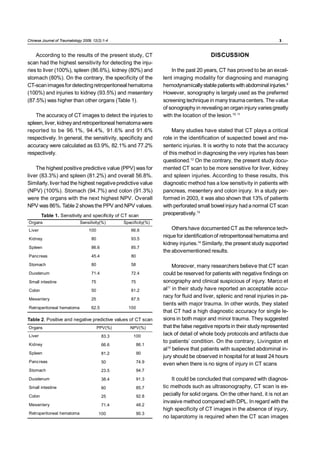
This study evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of CT scans for detecting injuries in 100 patients with blunt abdominal trauma. CT scans had high sensitivity for liver (100%) and spleen (86.6%) injuries. Specificity was highest for retroperitoneal hematoma (100%) and kidney injuries (93.5%). The accuracy of CT scans for detecting injuries to spleen, liver, kidney, and retroperitoneal hematoma ranged from 91.6% to 96.1%. The study concluded that CT scans are a good tool for evaluating blunt abdominal trauma in teaching hospitals.