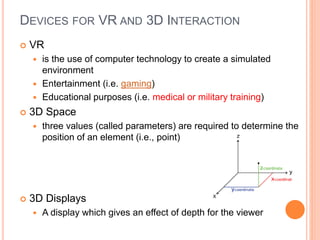
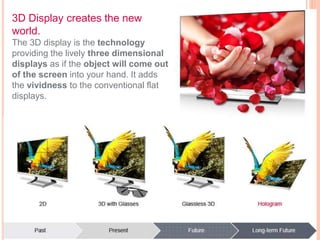
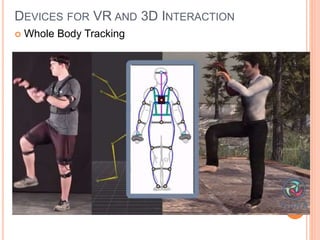
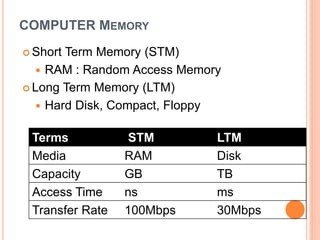
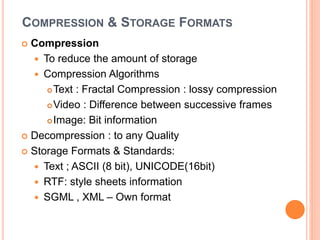
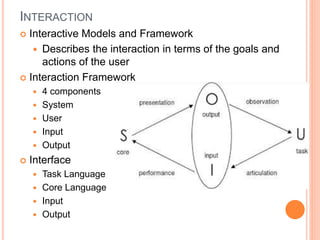
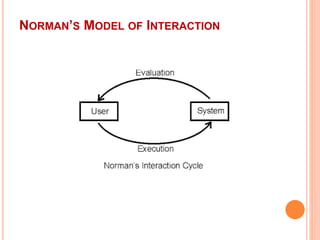
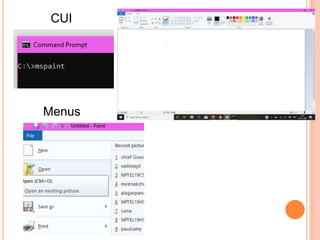
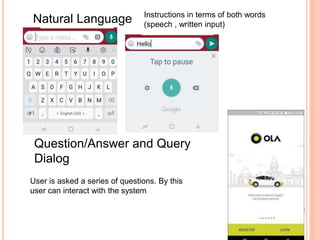
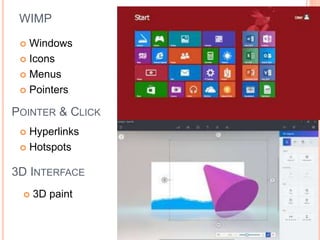
This document discusses human-computer interaction and devices for virtual and 3D interaction. It covers topics like virtual reality used for entertainment and education, 3D displays that provide a sense of depth, and input devices like 3D mice, data gloves, and VR helmets. It also discusses computer memory, storage formats, networks, models of interaction, and styles of interaction like command-line, menus, natural language, and 3D interfaces.