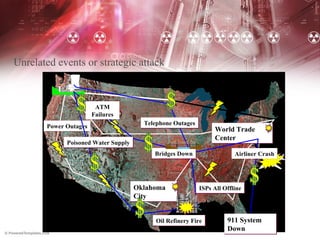
Cyber terrorism poses a significant threat to India according to experts. Pakistani cyber criminals deface dozens of Indian websites daily, far more than the number of Pakistani sites defaced in retaliation. While India is an IT leader, it lags behind in cyber security. Cyber terrorism can involve hacking critical infrastructure to harm the public and includes acts that are highly publicized on a large scale. International cooperation and domestic security improvements are needed to address this growing issue.