Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times





The document discusses cubic numbers, which are numbers multiplied by themselves three times. It provides examples such as 3 cubed equaling 27 and 4 cubed equaling 64. The cubic root of a number is the value that when cubed produces the original number. Perfect cubes are the results of cubing whole numbers, with examples including 8 from 2 cubed and 1331 from 11 cubed. Cubic numbers can also have roots that are not whole numbers, such as the cubic root of 40 being between 3.4 and 3.5.







A cubic number is formed by multiplying a number by itself three times. Examples include 3³=27, 4³=64, etc.
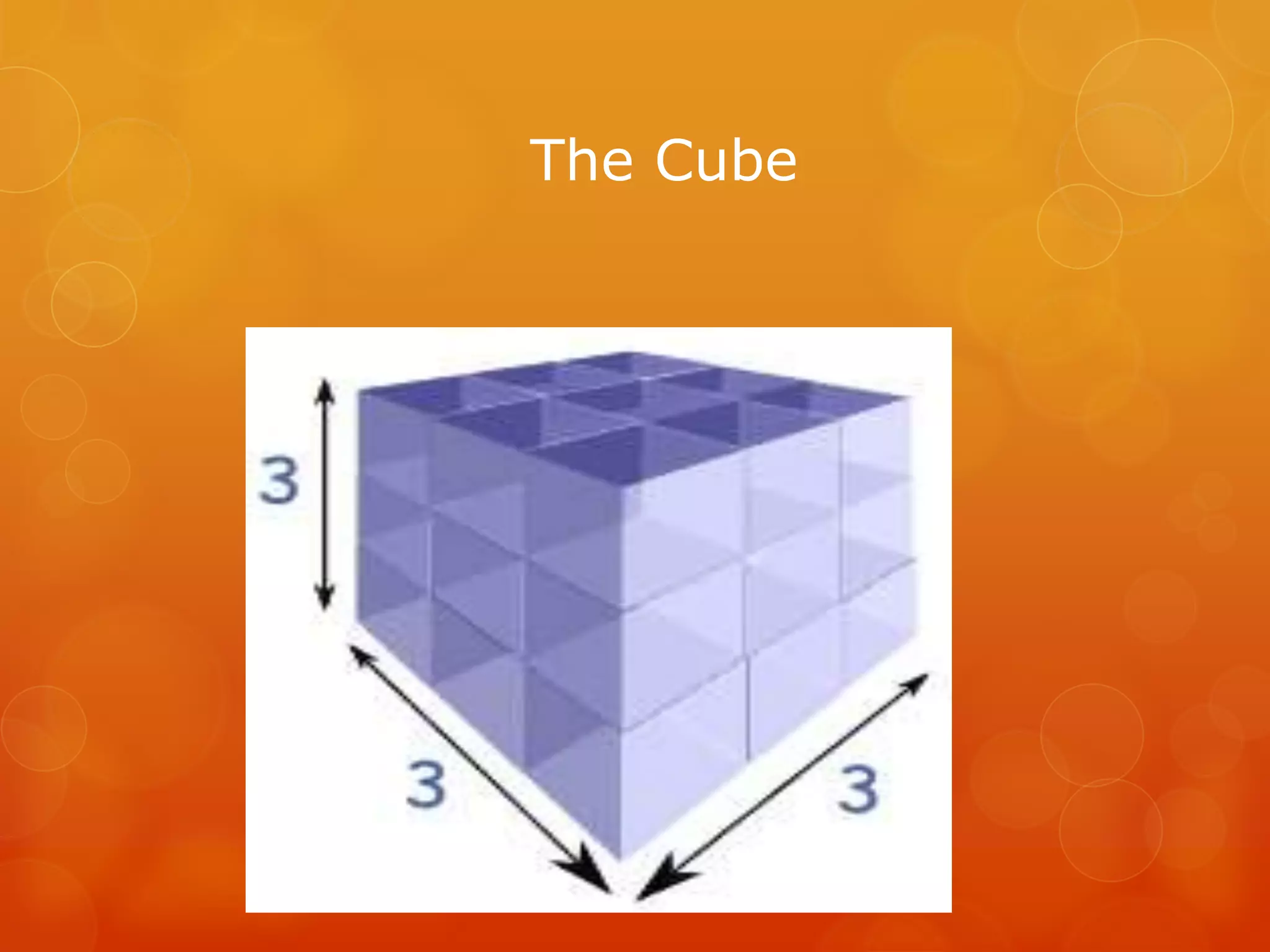
An introductory slide titled 'The Cube' is presented.
