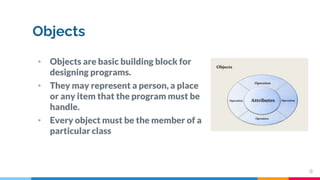
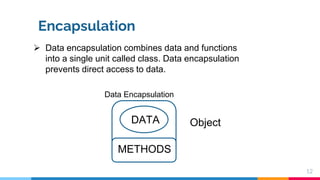
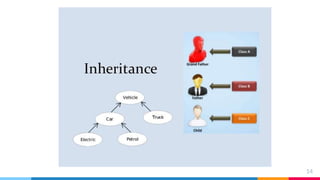
C++ session 1 introduces object oriented programming concepts including objects, classes, data encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, dynamic binding, and message passing. Objects are the basic building blocks and are members of classes. Classes define user-defined data types that contain both code and data. Data encapsulation combines data and functions into a single unit called a class. Inheritance allows classes to inherit features from other classes without modifying them. Polymorphism allows functions to take on multiple forms based on argument types. Dynamic binding determines which code to run at runtime. Message passing involves sending requests to objects to execute procedures.