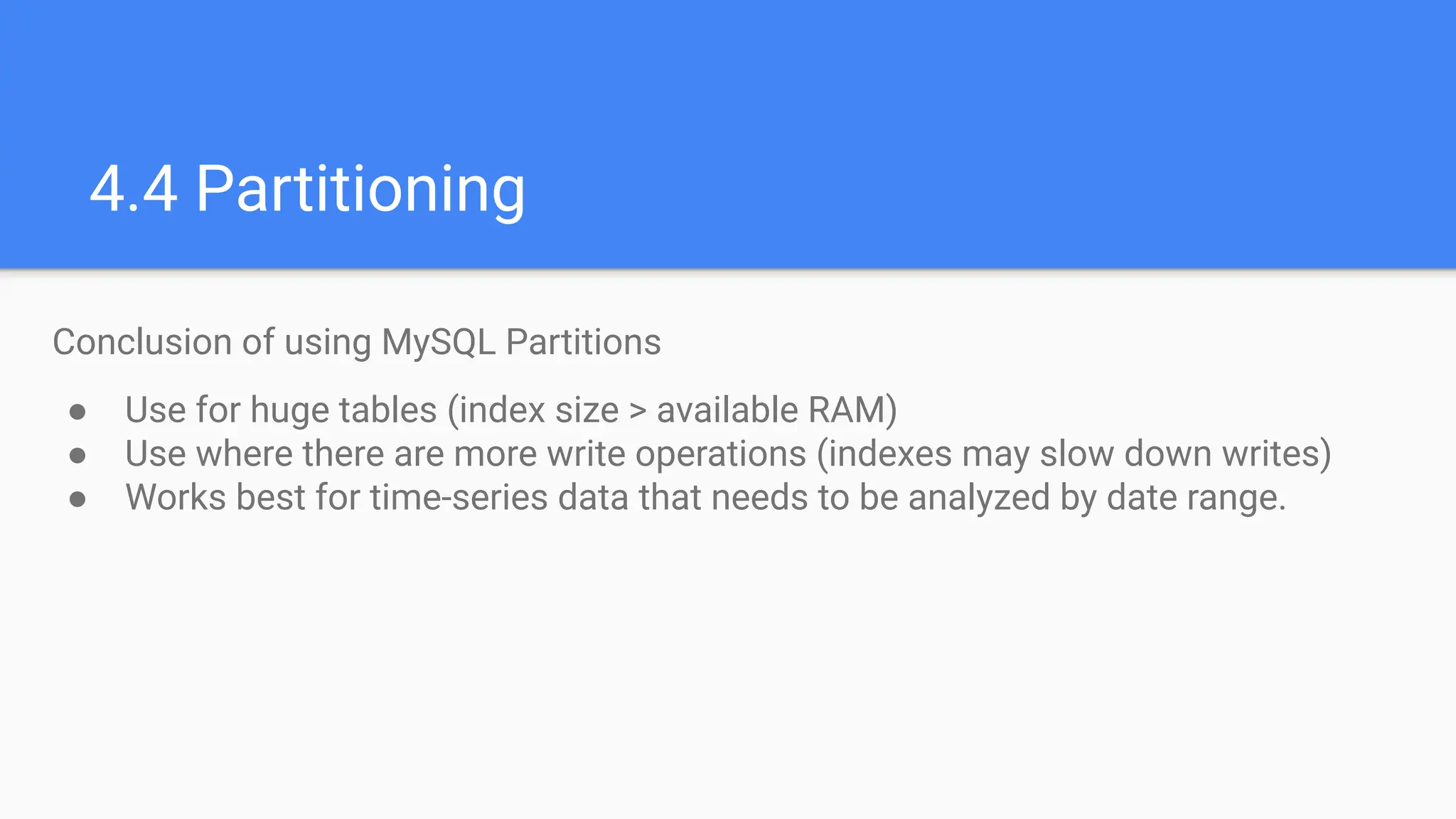
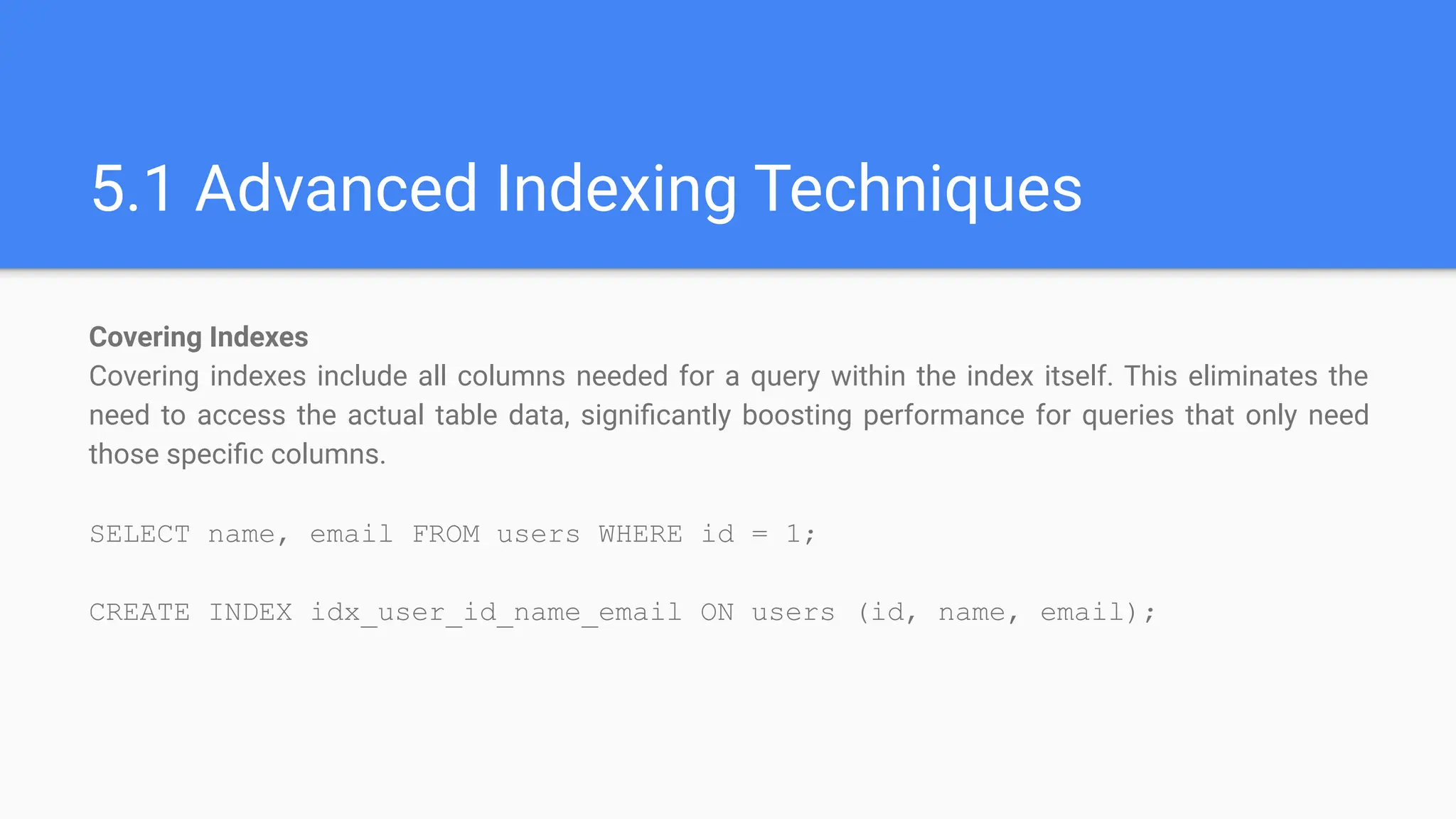