The cubic root of a number is the value that, when cubed, equals the original number. The symbol for cubic root is introduced.
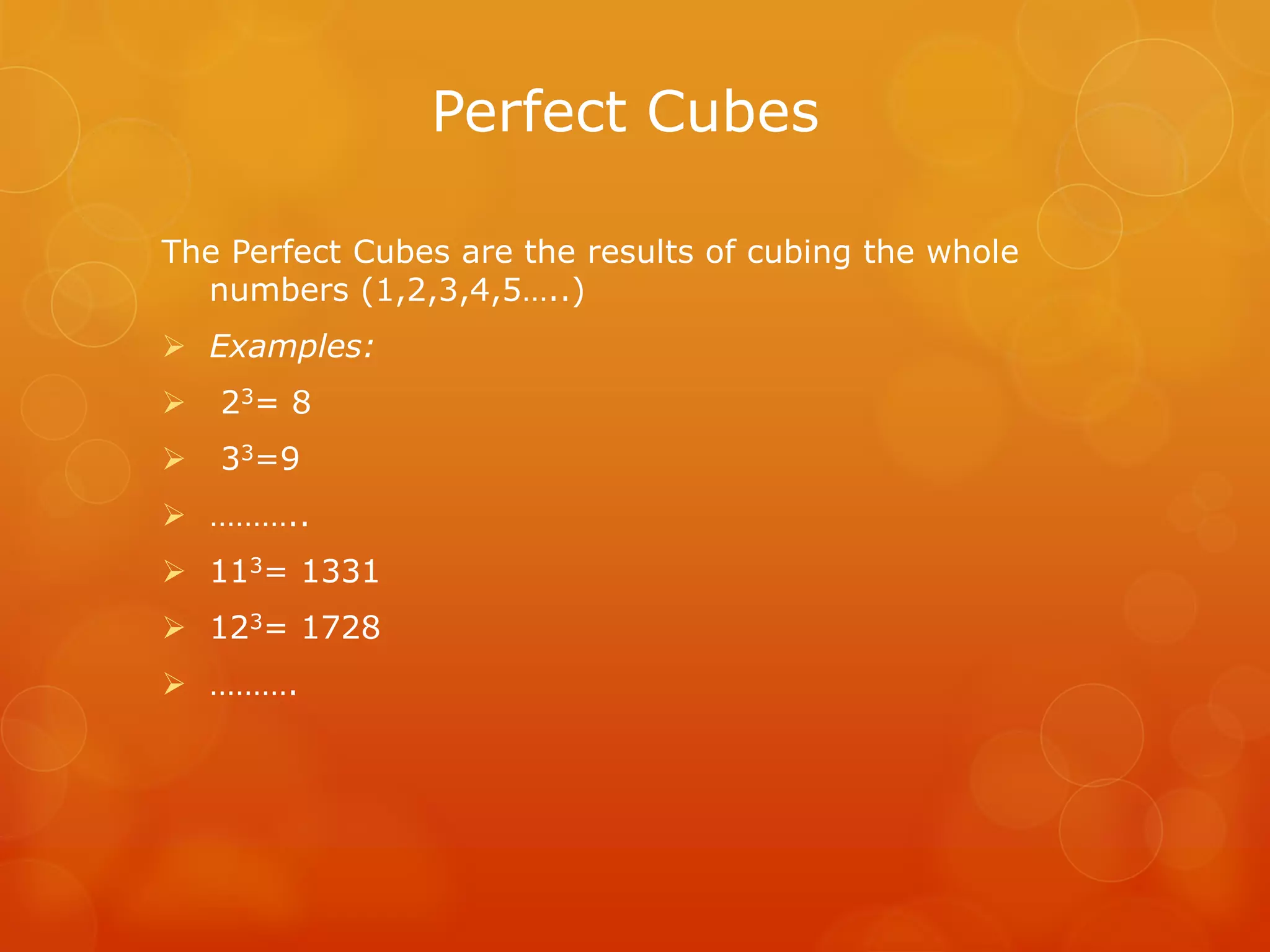
Perfect cubes are outcomes of cubing whole numbers. Examples include 2³=8, 3³=27, etc.
Cubic numbers can also have non-integer roots. Example demonstrated with cubic root of 40 lying between 3.4 and 3.5.
A thank you note from the authors: Paveliu Andrei, Parlea Teodor, Cataraga Daniel, and Zaharia Yani.