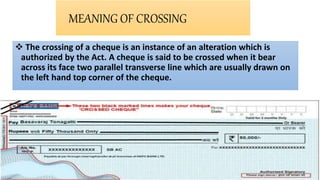
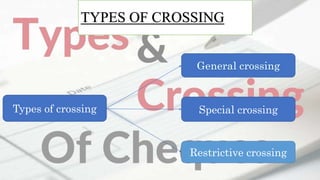
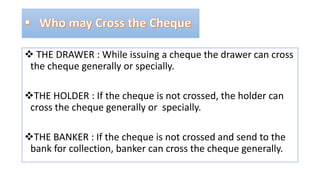
This document discusses crossing of cheques under section 123 of the Negotiable Instruments Act. It defines a cheque and explains the meaning and characteristics of crossing a cheque. There are two main types of crossing - general crossing and special crossing. General crossing involves drawing two parallel lines on the cheque, while special crossing adds the name of the banker. A third type, restrictive crossing, adds words like "account payee only" to make the cheque non-transferable. The document outlines who can cross a cheque - the drawer, holder or collecting banker. It also explains how a drawer can cancel the crossing on a cheque.