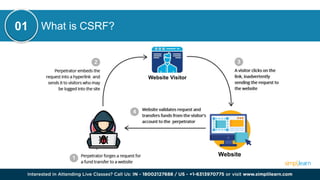
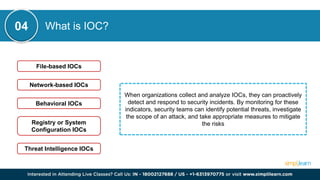
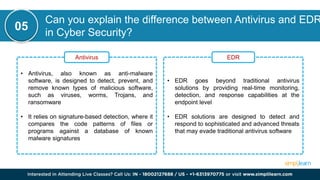
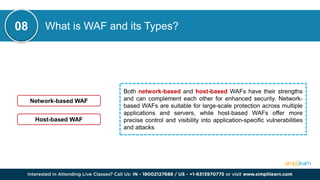
CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) is a security vulnerability where an attacker tricks an authenticated user into performing unintended actions on a web application. This document also discusses other cybersecurity concepts including XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), IOC (Indicators of Compromise), and differences between security measures like antivirus versus EDR, and firewalls versus intrusion prevention systems. It covers various topics related to cybersecurity, such as misconfigurations, web application firewalls, and network protocols, to enhance organizational security.