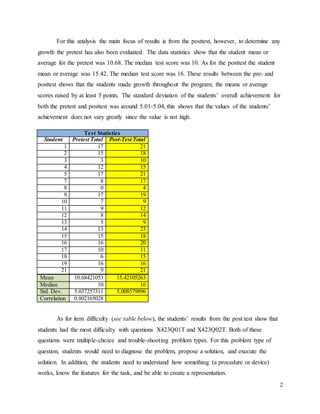
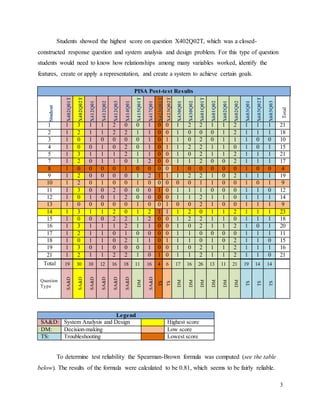
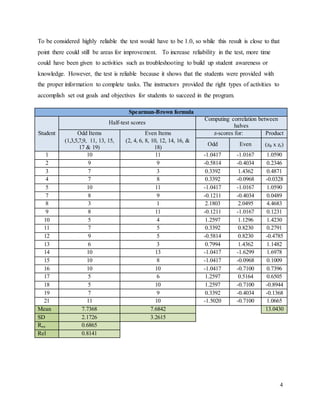
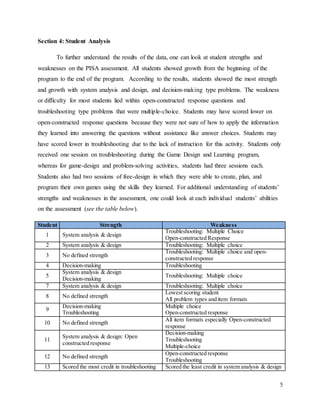
The document details a summer game design program for self-selected middle school students in Istanbul, aiming to improve their problem-solving skills through digital game creation and related activities. Assessment data indicate significant growth in students' scores from pretest to posttest, with an average increase of at least 5 points, and highlight strengths in system analysis and decision-making while noting challenges with troubleshooting problems. Recommendations for program improvement emphasize increasing troubleshooting sessions and preparing students for open-constructed response questions to address identified weaknesses.