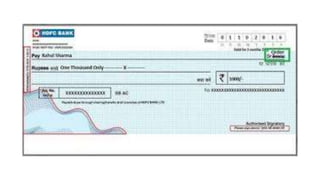
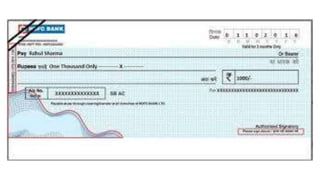
This document discusses different types of cheques, including their key elements and parties involved. It defines a cheque as a negotiable instrument that allows for payment through a bank. The three main parties in a cheque transaction are the drawer (account holder), drawee (bank), and payee (recipient of funds). It then describes different types of cheques such as bearer, order, crossed, anti-dated, post-dated, and stale cheques. The document also outlines the key components of a cheque like the bank and account details, date, amount, and signature. Finally, it discusses general and special/restrictive types of cheque crossings.