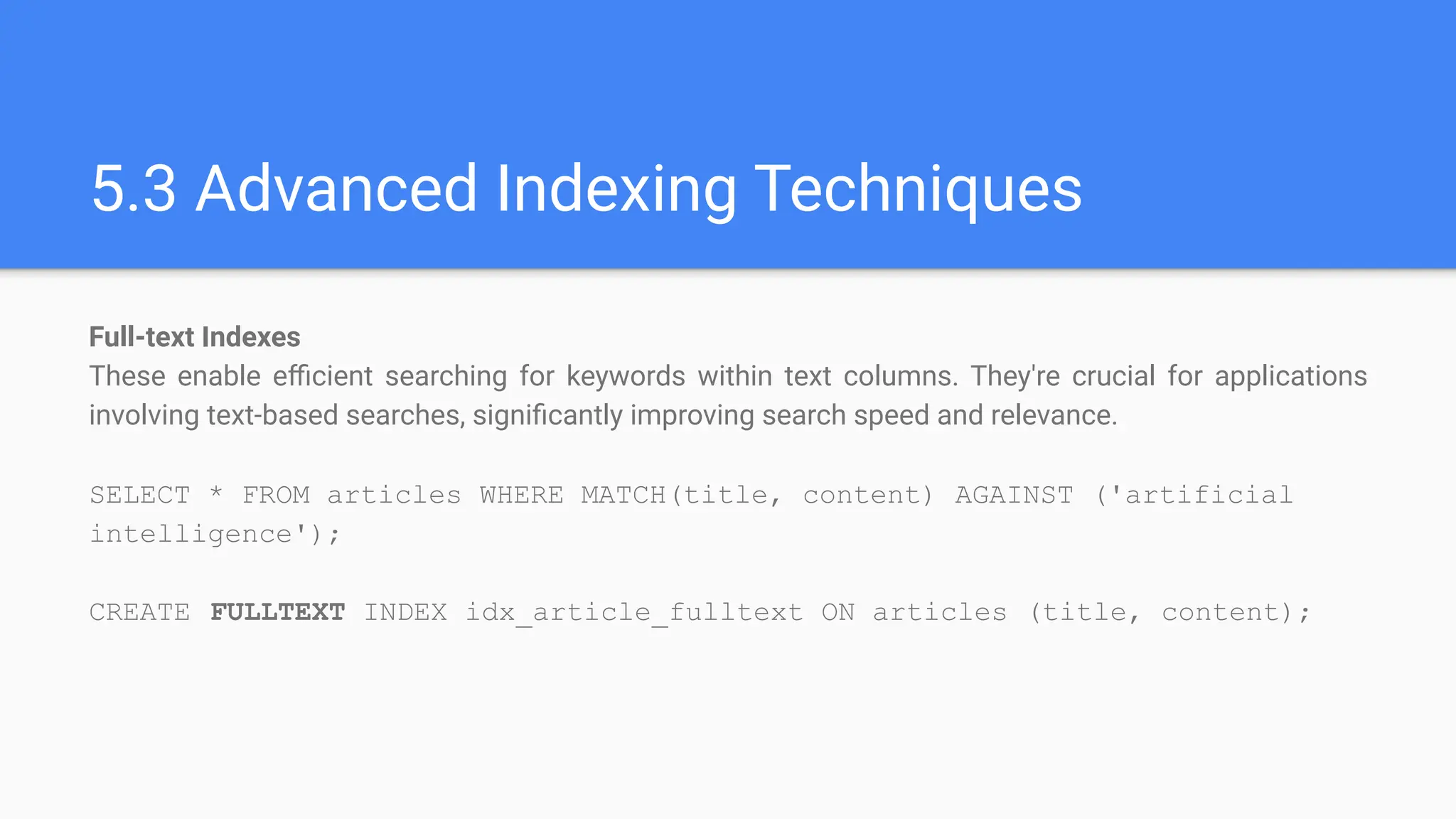
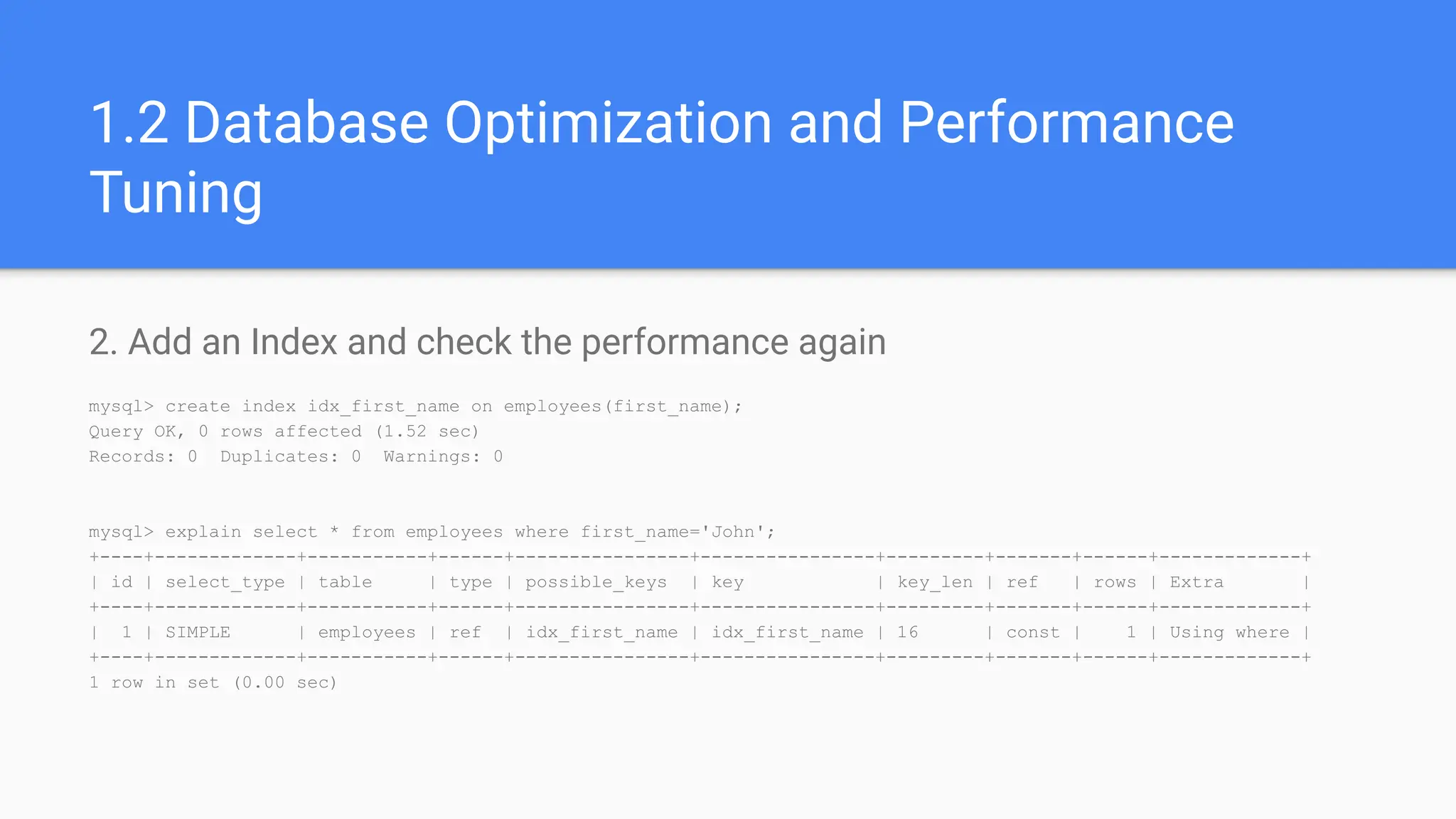
