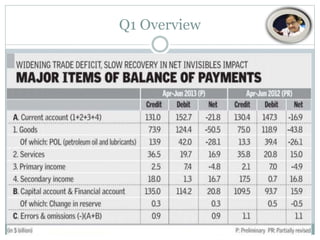
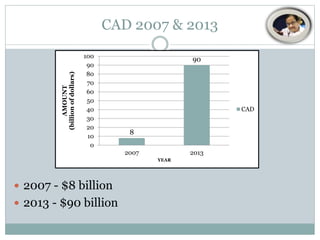
The document discusses India's current account deficit (CAD), which was $22.8 billion or 4.9% of GDP in 2013. A large CAD can drain foreign exchange reserves and cause the currency to depreciate. India's CAD is driven by gold and oil imports. Though coal imports have increased due to domestic shortages, reducing oil and coal imports is not feasible. Exports have fallen while FDI has declined from $35.12 billion in 2011 to $22.42 billion in 2012. A large CAD can force India to raise interest rates to attract foreign investment. The RBI has taken steps like raising FII limits and removing lock-in periods on government bonds to attract foreign inflows and contain the CAD