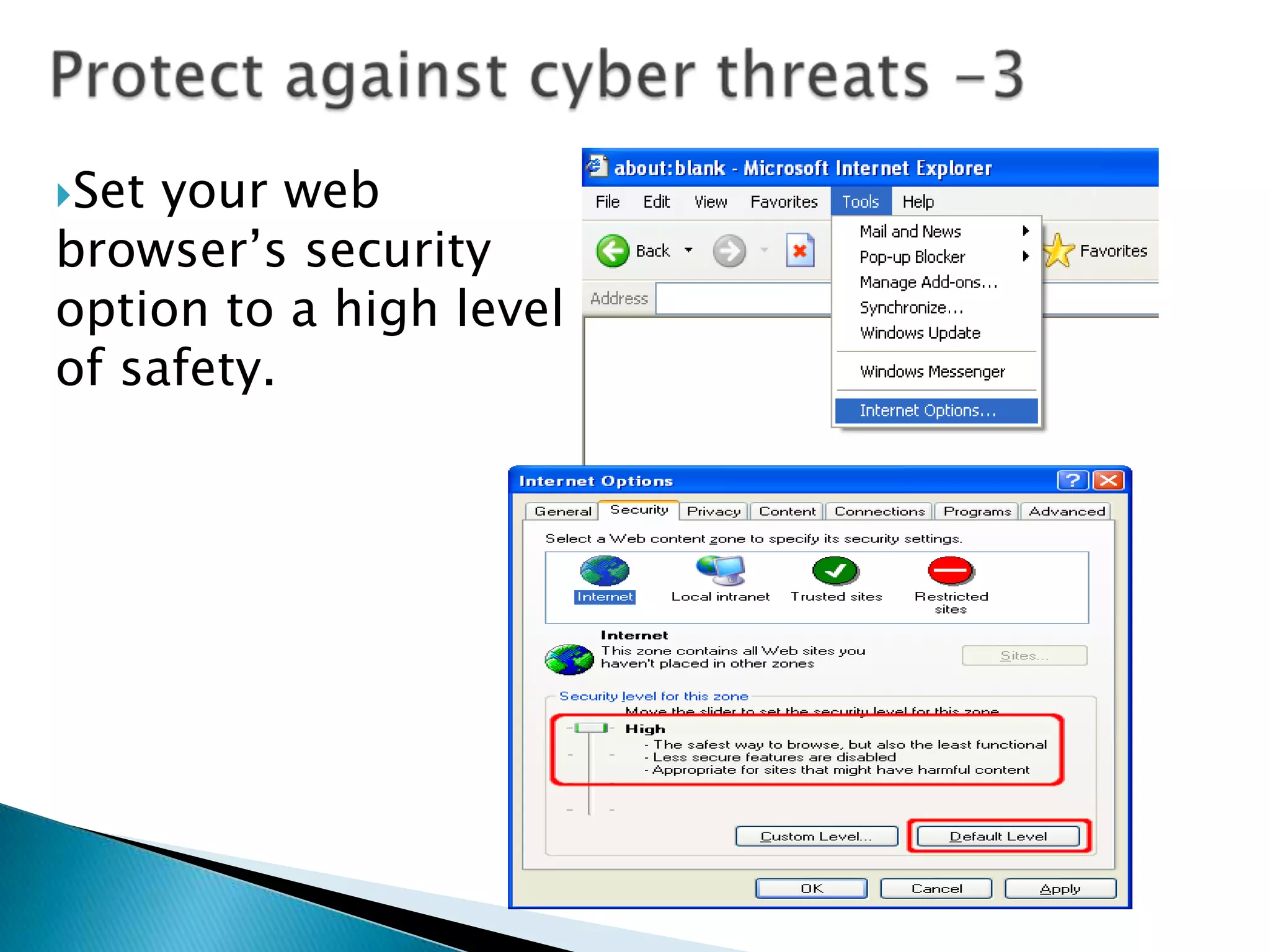
Educators play an important role in cyber security, cyber ethics, and cyber safety. They must understand cyber threats like piracy, intrusion, identity theft, viruses, spam, and more. These threats can result in legal fines, data loss, and network damage. To protect themselves and students, educators should teach and model safe practices like using strong passwords, backing up data, updating software, and being wary of unexpected emails or attachments.



![What is the Internet? The Internet is a global network that connects over one billion people and more than 600 million computers. More than 100 countries are linked into exchanges of data, news, and opinions. [http://www.internet.com]What kind of technologies are connect to the Internet?ComputersPersonal digital assistants (PDAs)Cell phonesDigital cable or satellite television and radioATM machines, credit cards, and debit cardsGlobal positioning system (GPS) devices and softwareTechnology Connects Schools to the Internet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02educators-role-100221120825-phpapp01/75/cyber_security-4-2048.jpg)