The document summarizes key concepts in atomic theory:
1) The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound contains elements in fixed ratios by mass.
2) The law of multiple proportions states that ratios of masses of one element combined with a fixed mass of another are ratios of small whole numbers.
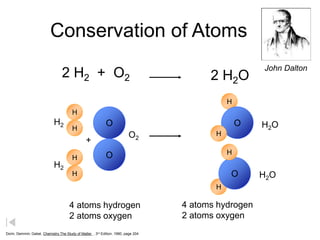
3) The law of conservation of mass states that mass is conserved in chemical reactions.