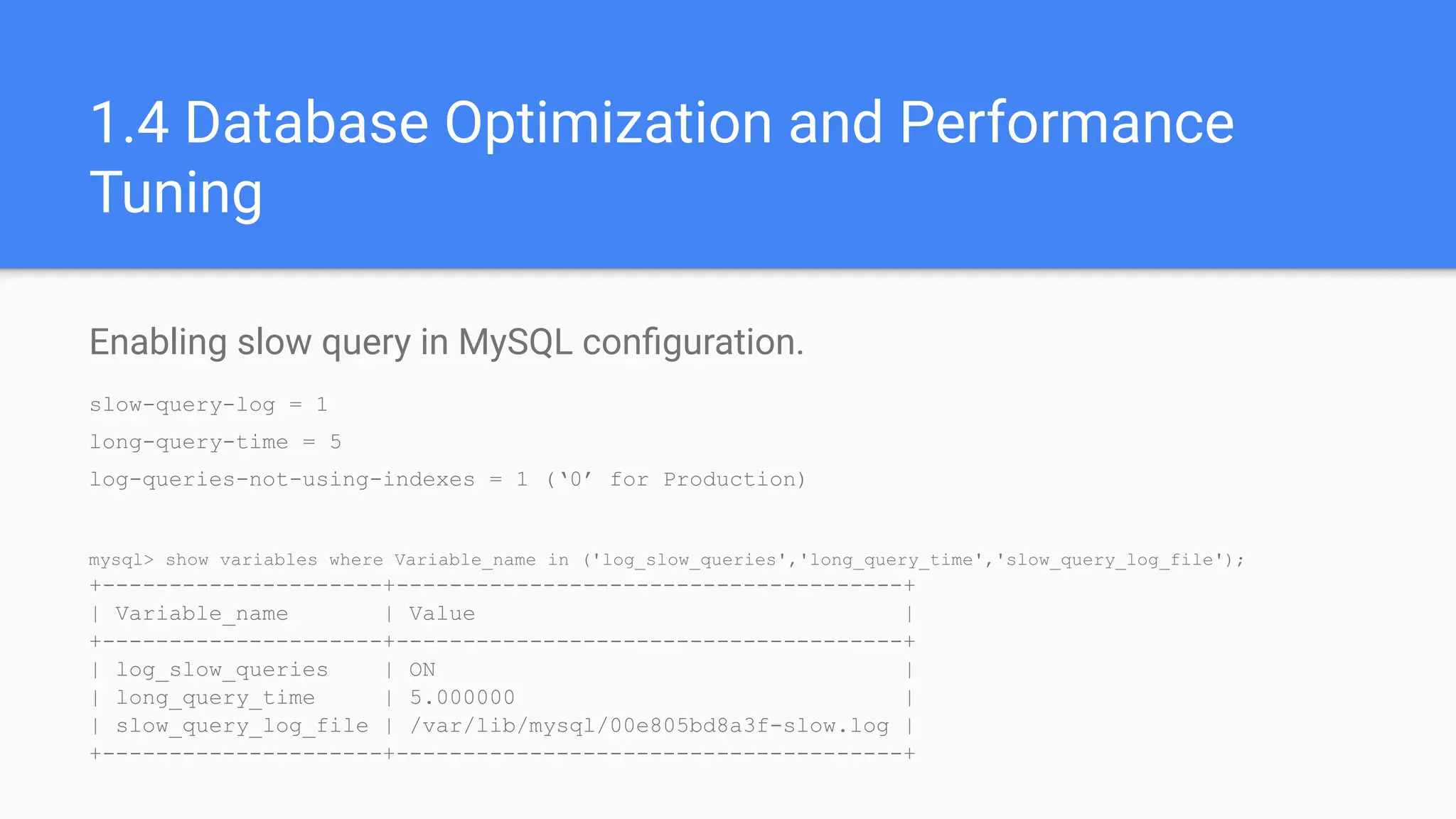
1.5 Database Optimization and Performance
Tuning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advance-mysql-training-240525152150-8d42a9bb/75/Advance-MySQL-Training-by-Pratyush-Majumdar-8-2048.jpg)