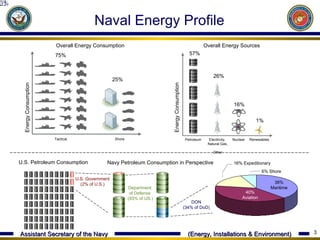
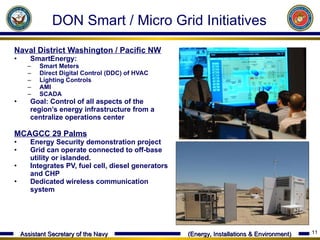
The document discusses the US Department of Defense's and Navy's goals and efforts to increase their use of renewable and alternative energy sources in order to improve energy security and reduce dependence on petroleum. Some key goals include having 50% of total energy consumption from alternative sources by 2020 and demonstrating a "Great Green Fleet" that relies on biofuel by 2016. The Navy has implemented various renewable energy pilot projects and installations using technologies like solar, wind, geothermal, and wave/tidal power.