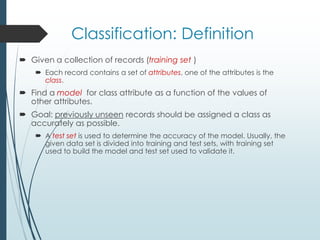
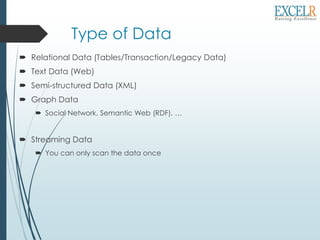
The document introduces big data and its various types, emphasizing the enormous volumes being generated from web data, transactions, and scientific projects. It details data mining tasks and techniques such as classification, clustering, and association rule discovery, which help extract meaningful patterns from large datasets. Additionally, the document discusses data streams and the necessity for real-time processing due to the rapid influx and size of the data.





![Data Mining Tasks
Classification [Predictive]
Clustering [Descriptive]
Association Rule Discovery [Descriptive]
Sequential Pattern Discovery [Descriptive]
Regression [Predictive]
Deviation Detection [Predictive]
Collaborative Filter [Predictive]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataanalyticscourses-191009093327/85/Data-analytics-courses-9-320.jpg)